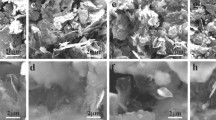
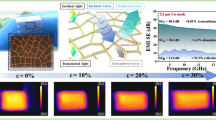
Abstract
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) incorporated polymeric composites have been extensively investigated for microwave absorption at target frequencies to meet the requirement of radar cross-section reduction. In this work, a strategy of efficient utilization of CNT in producing CNT incorporated aramid papers is demonstrated. The layer-by-layer self-assembly technique is used to coat the surfaces of meta-aramid fibers and fibrils with CNT, providing novel raw materials available for the large-scale papermaking. The hierarchical construction of CNT networks resolves the dilemma of increasing CNT content and avoiding the agglomeration of CNT, which is a frequent challenge for CNT incorporated polymeric composites. The composite paper, which contains abundant heterogeneous interfaces and long-range conductive networks, is capable of reaching a high permittivity and dielectric loss tangent at a low CNT loading, and its complex permittivity is, so far, adjustable in the range of (1.20–j0.05) to (25.17–j18.89) at 10 GHz. Some papers with optimal matching thicknesses achieve a high-efficiency microwave absorption with a reflection loss lower than −10 dB in the entire X-band.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zaker, R.; Sadeghzadeh. A. Passive techniques for target radar cross section reduction: A comprehensive review. Int. J. RF Microw. Comput. Aided Eng. 2020, 30, e22411.
Zohuri, B. Radar Energy Warfare and the Challenges of Stealth Technology; Springer: Cham, 2020.
Gaylor, K. Radar Absorbing Materials-Mechanisms and Materials. MRL Technical Report MRL-TR-89-1, Victoria, Australia, 1989; pp 1–25.
Mu, Z. G.; Wei, G. K.; Zhang, H.; Gao, L.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, S. L.; Ji, G. B. The dielectric behavior and efficient microwave absorption of doped nanoscale LaMnO3 at elevated temperature. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 7731–7741.
Xu, H. X.; Zhang, G. Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. R.; Wang, H. L.; Huang, Y.; Liu. P. B. Heteroatoms-doped carbon nanocages with enhanced dipolar and defective polarization toward light-weight microwave absorbers. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 8705–8713.
Zhao, P. Y.; Wang, H. Y.; Cai, B.; Sun, X. B.; Hou, Z. L.; Wu, J. T.; Bai, M.; Wang. G. S. Electrospinning fabrication and ultra-wideband electromagnetic wave absorption properties of CeO2/N-doped carbon nanofibers. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 7788–7796.
Qin, F. X.; Peng, M. Y.; Estevez, D.; Brosseau, C. Electromagnetic composites: From effective medium theories to metamaterials. J. Appl. Phys. 2022, 132, 101101.
Zhang, Y. L.; Ruan, K. P.; Zhou, K.; Gu, J. W. Controlled distributed Ti3C2Tx hollow microspheres on thermally conductive polyimide composite films for excellent electromagnetic interference shielding. Adv. Mater. 2023, https://doi.org/10.1202/adma.202211642.
Han, Y. X.; He, M. K.; Hu, J. W.; Liu, P. B.; Liu, Z. W.; Ma, Z. L.; Ju, W. B.; Gu, J. W. Hierarchical design of FeCo-based microchains for enhanced microwave absorption in C band. Nano Res. 2020, 16, 1773–1778.
Ruiz-Perez, F.; López-Estrada, S. M.; Tolentino-Hernández. R. V.; Caballero-Briones, F. Carbon-based radar absorbing materials: A critical review. J. Sci.: Adv. Mater. Devices 2022, 7, 100454.
Qin, M.; Zhang, L. M.; Wu. H. J. Dielectric loss mechanism in electromagnetic wave absorbing materials. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2105553.
Coleman, J. N.; Curran, S.; Dalton, A. B.; Davey, A. P.; McCarthy, B.; Blau, W.; Barklie. R. C. Percolation-dominated conductivity in a conjugated-polymer-carbon-nanotube composite. Phys. Rev. B 1998, 58, R7492–R7495.
Sandler, J.; Shaffer, M. S. P.; Prasse, T.; Bauhofer, W.; Schulte, K.; Windle. A. H. Development of a dispersion process for carbon nanotubes in an epoxy matrix and the resulting electrical properties. Polymer 1999, 40, 5967–5971.
Qi, X. S.; Xu, J. L.; Hu, Q.; Deng, Y.; Xie, R.; Jiang, Y.; Zhong, W.; Du. Y. W. Metal-free carbon nanotubes: Synthesis, and enhanced intrinsic microwave absorption properties. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28310.
Yang, R. B.; Kuo, W. S.; Lai. H. C. Effect of carbon nanotube dispersion on the complex permittivity and absorption of nanocomposites in 2–18 GHz ranges. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 40963.
Lee, S. E.; Kang, J. H.; Kim. C. G. Fabrication and design of multi-layered radar absorbing structures of MWNT-filled glass/epoxy plain-weave composites. Compos. Struct. 2006, 76, 397–405.
Choi, W. H.; Shin, J. H.; Song, T. H.; Kim, J. B.; Lee, W. Y.; Kim, C. G. A thin hybrid circuit-analog (CA) microwave absorbing double-slab composite structure. Compos. Struct. 2015, 124, 310–316.
Lee, S. E.; Lee, W. J.; Oh, K. S.; Kim. C. G. Broadband all fiber-reinforced composite radar absorbing structure integrated by inductive frequency selective carbon fiber fabric and carbon-nanotube-loaded glass fabrics. Carbon 2016, 107, 564–572.
Li, K.; Zhao, R.; Xia, J. X.; Zhao. G. L. Reinforcing microwave absorption multiwalled carbon nanotube-epoxy composites using glass fibers for multifunctional applications. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2020, 22, 2070008.
Cheon, J.; Lim, S. J.; Kim. M. A composite RAS with an enhanced uniformity of absorbing performance using a MWCNT-anchored aramid fiber. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 200, 108442.
Wang, H.; Xiu, X.; Wang, Y.; Xue, Q.; Ju, W. B.; Che, W. Q.; Liao, S. W.; Jiang, H. Y.; Tang, M.; Long, J. et al. Paper-based composites as a dual-functional material for ultralight broadband radar absorbing honeycombs. Compos. B Eng. 2020, 202, 108378.
Chen, S. H.; Kuo, W. S.; Yang. R. B. Microwave absorbing properties of a radar absorbing structure composed of carbon nanotube papers/glass fabric composites. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2019, 16, 2065–2072.
Zhao, D. L.; Zhang, J. M.; Li, X.; Shen. Z. M. Electromagnetic and microwave absorbing properties of Co-filled carbon nanotubes. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 505, 712–716.
Zhang, X.; Wang, X. Q.; Sha, P.; Wang, B. D.; Ding, Y.; Du, S. Y. High-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorption of epoxy composites filled with ultralow content of reduced graphene/carbon nanotube oxides. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 189, 108020.
Liang, J. J.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Li, N.; Ma, Y. F.; Li, F. F.; Chen, Y. S. High microwave absorption performances for single-walled carbon nanotube—Epoxy composites with ultra-low loadings. Chin. Phys. B 2014, 23, 088802.
Micheli, D.; Pastore, R.; Apollo, C.; Marchetti, M.; Gradoni, G.; Mariani Primiani, V.; Moglie. F. Broadband electromagnetic absorbers using carbon nanostructure-based composites. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2011, 59, 2633–2646.
Lin, H. Y.; Zhu, H.; Guo, H. F.; Yu. L. F. Investigation of the microwave-absorbing properties of Fe-filled carbon nanotubes. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 3547–3550.
Ting, T. H.; Chiang, C. C.; Lin, P. C.; Lin. C. H. Optimisation of the electromagnetic matching of manganese dioxide/multi-wall carbon nanotube composites as dielectric microwave-absorbing materials. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2013, 339, 100–105.
Tang, J.; Bi, S.; Su, Z. A.; Hou, G. L.; Liu, C. H.; Li, H.; Lin. Y. Y. Surface modification and microwave absorption properties of lightweight CNT absorbent. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 21048–21058.
Correa-Duarte, M. A.; Kosiorek, A.; Kandulski, W.; Giersig, M.; Liz-Marzán. L. M. Layer-by-layer assembly of multiwall carbon nanotubes on spherical colloids. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 3268–3272.
Decher. G. Fuzzy nanoassemblies: Toward layered polymeric multicomposites. Science 1997, 277, 1232–1237.
Xie, B.; Liu, Y. L.; Ding, Y. T.; Zheng, Q. S.; Xu. Z. P. Mechanics of carbon nanotube networks: Microstructural evolution and optimal design. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 10039–10047.
Ryu, S. Y.; Chung, J. W.; Kwak. S. Y. Amphiphobic meta-aramid nanofiber mat with improved chemical stability and mechanical properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 91, 111–120.
Alava, M.; Niskanen. K. The physics of paper. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2006, 69, 669–723.
Shaffner. T. J.; Van Veld, R. D. ‘Charging’ effects in the scanning electron microscope. J. Phys. E:Sci. Instrum. 1971, 4, 633–637.
Gingold, D. B.; Lobb. C. J. Percolative conduction in three dimensions. Phys. Rev. B 1990, 42, 8220–8224.
Deng, F.; Ito, M.; Noguchi, T.; Wang, L. F.; Ueki, H.; Niihara, K. I.; Kim, Y. A.; Endo, M.; Zheng. Q. S. Elucidation of the reinforcing mechanism in carbon nanotube/rubber nanocomposites. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 3858–3866.
Luo, F.; Liu, D. Q.; Cao, T. S.; Cheng, H. F.; Kuang, J. C.; Deng, Y. J.; Xie. W. Study on broadband microwave absorbing performance of gradient porous structure. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2021, 4, 591–601.
Younes, H.; Li, R.; Lee, S. E.; Kim, Y. K.; Choi, D. Gradient 3D-printed honeycomb structure polymer coated with a composite consisting of Fe3O4 multi-granular nanoclusters and multi-walled carbon nanotubes for electromagnetic wave absorption. Synth. Met. 2021, 275, 116731.
Zhao, Y. C.; Ren, F.; He, L.; Zhang, J. S.; Yuan, Y. N.; Xi. X. L. Design of graded honeycomb radar absorbing structure with wideband and wide-angle properties. Int. J. Microwave Wireless Technol. 2019, 11, 143–150.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. U21A2093). This work is partially financed by the Polymer Electromagnetic Functional Materials Innovation Team of Shaanxi Sanqin Scholars.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Y., Chen, L., Han, Y. et al. Hierarchical construction of CNT networks in aramid papers for high-efficiency microwave absorption. Nano Res. 16, 7801–7809 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-5522-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-5522-4