Abstract
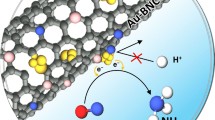
For electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction (CO2RR), CO2-to-CO conversion is considered an ideal route towards carbon neutrality for practical applications. Gold (Au) is known as a promising catalyst with high selectivity for CO; however, it suffers from high cost and low mass-specific activity. In this study, we design and prepare a catalyst featuring uniform S-doped Au nanoparticles on N-doped carbon support (denoted as S-Au/NC) by an in situ synthesis strategy using biomolecules. The S-Au/NC displays high activity and selectivity for CO in CO2RR with a Au loading as low as 0.4 wt.%. The Faradaic efficiency of CO (FECO) for S-Au/NC is above 95% at −0.75 V (vs. RHE); by contrast, the FECO of Au/NC (without S) is only 58%. The Tafel slope is 77.4 mV·dec−1, revealing a favorable kinetics process. Furthermore, S-Au/NC exhibits an excellent long-term stability for CO2RR. Density functional theory (DFT) calculations reveal that the S dopant can boost the activity by reducing the free energy change of the potential-limiting step (formation of the *COOH intermediate). This work not only demonstrates a model catalyst featuring significantly reduced use of noble metals, but also establishes an in situ synthesis strategy for preparing high-performance catalysts.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lin, L.; Li, H. B.; Wang, Y.; Li, H. F.; Wei, P. F.; Nan, B.; Si, R.; Wang, G. X.; Bao, X. H. Temperature-dependent CO2 electroreduction over Fe—N—C and Ni—N—C single-atom catalysts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 26582–26586.
Li, R. Z.; Wang, D. S. Understanding the structure-performance relationship of active sites at atomic scale. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 6888–6923.
Rong, X.; Wang, H. J.; Lu, X. L.; Si, R.; Lu, T. B. Controlled synthesis of a vacancy-defect single-atom catalyst for boosting CO2 electroreduction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 1961–1965.
Zheng, X. B.; Li, B. B.; Wang, Q. S.; Wang, D. S.; Li, Y. D. Emerging low-nuclearity supported metal catalysts with atomic level precision for efficient heterogeneous catalysis. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 7806–7839.
Zhu, P.; Xiong, X.; Wang, D. S. Regulations of active moiety in single atom catalysts for electrochemical hydrogen evolution reaction. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 5792–5815.
Zheng, X. B.; Yang, J. R.; Xu, Z. F.; Wang, Q. S.; Wu, J. B.; Zhang, E. H.; Dou, S. X.; Sun, W. P.; Wang, D. S.; Li, Y. D. Ru—Co pair sites catalyst boosts the energetics for the oxygen evolution reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 134, e202205946.
Jin, S.; Hao, Z. M.; Zhang, K.; Yan, Z. H.; Chen, J. Advances and challenges for the electrochemical reduction of CO2 to CO: From fundamentals to industrialization. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 20627–20648.
Jiao, J. Q.; Zhang, N. N.; Zhang, C.; Sun, N.; Pan, Y.; Chen, C.; Li, J.; Tan, M. J.; Cui, R. X.; Shi, Z. L. et al. Doping ruthenium into metal matrix for promoted pH-universal hydrogen evolution. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2200010.
Yun, Y. P.; Sheng, H. T.; Bao, K.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Astruc, D.; Zhu, M. Z. Design and remarkable efficiency of the robust sandwich cluster composite nanocatalysts ZIF-8@Au25@ZIF-67. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 4126–4130.
Wu, J. J.; Yadav, R. M.; Liu, M. J.; Sharma, P. P.; Tiwary, C. S.; Ma, L. L.; Zou, X. L.; Zhou, X. D.; Yakobson, B. I.; Lou, J. et al. Achieving highly efficient, selective, and stable CO2 reduction on nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 5364–5371.
Wang, Y. F.; Li, Y. X.; Wang, Z. Y.; Allan, P.; Zhang, F. C.; Lu, Z. G. Reticular chemistry in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction. Sci. China Mater. 2020, 63, 1113–1141.
Li, Z.; Ji, S. F.; Liu, Y. W.; Cao, X.; Tian, S. B.; Chen, Y. J.; Niu, Z. Q.; Li, Y. D. Well-defined materials for heterogeneous catalysis: From nanoparticles to isolated single-atom sites. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 623–682.
Zhao, S.; Jin, R. X.; Jin, R. C. Opportunities and challenges in CO2 reduction by gold- and silver-based electrocatalysts: From bulk metals to nanoparticles and atomically precise nanoclusters. ACS Energy Lett. 2018, 3, 452–462.
Souza, M. L.; Lima, F. H. B. Dibenzyldithiocarbamate-functionalized small gold nanoparticles as selective catalysts for the electrochemical reduction of CO2 to CO. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 12208–12219.
Zhu, W. L.; Zhang, Y. J.; Zhang, H. Y.; Lv, H. F.; Li, Q.; Michalsky, R.; Peterson, A. A.; Sun, S. H. Active and selective conversion of CO2 to CO on ultrathin Au nanowires. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 16132–16135.
Gao, D. F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Z. W.; Cai, F.; Zhao, X. F.; Huang, W. G.; Li, Y. S.; Zhu, J. F.; Liu, P.; Yang, F. et al. Enhancing CO2 electroreduction with the metal-oxide interface. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 5652–5655.
Zhu, W. L.; Michalsky, R.; Metin, Ö.; Lv, H. F.; Guo, S. J.; Wright, C. J.; Sun, X. L.; Peterson, A. A.; Sun, S. H. Monodisperse Au nanoparticles for selective electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 to CO. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 16833–16836.
Mistry, H.; Reske, R.; Zeng, Z. H.; Zhao, Z. J.; Greeley, J.; Strasser, P.; Cuenya, B. R. Exceptional size-dependent activity enhancement in the electroreduction of CO2 over Au nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 16473–16476.
Guo, H.; Si, D. H.; Zhu, H. J.; Li, Q. X.; Huang, Y. B.; Cao, R. Ni single-atom sites supported on carbon aerogel for highly efficient electroreduction of carbon dioxide with industrial current densities. eScience 2022, 2, 295–303.
Hossain, M. N.; Liu, Z. G.; Wen, J. L.; Chen, A. C. Enhanced catalytic activity of nanoporous Au for the efficient electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2018, 236, 483–489.
Back, S.; Yeom, M. S.; Jung, Y. Active sites of Au and Ag nanoparticle catalysts for CO2 electroreduction to CO. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 5089–5096.
Cao, T.; Lin, R.; Liu, S. J.; Cheong, W. C.; Li, Z.; Wu, K. L.; Zhu, Y. Q.; Wang, X. L.; Zhang, J.; Li, Q. H. et al. Atomically dispersed Ni anchored on polymer-derived mesh-like N-doped carbon nanofibers as an efficient CO2 electrocatalytic reduction catalyst. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 3959–3963.
Jiao, J. Q.; Yang, W. J.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, S. J.; Chen, C.; Wang, D. S. Interface engineering of partially phosphidated Co@Co-P@NPCNTs for highly enhanced electrochemical overall water splitting. Small 2020, 16, 2002124.
Wang, Y.; Zheng, X. B.; Wang, D. S. Design concept for electrocatalysts. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 1730–1752.
Li, S. T.; Nagarajan, A. V.; Alfonso, D. R.; Sun, M. K.; Kauffman, D. R.; Mpourmpakis, G.; Jin, R. C. Boosting CO2 electrochemical reduction with atomically precise surface modification on gold nanoclusters. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 6351–6356.
Chen, Y. H.; Li, C. W.; Kanan, M. W. Aqueous CO2 reduction at very low overpotential on oxide-derived Au nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 19969–19972.
Jia, C.; Tan, X.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, W. H.; Li, Y. B.; Su, Z.; Smith, S. C.; Zhao, C. Sulfur-dopants promoted electroreduction of CO2 over coordinatively unsaturated Ni-N2 moieties. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 23342–23348.
Li, M. F.; Zhang, B.; Cheng, T.; Yu, S.; Louisia, S.; Chen, C. B.; Chen, S. P.; Cestellos-Blanco, S.; Goddard, W. A.; Yang, P. D. Sulfur-doped graphene anchoring of ultrafine Au25 nanoclusters for electrocatalysis. Nano Res. 2021, 14, 3509–3513.
Chen, S. H.; Li, W. H.; Jiang, W. J.; Yang, J. R.; Zhu, J. X.; Wang, L. Q.; Ou, H. H.; Zhuang, Z. C.; Chen, M. Z.; Sun, X. H. et al. MOF encapsulating N-heterocyclic carbene-ligated copper single-atom site catalyst towards efficient methane electrosynthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202114450.
Chen, Z. W.; Zhang, J. W.; Zhang, C.; Cui, R. X.; Tan, M. J.; Guo, S.; Wang, H. J.; Jiao, J. Q.; Lu, T. B. Regulating the coordination metal center in immobilized molecular complexes as single-atomic electrocatalysts for highly active, selective and durable electrochemical CO2 reduction. J. Power. Sources 2022, 519, 230788.
Tan, Y.; Yan, L.; Huang, C. Q.; Zhang, W. N.; Qi, H. F.; Kang, L. L.; Pan, X. L.; Zhong, Y. J.; Hu, Y.; Ding, Y. J. Fabrication of an Au25-Cys-Mo electrocatalyst for efficient nitrogen reduction to ammonia under ambient conditions. Small 2021, 17, 2100372.
Zhang, N. Q.; Ye, C. L.; Yan, H.; Li, L. C.; He, H.; Wang, D. S.; Li, Y. D. Single-atom site catalysts for environmental catalysis. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 3165–3182.
Tai, H. L.; Nishikawa, K.; Higuchi, Y.; Mao, Z. W.; Hirota, S. Cysteine SH and glutamate COOH contributions to Ni-Fe hydrogenase proton transfer revealed by highly sensitive FTIR spectroscopy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 13285–13290.
Bao, L. R.; Zhu, S. H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Meng, W. H.; Xu, S.; Lin, Z. H.; Li, X. Y.; Sun, M.; Guo, L. M. Anionic defects engineering of Co3O4 catalyst for toluene oxidation. Fuel 2022, 314, 122774.
Shi, Q. Q.; Peng, F.; Liao, S. X.; Wang, H. J.; Yu, H.; Liu, Z. W.; Zhang, B. S.; Su, D. S. Sulfur and nitrogen co-doped carbon nanotubes for enhancing electrochemical oxygen reduction activity in acidic and alkaline media. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 14853–14857.
Gadgil, B.; Damlin, P.; Viinikanoja, A.; Heinonen, M.; Kvarnström, C. One-pot synthesis of an Au/Au2S viologen hybrid nanocomposite for efficient catalytic applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 9731–9737.
Zhao, S. Q.; Tang, Z. Y.; Guo, S. J.; Han, M. M.; Zhu, C.; Zhou, Y. J.; Bai, L.; Gao, J.; Huang, H.; Li, Y. Y. et al. Enhanced activity for CO2 electroreduction on a highly active and stable ternary Au-CDots-C3N4 electrocatalyst. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 188–197.
Wan, X. K.; Wang, J. Q.; Wang, Q. M. Ligand-protected Au55 with a novel structure and remarkable CO2 electroreduction performance. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 133, 20916–20921.
Sun, X. H.; Tuo, Y. X.; Ye, C. L.; Chen, C.; Lu, Q.; Li, G. N.; Jiang, P.; Chen, S. H.; Zhu, P.; Ma, M. et al. Phosphorus induced electron localization of single iron sites for boosted CO2 electroreduction reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 23614–23618.
Jing, H. Y.; Zhu, P.; Zheng, X. B.; Zhang, Z. D.; Wang, D. S.; Li, Y. D. Theory-oriented screening and discovery of advanced energy transformation materials in electrocatalysis. Adv. Powder Mater. 2022, 1, 100013.
Wang, B. Q.; Chen, S. H.; Zhang, Z. D.; Wang, D. S. Low-dimensional material supported single-atom catalysts for electrochemical CO2 reduction. SmartMat 2022, 3, 84–110.
Zhang, N. Q.; Zhang, X. X.; Tao, L.; Jiang, P.; Ye, C. L.; Lin, R.; Huang, Z. W.; Li, A.; Pang, D. W.; Yan, H. et al. Silver single-atom catalyst for efficient electrochemical CO2 reduction synthesized from thermal transformation and surface reconstruction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 6170–6176.
Zhang, N. Q.; Zhang, X. X.; Kang, Y. K.; Ye, C. L.; Jin, R.; Yan, H.; Lin, R.; Yang, J. R.; Xu, Q.; Wang, Y. et al. A supported Pd2 dual-atom site catalyst for efficient electrochemical CO2 reduction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 13388–13393.
Acknowledgements
The work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 52072260, 21931007, 21790052, and U21A20317), the Science and Technology Support Program for Youth Innovation in Universities of Shangdong Province (No. 2020KJA012), the Tianjin Natural Science Foundation (Nos. 21JCZXJC00130 and B2021201074), the Haihe Laboratory of Sustainable Chemical Transformations, National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2017YFA0700104), and the University Synergy Innovation Program of Anhui Province (No. GXXT-2020-001). Supercomputing of Anhui University and National Supercomputing Center in Shanghai was acknowledged for computational support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
12274_2022_4878_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Low-loading gold in situ doped with sulfur by biomolecule-assisted approach for promoted electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, M., Han, X., Ru, S. et al. Low-loading gold in situ doped with sulfur by biomolecule-assisted approach for promoted electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction. Nano Res. 16, 2059–2064 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-4878-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-4878-3