Abstract
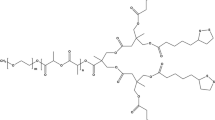
Many anticancer drugs have limited clinical applications owing to their unsatisfactory therapeutic efficacy or side effects. This situation can be improved by drug delivery systems or drug modification strategies. Herein, to improve the therapeutic efficacy and safety of the traditional anticancer drug 6-mercaptopurine (6-MP), we dimerized 6-MP to form a disulfide bond-containing drug dimer and prepared a cysteine-based poly (disulfide amide) with redox-responsive capability as a drug carrier. Briefly, dimeric 6-MP (DMP) was synthesized via the oxidization of iodine and self-assembled with the poly (disulfide amide) to form dual redox-responsive DMP-loaded NPs (DMP-NPs). The 6-MP itself could hardly be loaded into nanoparticles (NPs) owing to its hydrophobicity, while the DMP-NPs showed a higher drug loading capacity over 6-MP, small particle size, and favorable stability. With abundant disulfide bonds in polymer backbones and drug payloads, DMP-NPs could rapidly respond to high levels of glutathione (GSH) and release drugs in a controllable manner. More importantly, both cellular and animal experiments demonstrated the enhanced anticancer efficacy of DMP-NPs against lymphoma and their high safety. Overall, this drug dimer-loaded dual redox-responsive drug delivery system provides new options for improving the applications of traditional drugs and developing drug delivery systems with enhanced drug effects and high safety.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nguyen, D. D.; Lai, J.-Y. Advancing the stimuli response of polymer-based drug delivery systems for ocular disease treatment, Poly. Chem. 2020, 11, 6988–7008.
Ku, K. H. Responsive nanostructured polymer particles, Polymers 2021, 13, 273.
Wang, J.; Xu, W.; Zhang, N.; Yang, C.; Xu, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, B.; Ding, J.; Chen, X. X-ray-responsive polypeptide nanogel for concurrent chemoradiotherapy, J. Control. Release 2021, 332, 1–9.
Li, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, Q.; Chen, Y. A GSH-responsive PET-based fluorescent probe for cancer cells imaging, Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 1541–1544.
Hajebi, S.; Rabiee, N.; Bagherzadeh, M.; Ahmadi, S.; Rabiee, M.; Roghani-Mamaqani, H.; Tahriri, M.; Tayebi, L.; Hamblin, M. R. Stimulus-responsive polymeric nanogels as smart drug delivery systems, Acta Biomater. 2019, 92, 1–18.
Grzelczak, M.; Liz-Marzan, L. M.; Klajn, R. Stimuli-responsive self-assembly of nanoparticles, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 1342–1361.
Chen, J.; Jiang, Z.; Xu, W.; Sun, T.; Zhuang, X.; Ding, J.; Chen, X. Spatiotemporally targeted nanomedicine overcomes hypoxia-induced drug resistance of tumor cells after disrupting neovasculature, Nano lett. 2020, 20, 6191–6198.
Hsu, P.-H.; Almutairi, A. Recent progress of redox-responsive polymeric nanomaterials for controlled release, J. Mater. Chem. B. 2021, 9, 2179–2188.
Feng, X.; Xu, W.; Xu, X.; Li, G.; Ding, J.; Chen, X. Cystine proportion regulates fate of polypeptide nanogel as nanocarrier for chemotherapeutics, Sci. China Chem. 2021, 64, 293–301.
Fang, Z.; Wang, X.; Sun, Y.; Fan, R.; Liu, Z.; Guo, R.; Xie, D. Sgc8 aptamer targeted glutathione-responsive nanoassemblies containing Ara-C prodrug for the treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia, Nanoscale 2019, 11, 23000–23012.
Masood, F. Polymeric nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery system for cancer therapy, Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 60, 569–578.
You, X.; Kang, Y.; Hollett, G.; Chen, X.; Zhao, W.; Gu, Z.; Wu, J. Polymeric nanoparticles for colon cancer therapy: Overview and perspectives, J. Mater. Chem. B. 2016, 4, 7779–7792.
Li, D.; Zhang, R.; Liu, G.; Kang, Y.; Wu, J. Redox-responsive self-assembled nanoparticles for cancer therapy, Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2020, 9, 2000605.
Zhong, W.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, Y.; Lin, D.; Wu, J. Recent applications and strategies in nanotechnology for lung diseases, Nano Res. 2021, 14, 2067–2089.
Feng, X.; Xu, W.; Liu, J.; Li, D.; Li, G.; Ding, J.; Chen, X. Polypeptide nanoformulation-induced immunogenic cell death and remission of immunosuppression for enhanced chemoimmunotherapy, Sci. Bull. 2021, 66, 362–373.
Huang, J.; You, X.; Xin, P.; Gu, Z.; Chen, C.; Wu, J. Egg white as a natural and safe biomaterial for enhanced cancer therapy, Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 1737–1742.
Xie, J.; Lu, Y.; Yu, B.; Wu, J.; Liu, J. Galactose-modified enzymatic synthesis of poly (amino-co-ester) micelles for co-delivery miR122 and sorafenib to inhibit hepatocellular carcinoma development, Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 1173–1177.
Zheng, Y.; You, X.; Guan, S.; Huang, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wu, J. Poly (ferulic acid) with an anticancer effect as a drug nanocarrier for enhanced colon cancer therapy, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1808646.
You, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Wu, J. Rebirth of aspirin synthesis byproduct: Prickly poly (salicylic acid) nanoparticles as self-anticancer drug carrier, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2100805.
Ou, K.; Xu, X.; Guan, S.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, X.; Kang, Y.; Wu, J. Nanodrug carrier based on poly (ursolic acid) with self — anticancer activity against colorectal cancer, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 30, 1907857.
Zhang, F.; Ni, Q.; Jacobson, O.; Cheng, S.; Liao, A.; Wang, Z.; He, Z.; Yu, G.; Song, J.; Ma, Y.; Niu, G.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, G.; Chen, X. Polymeric nanoparticles with a glutathione-sensitive heterodimeric multifunctional prodrug for in vivo drug monitoring and synergistic cancer therapy, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 7066–7070.
Su, L.; Li, R.; Khan, S.; Clanton, R.; Zhang, F.; Lin, Y.-N.; Song, Y.; Wang, H.; Fan, J.; Hernandez, S.; Butters, A. S.; Akabani, G.; MacLoughlin, R.; Smolen, J.; Wooley, K. L. Chemical design of both a glutathione-sensitive dimeric drug guest and a glucose-derived nanocarrier host to achieve enhanced osteosarcoma lung metastatic anticancer selectivity, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 1438–1446.
Pei, Q.; Hu, X.; Zheng, X.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Jing, X.; Xie, Z. Light-activatable red blood cell membrane-camouflaged dimeric prodrug nanoparticles for synergistic photodynamic/chemotherapy, Acs Nano. 2018, 12, 1630–1641.
Guo, X.; Wang, L.; Duval, K.; Fan, J.; Zhou, S.; Chen, Z. Dimeric drug polymeric micelles with acid-active tumor targeting and FRET-traceable drug release, Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1705436.
Cheng, Q.; Li, S.; Ma, Y.; Yin, H.; Wang, R. pH-Responsive supramolecular DOX-dimer based on cucurbit 8 uril for selective drug release, Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 1235–1238.
Cai, K.; He, X.; Song, Z.; Yin, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Uckun, F. M.; Jiang, C.; Cheng, J. Dimeric drug polymeric nanoparticles with exceptionally high drug loading and quantitative loading efficiency, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 3458–3461.
Zhou, L.; Xie, H.; Chen, X.; Wan, J.; Xu, S.; Han, Y.; Chen, D.; Qiao, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, S.; Wang, H. Dimerization-induced self-assembly of a redox-responsive prodrug into nanoparticles for improved therapeutic index, Acta Biomater. 2020, 113, 464–477.
Zhuang, Y.; Su, Y.; Peng, Y.; Wang, D.; Deng, H.; Xi, X.; Zhu, X.; Lu, Y. Facile fabrication of redox-responsive thiol-containing drug delivery system via RAFT polymerization, Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 1408–1418.
Kamojjala, R.; Bostrom, B. Allopurinol to prevent mercaptopurine adverse effects in children and young adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia, J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 43, 95–100.
Yao, J.; Chen, J.-M.; Xu, Y.-B.; Lu, T.-B. Enhancing the solubility of 6-mercaptopurine by formation of ionic cocrystal with zinc trifluoromethanesulfonate: Single-crystal-to-single-crystal transformation, Cryst. Growth Des. 2014, 14, 5019–5025.
Hussein, A.; Badr, Y. A.; Shouman, S. A.; Sliem, M. A. Improvement of 6 mercaptopurine efficiency by encapsulated in chitosan nanoparticles, Arab J. Nucl. Sci. Appl. 2018, 51, 181–186.
Zacchigna, M.; Cateni, F.; Di Luca, G.; Drioli, S. A simple method for the preparation of PEG-6-mercaptopurine for oral administration, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 6607–6609.
Wu, J.; Zhao, L.; Xu, X.; Bertrand, N.; Choi, W. I.; Yameen, B.; Shi, J.; Shah, V.; Mulvale, M.; MacLean, J. L.; Farokhzad, O. C. Hydrophobic cysteine poly (disulfide)-based redox-hypersensitive nanoparticle platform for cancer theranostics. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed, Engl. 2015, 54, 9218–23.
Wang, J.-Q.; Wang, L.-Y.; Li, S.-J.; Tong, T.; Wang, L.; Huang, C.-S.; Xu, Q.-C.; Huang, X.-T.; Li, J.-H.; Wu, J.; Zhao, W.; Yin, X.-Y. Histone methyltransferase G9a inhibitor-loaded redox-responsive nanoparticles for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma therapy, Nanoscale 2020, 12, 15767–15774.
Wang, L.; You, X.; Lou, Q.; He, S.; Zhang, J.; Dai, C.; Zhao, M.; Zhao, M.; Hu, H.; Wu, J. Cysteine-based redox-responsive nanoparticles for small-molecule agent delivery, Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 4218–4229.
Ibrahim, A.; Twizeyimana, E.; Lu, N.; Ke, W.; Mukerabigwi, J. F.; Mohammed, F.; Japir, A. A.-W. M. M.; Ge, Z. Reduction-responsive polymer prodrug micelles with enhanced endosomal escape capability for efficient intracellular translocation and drug release, ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2019, 2, 5099–5109.
He, W.; Xing, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, D.; Wu, W.; Guo, J.; Mitragotri, S. Nanocarrier-mediated cytosolic delivery of biopharmaceuticals, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1910566.
Wilhelm, S.; Tavares, A. J.; Oin, D.; Ohta, S.; Audet, J.; Dvorak, H. F.; Chan, W. C. W. Analysis of nanoparticle delivery to tumours, Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 1–12.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51973243 and 52173150), International Cooperation and Exchange of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51820105004), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2020M683058), the Science and Technology Planning Project of Shenzhen (No. JCYJ20190807155801657), Guangdong Innovative and Entrepreneurial Research Team Program (No. 2016ZT06S029).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
12274_2021_4037_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
A drug/carrier dual redox-responsive system based on 6-mercaptopurine dimer-loaded cysteine polymer nanoparticles for enhanced lymphoma therapy
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Dai, C., Fang, Y. et al. A drug/carrier dual redox-responsive system based on 6-mercaptopurine dimer-loaded cysteine polymer nanoparticles for enhanced lymphoma therapy. Nano Res. 15, 4544–4551 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-021-4037-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-021-4037-0