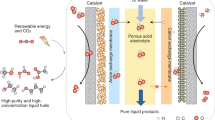
Abstract
Most organic commodity chemicals are derived from fossil carbon resources. The dependency is so immense that it is difficult to compensate for the accompanying carbon footprint with current technology and chemical infrastructure. To mitigate the future fossil fuel usage, it is crucial to explore alternative chemical pathways, which are both sustainable and suitable for large-scale productions. Here we demonstrate a closed-loop carbon-neutral chemical route, using standard coin catalyst, to produce high concentrated formate and formic acid. The catalyst’s Faradaic efficiency (FE) of formate is ∼ 95.3% with great durability. The chemicals are not only synthesized but also purified and utilized in zero-carbon scenarios. We successfully harvested 45% formate salt and 86.2% formic acid, for applications like anti-freezing reagent and green liquid fuel to power the fuel-cell vehicles.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mora Rollo, A.; Rollo, A.; Mora, C. The tree-lined path to carbon neutrality. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 332–332.
Koh, L. P.; Zeng, Y. W.; Sarira, T. V.; Siman, K. Carbon prospecting in tropical forests for climate change mitigation. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1271.
Honegger, M.; Michaelowa, A.; Roy, J. Potential implications of carbon dioxide removal for the sustainable development goals. Climate Policy 2021, 21, 678–698.
Zeyringer, M.; Price, J.; Fais, B.; Li, P. H.; Sharp, E. Designing low-carbon power systems for great Britain in 2050 that are robust to the spatiotemporal and inter-annual variability of weather. Nat. Energy 2018, 3, 395–403.
Mallapaty, S. How China could be carbon neutral by mid-century. Nature 2020, 586, 482–483.
Keyßer, L. T.; Lenzen, M. 1.5 °C degrowth scenarios suggest the need for new mitigation pathways. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2676.
Liu, C.; Colón, B. C.; Ziesack, M.; Silver, P. A.; Nocera, D. G. Water splitting-biosynthetic system with CO2 reduction efficiencies exceeding photosynthesis. Science 2016, 352, 1210–1213.
Price, J. S.; Grede, A. J.; Wang, B. M.; Lipski, M. V.; Fisher, B.; Lee, K. T.; He, J. W.; Brulo, G. S.; Ma, X. K.; Burroughs, S. et al. High-concentration planar microtracking photovoltaic system exceeding 30% efficiency. Nat. Energy 2017, 2, 17113.
Williams, J. H.; DeBenedictis, A.; Ghanadan, R.; Mahone, A.; Moore, J.; Morrow III, W. R.; Price, S.; Torn, M. S. The technology path to deep greenhouse gas emissions cuts by 2050: The pivotal role of electricity. Science 2012, 335, 53–59.
Bushuyev, O. S.; De Luna, P.; Dinh, C. T.; Tao, L.; Saur, G.; van de Lagemaat, J.; Kelley, S. O.; Sargent, E. H. What should we make with CO2 and how can we make it. Joule 2018, 2, 825–832.
De Luna, P.; Hahn, C.; Higgins, D.; Jaffer, S. A.; Jaramillo, T. F.; Sargent, E. H. What would it take for renewably powered electrosynthesis to displace petrochemical processes. Science 2019, 364, eaav3506.
Chu, S.; Cui, Y.; Liu, N. The path towards sustainable energy. Nat. Mater. 2017, 16, 16–22.
Kuhl, K. P.; Cave, E. R.; Abram, D. N.; Jaramillo, T. F. New insights into the electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide on metallic copper surfaces. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 7050–7059.
Lei, Q.; Zhu, H.; Song, K. P.; Wei, N. N.; Liu, L. M.; Zhang, D. L.; Yin, J.; Dong, X. L.; Yao, K. X.; Wang, N. et al. Investigating the origin of enhanced C2+ selectivity in oxide-/hydroxide-derived copper electrodes during CO2 electroreduction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 4213–4222.
Gao, D. F.; Arán-Ais, R. M.; Jeon, H. S.; Cuenya, B. R. Rational catalyst and electrolyte design for CO2 electroreduction towards multicarbon products. Nat. Catal. 2019, 2, 198–210.
Vasileff, A.; Xu, C. C.; Jiao, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Qiao, S. Z. Surface and interface engineering in copper-based bimetallic materials for selective CO2 electroreduction. Chem 2018, 4, 1809–1831.
Zhu, P, Wang, H. T. Structural evolution of oxide-/hydroxide-derived copper electrodes accounts for the enhanced C2+ product selectivity during electrochemical CO2 reduction. Sci. Bull. 2020, 65, 977–979.
Sholl, D. S.; Lively, R. P. Seven chemical separations to change the world. Nature 2016, 532, 435–437.
Chen, K. J.; Madden, D. G.; Mukherjee, S.; Pham, T.; Forrest, K. A.; Kumar, A.; Space, B.; Kong, J.; Zhang, Q. Y.; Zaworotko, M. J. Synergistic sorbent separation for one-step ethylene purification from a four-component mixture. Science 2019, 366, 241–246.
Tang, C.; Gong, P.; Xiao, T. S.; Sun, Z. Z. Direct electrosynthesis of 52% concentrated Co on silver’s twin boundary. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2139.
Xia, C.; Zhu, P.; Jiang, Q.; Pan, Y.; Liang, W. T.; Stavitski, E.; Alshareef, H. N.; Wang, H. T. Continuous production of pure liquid fuel solutions via electrocatalytic CO2 reduction using solid-electrolyte devices. Nat. Energy 2019, 4, 776–785.
Ma, W. C.; Xie, S. J.; Liu, T. T.; Fan, Q. Y.; Ye, J. Y.; Sun, F. F.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, Q. H.; Cheng, J.; Wang, Y. Electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 to ethylene and ethanol through hydrogen-assisted C-C coupling over fluorine-modified copper. Nat. Catal. 2020, 3, 478–487.
Zhong, M.; Tran, K.; Min, Y. M.; Wang, C. H.; Wang, Z. Y.; Dinh, C. T.; De Luna, P.; Yu, Z. Q.; Rasouli, A. S.; Brodersen, P. et al. Accelerated discovery of CO2 electrocatalysts using active machine learning. Nature 2020, 581, 178–183.
Wang, L.; Jin, P.; Duan, S.; She, H.; Huang, J.; Wang, Q. In-situ incorporation of Copper (II) porphyrin functionalized zirconium MOF and TiO2 for efficient photocatalytic CO2 reduction. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 926–933.
Ye, K.; Cao, A.; Shao, J. Q.; Wang, G.; Si, R.; Ta, N.; Xiao, J. P.; Wang, G. X. Synergy effects on Sn-Cu alloy catalyst for efficient CO2 electroreduction to formate with high mass activity. Sci. Bull. 2020, 65, 711–719.
Brunning, A. Periodic graphics: The compositions of U. S. coins. CEN ACS ORG 94, 28 (2016).
Japan MINT [Online]. https://www.mint.go.jp/eng/operations/eng/eng_operations_coin_in-dex.html.
The Metals in UK Coins [Online]. https://www.compoundchem.com/2014/03/27/the-metals-in-uk-coins/.
Copper and the EURO [Online]. https://copperalliance.eu/about-copper/applications/coinage/.
China 5 Jiao, 2016 [Online]. https://en.ucoin.net/coin/china-5-jiao-2016/?cid=61867.
Cheng, Y. C.; Wu, C. J.; Chiang, R. C. Free energy of surface segregation in binary alloys. Phys. Rev. B 1985, 32, 4224–4227.
Chang, X. X.; Wang, T.; Zhao, Z. J.; Yang, P. P.; Greeley, J.; Mu, R. T.; Zhang, G.; Gong, Z. M.; Luo, Z. B.; Chen, J. et al. Tuning Cu/Cu2O interfaces for the reduction of carbon dioxide to methanol in aqueous solutions. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 15415–15419.
Xiong, W.; Yang, J.; Shuai, L.; Hou, Y.; Qiu, M.; Li, X. Y.; Leung, M. K. H. CuSn alloy nanoparticles on nitrogen-doped graphene for electrocatalytic CO2 reduction. ChemElectroChem 2019, 6, 5951–5957.
Ye, K.; Zhou, Z. W.; Shao, J. Q.; Lin, L.; Gao, D. F.; Ta, N.; Si, R.; Wang, G. X.; Bao, X. H. In situ reconstruction of a hierarchical Sn-Cu/SnOx core/shell catalyst for high-performance CO2 electroreduction. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 4814–4821.
Tang, C.; Shi, J. J.; Bai, X. W.; Hu, A. Q.; Xuan, N. N.; Yue, Y. W.; Ye, T.; Liu, B.; Li, P. X.; Zhuang, P. Y. et al. CO2 reduction on copper’s twin boundary. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 2026–2032.
Liu, H.; Su, Y. Q.; Kuang, S. Y.; Hensen, E. J. M.; Zhang, S.; Ma, X. B. Highly efficient CO2 electrolysis within a wide operation window using octahedral tin oxide single crystals. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 7848–7856.
Tan, D. X.; Zhang, J. L.; Cheng, X. Y.; Tan, X. N.; Shi, J. B.; Zhang, B. X.; Han, B. X.; Zheng, L. R.; Zhang, J. CuxNiy alloy nanoparticles embedded in a nitrogen-carbon network for efficient conversion of carbon dioxide. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 4491–4496.
Feng, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, H.; Dong, C. K.; Wang, J. Q.; Kulinich, S. A.; Du, X. W. Laser-prepared CuZn alloy catalyst for selective electrochemical reduction of CO2 to ethylene. Langmuir 2018, 34, 13544–13549.
Kim, D.; Resasco, J.; Yu, Y.; Asiri, A. M.; Yang, P. D. Synergistic geometric and electronic effects for electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide using gold-copper bimetallic nanoparticles. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4948.
Pander III, J. E.; Baruch, M. F.; Bocarsly, A. B. Probing the mechanism of aqueous CO2 reduction on post-transition-metal electrodes using ATR-IR spectroelectrochemistry. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 7824–7833.
Hollingsworth, N.; Taylor, S. R. R.; Galante, M. T.; Jacquemin, J.; Longo, C.; Holt, K. B.; de Leeuw, N. H.; Hardacre, C. Reduction of carbon dioxide to formate at low overpotential using a superbase ionic liquid. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 127, 14370–14374.
Li, F. W.; Chen, L.; Xue, M. Q.; Williams, T.; Zhang, Y.; MacFarlane, D. R.; Zhang, J. Towards a better Sn: Efficient electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 to formate by Sn/SnS2 derived from SnS2 nanosheets. Nano Energy 2017, 31, 270–277.
Lei, F. C.; Liu, W.; Sun, Y. F.; Xu, J. Q.; Liu, K. T.; Liang, L.; Yao, T.; Pan, B. C.; Wei, S. Q.; Xie, Y. Metallic tin quantum sheets confined in graphene toward high-efficiency carbon dioxide electroreduction. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12697.
Gao, S.; Lin, Y.; Jiao, X. C.; Sun, Y. F.; Luo, Q. Q.; Zhang, W. H.; Li, D. Q.; Yang, J. L.; Xie, Y. Partially oxidized atomic cobalt layers for carbon dioxide electroreduction to liquid fuel. Nature 2016, 529, 68–71.
Bulushev, D. A.; Ross, J. R. H. Towards sustainable production of formic acid. ChemSusChem 2018, 11, 821–836.
Zhang, S.; Kang, P.; Meyer, T. J. Nanostructured tin catalysts for selective electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide to formate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 1734–1737.
Luc, W.; Collins, C.; Wang, S. W.; Xin, H. L.; He, K.; Kang, Y. J.; Jiao, F. Ag-Sn bimetallic catalyst with a core-shell structure for CO2 reduction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 1885–1893.
Kumar, B.; Atla, V.; Brian, J. P.; Kumari, S.; Nguyen, T. Q.; Sunkara, M.; Spurgeon, J. M. Reduced SnO2 porous nanowires with a high density of grain boundaries as catalysts for efficient electrochemical CO2-into-hcooh conversion. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 3645–3649.
Zheng, X. L.; De Luna, P.; de Arquer, F. P. G.; Zhang, B.; Becknell, N.; Ross, M. B.; Li, Y. F.; Banis, M. N.; Li, Y. Z.; Liu, M. et al. Sulfur-modulated Tin sites enable highly selective electrochemical reduction of CO2 to formate. Joule 2017, 1, 794–805.
He, J. F.; Dettelbach, K. E.; Huang, A. X.; Berlinguette, C. P. Brass and bronze as effective CO2 reduction electrocatalysts. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017, 129, 16806–16809.
Strong, C. K.; Ye, Z. R.; Shi, X. M. Safety effects of winter weather: The state of knowledge and remaining challenges. Transp. Rev. 2010, 30, 677–699.
Xu, C.; Kohler, T. A.; Lenton, T. M.; Svenning, J. C.; Scheffer, M. Future of the human climate niche. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 11350–11355.
Hellstén, P.; Salminen, J.; Jørgensen, K.; Nystén, T. Use of potassium formate in road winter deicing can reduce groundwater deterioration. Environ. Sci. & Technol. 2005, 39, 5095–5100.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21771040 and 62074043), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Nos. 2017YFA0207303 and 2016YFA0203900).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
T. X. and Z. S. conceived the project, analyzed the data and wrote the paper. T. X. prepared all the coin catalysts. T. X. and C. T. performed the CO2RR including the liquid products evaluation and analyzed the gas products. T. X. and H. Li. contributed to the solar salt, pure formic acid preparation, and characterizations of material. Z. S. supervised all research phases and revised the manuscript. All authors read and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All authors declare no competing interests.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, T., Tang, C., Li, H. et al. CO2 reduction with coin catalyst. Nano Res. 15, 3859–3865 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-021-3990-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-021-3990-y