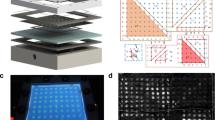
Abstract
Despite outstanding accomplishments in catalyst discovery, finding new, more efficient, environmentally neutral, and noble metal-free catalysts remains challenging and unsolved. Recently, complex solid solutions consisting of at least five different elements and often named as high-entropy alloys have emerged as a new class of electrocatalysts for a variety of reactions. The multicomponent combinations of elements facilitate tuning of active sites and catalytic properties. Predicting optimal catalyst composition remains difficult, making testing of a very high number of them indispensable. We present the high-throughput screening of the electrochemical activity of thin film material libraries prepared by combinatorial co-sputtering of metals which are commonly used in catalysis (Pd, Cu, Ni) combined with metals which are not commonly used in catalysis (Ti, Hf, Zr). Introducing unusual elements in the search space allows discovery of catalytic activity for hitherto unknown compositions. Material libraries with very similar composition spreads can show different activities vs. composition trends for different reactions. In order to address the inherent challenge of the huge combinatorial material space and the inability to predict active electrocatalyst compositions, we developed a high-throughput process based on co-sputtered material libraries, and performed high-throughput characterization using energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), scanning transmission electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and conductivity measurements followed by electrochemical screening by means of a scanning droplet cell. The results show surprising material compositions with increased activity for the oxygen reduction reaction and the hydrogen evolution reaction. Such data are important input data for future data-driven materials prediction.

Article PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
References
Yeh, J. W.; Chen, Y. L.; Lin, S. J.; Chen, S. K. High-entropy alloys—A new era of exploitation. MSF 2007, 560, 1–9.
Guo, S.; Liu, C. T. Phase stability in high entropy alloys: Formation of solid-solution phase or amorphous phase. Progr. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2011, 21, 433–146.
Ye, Y. F.; Wang, Q.; Lu, J.; Liu, C. T.; Yang, Y. High-entropy alloy: Challenges and prospects. Mater. Today 2016, 19, 349–362.
Löffler, T.; Savan, A.; Garzón-Manjón, A.; Meischein, M.; Scheu, C.; Ludwig, A.; Schuhmann, W. Toward a paradigm shift in electrocatalysis using complex solid solution nanoparticles. ACS Energy Lett. 2019, 4, 1206–1214.
Wu, D. S.; Kusada, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Toriyama, T.; Matsumura, S.; Gueye, I.; Seo, O.; Kim, J.; Hiroi, S.; Sakata, O., et al. On the electronic structure and hydrogen evolution reaction activity of platinum group metal-based high-entropy-alloy nanoparticles. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 12731–12736.
Gludovatz, B.; Hohenwarter, A.; Catoor, D.; Chang, E. H.; George, E. P.; Ritchie, R. O. A fracture-resistant high-entropy alloy for cryogenic applications. Science 2014, 345, 1153–1158.
Ludwig, A. Discovery of new materials using combinatorial synthesis and high-throughput characterization of thin-film materials libraries combined with computational methods. npj Comput. Mater. 2019, 5, 70.
Ludwig, A.; Zarnetta, R.; Hamann, S.; Savan, A.; Thienhaus, S. Development of multifunctional thin films using high-throughput experimentation methods. Int. J. Mater. Res. 2008, 10, 1144–1149.
Gao, S. J.; Hao, S. Y.; Huang, Z. N.; Yuan, Y. F.; Han, S.; Lei, L. C.; Zhang, X. W.; Shahbazian-Yassar, R.; Lu, J. Synthesis of high-entropy alloy nanoparticles on supports by the fast moving bed pyrolysis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2016.
Li, Z. M.; Ludwig, A.; Savan, A.; Springer, H.; Raabe, D. Combinatorial metallurgical synthesis and processing of high-entropy alloys. J. Mater. Res. 2018, 33, 3156–3169.
Glasscott, M. W.; Pendergast, A. D.; Goines, S.; Bishop, A. R.; Hoang, A. T.; Renault, C.; Dick, J. E. Electrosynthesis of high-entropy metallic glass nanoparticles for designer, multi-functional electrocatalysis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2650.
Qiu, H. J.; Fang, G.; Gao, J. J.; Wen, Y. R.; Lv, J.; Li, H. L.; Xie, G. Q.; Liu, X. J.; Sun, S. H. Noble metal-free nanoporous high-entropy alloys as highly efficient electrocatalysts for oxygen evolution reaction. ACS Materials Lett. 2019, 1, 526–533.
Pedersen, J. K.; Batchelor, T. A. A.; Bagger, A.; Rossmeisl, J. High-Entropy alloys as catalysts for the CO2 and CO reduction reactions. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 2169–2176.
Chen, H.; Lin, W. W.; Zhang, Z. H.; Jie, K. C.; Mullins, D. R.; Sang, X. H.; Yang, S. Z.; Jafta, C. J.; Bridges, C. A.; Hu, X. B., et al. Mechanochemical synthesis of high entropy oxide materials under ambient conditions: Dispersion of catalysts via entropy maximization. ACS Materials Lett. 2019, 1, 83–88.
Löffler, T.; Meyer, H.; Savan, A.; Wilde, P.; Garzón Manjón, A.; Chen, Y. T.; Ventosa, E.; Scheu, C.; Ludwig, A.; Schuhmann, W. Discovery of a multinary noble metal-free oxygen reduction catalyst. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1802269.
Qiu, H. J.; Fang, G.; Wen, Y. R.; Liu, P.; Xie, G. Q.; Liu, X. J.; Sun, S. H. Nanoporous high-entropy alloys for highly stable and efficient catalysts. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 6499–6506.
Batchelor, T. A. A.; Löffler, T.; Xiao, B.; Krysiak, O. A.; Strotkötter, V.; Pedersen, J. K.; Clausen, C. M.; Savan, A.; Li, Y. J.; Schuhmann, W., et al. Complex solid solution electrocatalyst discovery by computational prediction and high-throughput experimentation. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 6932–6937.
Tsai, C. F.; Yeh, K. Y.; Wu, P. W.; Hsieh, Y. F.; Lin, P. Effect of platinum present in multi-element nanoparticles on methanol oxidation. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 478, 868–871.
Yusenko, K. V.; Riva, S.; Carvalho, P. A.; Yusenko, M. V.; Arnaboldi, S.; Sukhikh, A. S.; Hanfland, M.; Gromilov, S. A. First hexagonal close packed high-entropy alloy with outstanding stability under extreme conditions and electrocatalytic activity for methanol oxidation. Scr. Mater. 2017, 138, 22–27.
Yao, Y. G.; Huang, Z. N.; Xie, P. F.; Lacey, S. D.; Jacob, R. J.; Xie, H.; Chen, F. J., Nie, A. M.; Pu, T. C.; Rehwoldt, M., et al. Carbothermal shock synthesis of high-entropy-alloy nanoparticles. Science 2018, 359, 1489–1494.
Xie, P. F.; Yao, Y. G.; Huang, Z. N.; Liu, Z. Y.; Zhang, J. L.; Li, T. Y.; Wang, G. F.; Shahbazian-Yassar, R.; Hu, L. B.; Wang, C. Highly efficient decomposition of ammonia using high-entropy alloy catalysts. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4011.
Schäfer, D.; Mardare, C.; Savan, A.; Sanchez, M. D.; Mei, B.; Xia, W.; Muhler, M.; Ludwig, A.; Schuhmann, W. High-throughput characterization of Pt supported on thin film oxide material libraries applied in the oxygen reduction reaction. Anal. Chem. 2011, 1916–1923.
Grote, J. P.; Zeradjanin, A. R.; Cherevko, S.; Savan, A.; Breitbach, B.; Ludwig, A.; Mayrhofer, K. J. J. Screening of material libraries for electrochemical CO2 reduction catalysts—Improving selectivity of Cu by mixing with Co. J. Catal. 2016, 343, 248–256.
Sliozberg, K.; Schäfer, D.; Erichsen, T.; Meyer, R.; Khare, C.; Ludwig, A.; Schuhmann, W. High-throughput screening of thin-film semiconductor material libraries I: System development and case study for Ti-W-O. ChemSusChem 2015, 8, 1270–1278.
Batchelor, T. A. A.; Pedersen, J. K.; Winther, S. H.; Castelli, I. E.; Jacobsen, K. W.; Rossmeisl, J. High-entropy alloys as a discovery platform for electrocatalysis. Joule 2019, 3, 834–845.
Löffler, T.; Savan, A.; Meyer, H.; Meischein, M.; Strotkötter, V.; Ludwig, A.; Schuhmann, W. Design of complex solid-solution electrocatalysts by correlating configuration, adsorption energy distribution patterns, and activity curves. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 5844–5850.
Sarkar, S.; Peter, S. C. An overview on Pd-based electrocatalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2018, 5, 2060–2080.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge financial support by the German Research Foundation (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, DFG) in the framework of the projects AN 1570/2-1 (C. A., S. S.) and LU 1175/31-1) (A. L). This project has received funding from the European Research Council (ERC) under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme (grant agreement CasCat [833408], W. S.).
Funding
Funding note: Open Access funding enabled and organized by Projekt DEAL.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’ s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder.
To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Krysiak, O.A., Schumacher, S., Savan, A. et al. Searching novel complex solid solution electrocatalysts in unconventional element combinations. Nano Res. 15, 4780–4784 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-021-3637-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-021-3637-z