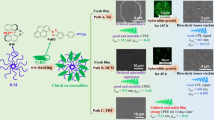
Abstract
Chiral metal-organic frameworks (chirMOFs) have been widely considered on enantioselective adsorption/separation, asymmetric catalysis, biological and nonlinear optical applications. However, chirMOFs are facing a great challenge in development of chiroptical thin films with circularly polarized luminescence (CPL) property. Here, we first report CPL thin films by encapsulating achiral lanthanide complexes Ln(acac)3 (Ln = EuaTbbGdc) into the pores of surface-coordinated chirMOF thin films (SURchirMOF) [Zn2(cam)2dabco]n with layer by layer (lbl) encapsulation strategy. Due to the unique combination of chiral porous MOF and adjustable luminescent complexes in the host-guest thin films, the obtained Ln(acac)3@SURchirMOF possess strong and tunable CPL property with high dissymmetry factors. The compared CPL and fluorescent lifetime results show that the advantage of this preparation strategy can effectively achieve energy transfer from Ln(acac)3 to SURchirMOF, resulting in an excellent CPL performance. This study not only provides a novel strategy to develop new types of chiral thin films but also offers an efficient approach for tunable chiroptical applications.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xu, H. C.; Chowdhury, S.; Ellman, J. A. Asymmetric synthesis of amines using tert-butanesulfinamide. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 2271–2280.
Song, J.; Chen, D. F.; Gong, L. Z. Recent progress in organocatalytic asymmetric total syntheses of complex indole alkaloids. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2017, 4, 381–396.
Kou, X. Z.; Shao, Q. H.; Ye, C. H.; Yang, G. Q.; Zhang, W. B. Asymmetric aza-wacker-type cyclization of N-Ts hydrazine-tethered tetrasubstituted olefins: Synthesis of pyrazolines bearing one quaternary or two vicinal stereocenters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 7587–7597.
Yutthalekha, T.; Wattanakit, C.; Lapeyre, V.; Nokbin, S.; Warakulwit, C.; Limtrakul, J.; Kuhn, A. Asymmetric synthesis using chiral-encoded metal. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12678.
Xue, Y. P.; Cao, C. H.; Zheng, Y. G. Enzymatic asymmetric synthesis of chiral amino acids. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 1516–1561.
Scanlon, S.; Aggeli, A.; Boden, N.; Koopmans, R. J.; Brydson, R.; Rayner, C. M. Peptide aerogels comprising self-assembling nanofibrils. Micro-Nano Lett. 2007, 2, 24–29.
Wang, Z. G.; Ding, B. Q. Engineering DNA self-assemblies as templates for functional nanostructures. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 1654–1662.
Agarwal, N. P.; Matthies, M.; Gür, F. N.; Osada, K.; Schmidt, T. L. Block copolymer micellization as a protection strategy for DNA origami. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 5460–5464.
Luo, Z. L.; Zhang, S. G. Designer nanomaterials using chiral self-assembling peptide systems and their emerging benefit for society. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 4736–4754.
Wang, L.; Li, Q. Photochromism into nanosystems: Towards lighting up the future nanoworld. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 1044–1097.
Pop, F.; Zigon, N.; Avarvari, N. Main-group-based electro- and photoactive chiral materials. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 8435–8478.
Huo, S. W.; Duan, P. F.; Jiao, T. F.; Peng, Q. M.; Liu, M. H. Self-assembled luminescent quantum dots to generate full-color and white circularly polarized light. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 12174–12178.
Li, M.; Li, S. H.; Zhang, D. D.; Cai, M. H.; Duan, L.; Fung, M. K.; Chen, C. F. Stable enantiomers displaying thermally activated delayed fluorescence: Efficient OLEDs with circularly polarized electroluminescence. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 2889–2893.
Yang, X. F.; Han, J. L.; Wang, Y. F.; Duan, P. F. Photon-upconverting chiral liquid crystal: Significantly amplified upconverted circularly polarized luminescence. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 172–178.
Zinna, F.; Albano, G.; Taddeucci, A.; Colli, T.; Aronica, L. A.; Pescitelli, G.; Di Bari, L. Emergent nonreciprocal circularly polarized emission from an organic thin film. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2002575.
Zhang, M. M.; Dong, X. Y.; Wang, Z. Y.; Li, H. Y.; Li, S. J.; Zhao, X. L.; Zang, S. Q. AIE triggers the circularly polarized luminescence of atomically precise enantiomeric copper(I) alkynyl clusters. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 10052–10058.
MacKenzie, L. E.; Pal, R. Circularly polarized lanthanide luminescence for advanced security inks. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2021, 5, 109–124.
Jiang, Z. Y.; Wang, X. Q.; Ma, J. P.; Liu, Z. P. Aggregation-amplified circularly polarized luminescence from axial chiral boron difluoride complexes. Sci. China Chem. 2019, 62, 355–362.
He, C. L.; Feng, Z. Y.; Shan, S. Z.; Wang, M. Q.; Chen, X.; Zou, G. Highly enantioselective photo-polymerization enhanced by chiral nanoparticles and in situ photopatterning of chirality. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1188.
Duan, Y. Y.; Han, L.; Zhang, J. L.; Asahina, S.; Huang, Z. H.; Shi, L.; Wang, B.; Cao, Y. Y.; Yao, Y.; Ma, L. G. et al. Optically active nanostructured ZnO films. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 15170–15175.
Shen, Z. C.; Wang, T. Y.; Shi, L.; Tang, Z. Y.; Liu, M. H. Strong circularly polarized luminescence from the supramolecular gels of an achiral gelator: Tunable intensity and handedness. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 4267–4272.
Roose, J.; Leung, A. C. S.; Wang, J.; Peng, Q.; Sung, H. H. Y.; Williams, I. D.; Tang, B. Z. A colour-tunable chiral AIEgen: Reversible coordination, enantiomer discrimination and morphology visualization. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 6106–6114.
Zhao, B.; Pan, K.; Deng, J. P. Intense circularly polarized luminescence contributed by helical chirality of monosubstituted polyacetylenes. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 7104–7111.
Zhang, J. H.; Dai, L. X.; Webster, A. M.; Chan, W. T. K.; Mackenzie, L. E.; Pal, R.; Cobb, S. L.; Law, G. L. Unusual magnetic field responsive circularly polarized luminescence probes with highly emissive chiral europium(III) complexes. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 1004–1010.
Haraguchi, S.; Numata, M.; Li, C.; Nakano, Y.; Fujiki, M.; Shinkai, S. Circularly polarized luminescence from supramolecular chiral complexes of achiral conjugated polymers and a neutral polysaccharide. Chem. Lett. 2009, 38, 254–255.
Vijayaraghavan, R. K.; Abraham, S.; Akiyama, H.; Furumi, S.; Tamaoki, N.; Das, S. Photoresponsive glass-forming butadiene-based chiral liquid crystals with circularly polarized photoluminescence. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, 2510–2517.
Sang, Y. T.; Han, J. L.; Zhao, T. H.; Duan, P. F.; Liu, M. H. Circularly polarized luminescence in nanoassemblies: Generation, amplification, and application. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1900110.
Wang, C. T.; Chen, K. Q.; Xu, P.; Yeung, F.; Kwok, H. S.; Li, G. J. Fully chiral light emission from CsPbX3 perovskite nanocrystals enabled by cholesteric superstructure stacks. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1903155.
Gao, J. X.; Zhang, W. Y.; Wu, Z. G.; Zheng, Y. X.; Fu, D. W. Enantiomorphic perovskite ferroelectrics with circularly polarized luminescence. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 4756–4761.
Jing, X.; He, C.; Dong, D. P.; Yang, L. L.; Duan, C. Y. Homochiral crystallization of metal-organic silver frameworks: Asymmetric [3+2] cycloaddition of an azomethine ylide. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 10127–10131.
Liu, Y.; Xi, X. B.; Ye, C. C.; Gong, T. F.; Yang, Z. W.; Cui, Y. Chiral metal-organic frameworks bearing free carboxylic acids for organocatalyst encapsulation. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 13821–13825.
Gu, Z. G.; Zhan, C. H.; Zhang, J.; Bu, X. H. Chiral chemistry of metal-camphorate frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 3122–3144.
Nickerl, G.; Henschel, A.; Grünker, R.; Gedrich, K.; Kaskel, S. Chiral metal-organic frameworks and their application in asymmetric catalysis and stereoselective separation. Chem. Ing. Tech. 2011, 83, 90–103.
Gong, W.; Zhang, W. Q.; Son, F. A.; Yang, K. W.; Chen, Z. J.; Chen, X. F.; Jiang, J. W.; Liu, Y.; Farha, O. K.; Cui, Y. Topological strain-induced regioselective linker elimination in a chiral Zr(IV)-based metal-organic framework. Chem 2021, 7, 190–201.
Wu, D.; Zhou, K.; Tian, J. D.; Liu, C. P.; Tian, J. Y.; Jiang, F. L.; Yuan, D. Q.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Q. H.; Hong, M. C. Induction of chirality in a metal-organic framework built from achiral precursors. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 3087–3094.
Ferguson, A.; Liu, L. J.; Tapperwijn, S. J.; Perl, D.; Coudert, F. X.; van Cleuvenbergen, S.; Verbiest, T.; van der Veen, M. A.; Telfer, S. G. Controlled partial interpenetration in metal-organic frameworks. Nat. Chem. 2016, 8, 250–257.
Cui, Y. J.; Li, B.; He, H. J.; Zhou, W.; Chen, B. L.; Qian, G. D. Metal-organic frameworks as platforms for functional materials. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 483–493.
Ma, X. J.; Chai, Y. T.; Li, P.; Wang, B. Metal-organic framework films and their potential applications in environmental pollution control. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 1461–1470.
Ding, M. L.; Flaig, R. W.; Jiang, H. L.; Yaghi, O. M. Carbon capture and conversion using metal-organic frameworks and MOF-based materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 2783–2828.
Zhang, J. P.; Zhang, Y. B.; Lin, J. B.; Chen, X. M. Metal azolate frameworks: From crystal engineering to functional materials. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 1001–1033.
Das, S.; Xu, S. X.; Ben, T.; Qiu, S. L. Chiral recognition and separation by chirality-enriched metal-organic frameworks. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 8629–8633.
Zhang, S. Y.; Yang, C. X.; Shi, W.; Yan, X. P.; Cheng, P.; Wojtas, L.; Zaworotko, M. J. A chiral metal-organic material that enables enantiomeric identification and purification. Chem 2017, 3, 281–289.
Martell, J. D.; Porter-Zasada, L. B.; Forse, A. C.; Siegelman, R. L.; Gonzalez, M. I.; Oktawiec, J.; Runčevski, T.; Xu, J. W.; Srebro-Hooper, M.; Milner, P. J. et al. Enantioselective recognition of ammonium carbamates in a chiral metal-organic framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 16000–16012.
Chang, L. M.; An, Y. Y.; Li, Q. H.; Gu, Z. G.; Han, Y. F.; Zhang, J. N-Heterocyclic carbene as a surface platform for assembly of homochiral metal-organic framework thin films in chiral sensing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 38357–38364.
Xuan, W. M.; Zhang, M. N.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Z. J.; Cui, Y. A chiral quadruple-stranded helicate cage for enantioselective recognition and separation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 6904–6907.
Hou, X. D.; Xu, T. T.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S. J.; Tong, J.; Liu, B. Superficial chiral etching on achiral metal-organic framework for enantioselective sorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 32264–32269.
Seo, J. S.; Whang, D.; Lee, H.; Jun, S. I.; Oh, J.; Jeon, Y. J.; Kim, K. A homochiral metal-organic porous material for enantioselective separation and catalysis. Nature 2000, 404, 982–986.
Corella-Ochoa, M. N.; Tapia, J. B.; Rubin, H. N.; Lillo, V.; González-Cobos, J.; Núñez-Rico, J. L.; Balestra, S. R. G.; Almora-Barrios, N.; Lledós, M.; Güell-Bara, A. et al. Homochiral metal-organic frameworks for enantioselective separations in liquid chromatography. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 14306–14316.
Peng, Y. W.; Gong, T. F.; Zhang, K.; Lin, X. C.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, J. W.; Cui, Y. Engineering chiral porous metal-organic frameworks for enantioselective adsorption and separation. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4406.
Liu, Y.; Xuan, W. M.; Cui, Y. Engineering homochiral metal-organic frameworks for heterogeneous asymmetric catalysis and enantioselective separation. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 4112–4135.
Cho, S. H.; Ma, B. Q.; Nguyen, S. T.; Hupp, J. T.; Albrecht-Schmitt, T. E. A metal-organic framework material that functions as an enantioselective catalyst for olefin epoxidation. Chem. Commun. 2006, 24, 2563–2565.
Ma, L. Q.; Falkowski, J. M.; Abney, C.; Lin, W. B. A series of isoreticular chiral metal-organic frameworks as a tunable platform for asymmetric catalysis. Nat. Chem. 2010, 2, 838–846.
Han, J.; Lee, M. S.; Thallapally, P. K.; Kim, M.; Jeong, N. Identification of reaction sites on metal-organic framework-based asymmetric catalysts for carbonyl-ene reactions. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 3969–3977.
Liang, X. Q.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, H. X.; Ye, W.; Long, L. S.; Zhu, G. S. A proton-conducting lanthanide metal-organic framework integrated with a dielectric anomaly and second-order nonlinear optical effect. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 6513–6516.
Wen, Q.; Tenenholtz, S.; Shimon, L. J. W.; Bar-Elli, O.; Beck, L. M.; Houben, L.; Cohen, S. R.; Feldman, Y.; Oron, D.; Lahav, M. et al. Chiral and SHG-active metal-organic frameworks formed in solution and on surfaces: Uniformity, morphology control, oriented growth, and postassembly functionalization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 14210–14221.
Guo, Z. G.; Cao, R.; Wang, X.; Li, H. F.; Yuan, W. B.; Wang, G. J.; Wu, H. H.; Li, J. A multifunctional 3D ferroelectric and NLO-active porous metal-organic framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 6894–6895.
Fu, H. R.; Wang, N.; Wu, X. X.; Li, F. F.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, L. F.; Du, M. Circularly polarized room-temperature phosphorescence and encapsulation engineering for MOF-based fluorescent/phosphorescent white light-emitting devices. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2020, 8, 2000330.
Zeng, M.; Ren, A.; Wu, W. B.; Zhao, Y. S.; Zhan, C. L.; Yao, J. N. Lanthanide MOFs for inducing molecular chirality of achiral stilbazolium with strong circularly polarized luminescence and efficient energy transfer for color tuning. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 9154–9161.
Shang, W. L.; Zhu, X. F.; Liang, T. L.; Du, C.; Hu, L. Y.; Li, T. S.; Liu, M. H. Chiral reticular self-assembly of achiral AIEgen into optically pure metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) with dual mechano-switchable circularly polarized luminescence. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 12811–12816.
Qu, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z. H.; Wang, X. C.; Fang, H. X.; Tian, Z. Q.; Cao, X. Y. Molecular face-rotating cube with emergent chiral and fluorescence properties. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 18142–18145.
Zhao, T. H.; Han, J. L.; Jin, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, M. H.; Duan, P. F. Enhanced circularly polarized luminescence from reorganized chiral emitters on the skeleton of a zeolitic imidazolate framework. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 4978–4982.
Hu, L. Y.; Li, K.; Shang, W. L.; Zhu, X. F.; Liu, M. H. Emerging cubic chirality in γCD-MOF for fabricating circularly polarized luminescent crystalline materials and the size effect. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 4953–4958.
Zhang, C.; Yan, Z. P.; Dong, X. Y.; Han, Z.; Li, S.; Fu, T.; Zhu, Y. Y.; Zheng, Y. X.; Niu, Y. Y.; Zang, S. Q. Enantiomeric MOF crystals using helical channels as palettes with bright white circularly polarized luminescence. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2002914.
Zhao, T. H.; Han, J. L.; Jin, X.; Zhou, M. H.; Liu, Y.; Duan, P. F.; Liu, M. H. Dual-mode induction of tunable circularly polarized luminescence from chiral metal-organic frameworks. Research 2020, 2020, 6452123.
Okur, S.; Qin, P.; Chandresh, A.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z. J.; Lemmer, U.; Heinke, L. Eine enantioselektive elektronische Nase: Ein array nano-poröser homochiraler MOF-filme zur stereospezifischen erkennung chiraler geruchsmoleküle. Angew. Chem. 2021, 133, 3609–3614.
Gu, Z. G.; Fu, H.; Neumann, T.; Xu, Z. X.; Fu, W. Q.; Wenzel, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wöll, C. Chiral porous metacrystals: Employing liquid-phase epitaxy to assemble enantiopure metal-organic nanoclusters into molecular framework pores. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 977–983.
Gu, Z. G.; Fu, W. Q.; Wu, X.; Zhang, J. Liquid-phase epitaxial growth of a homochiral MOF thin film on poly(L-DOPA) functionalized substrate for improved enantiomer separation. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 772–775.
Huang, K.; Dong, X. L.; Ren, R. F.; Jin, W. Q. Fabrication of homochiral metal-organic framework membrane for enantioseparation of racemic diols. AIChE J. 2013, 59, 4364–4372.
Chen, S. M.; Chang, L. M.; Yang, X. K.; Luo, T.; Xu, H.; Gu, Z. G.; Zhang, J. Liquid-phase epitaxial growth of azapyrene-based chiral metal-organic framework thin films for circularly polarized luminescence. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 31421–31426.
Gu, Z. G.; Bürck, J.; Bihlmeier, A.; Liu, J. X.; Shekhah, O.; Weidler, P. G.; Azucena, C.; Wang, Z. B.; Heissler, S.; Gliemann, H. et al. Oriented circular dichroism analysis of chiral surface-anchored metal-organic frameworks grown by liquid-phase epitaxy and upon loading with chiral guest compounds. Chem.—Eur. J. 2014, 20, 9879–9882.
Liu, B.; Shekhah, O.; Arslan, H. K.; Liu, J. X.; Wöll, C.; Fischer, R. A. Enantiopure metal-organic framework thin films: Oriented SURMOF growth and enantioselective adsorption. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 807–810.
Gu, Z. G.; Grosjean, S.; Bräse, S.; Wöll, C.; Heinke, L. Enantioselective adsorption in homochiral metal-organic frameworks: The pore size influence. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 8998–9001.
Gu, Z. G.; Chen, Z.; Fu, W. Q.; Wang, F.; Zhang, J. Liquid-phase epitaxy effective encapsulation of lanthanide coordination compounds into MOF film with homogeneous and tunable white-light emission. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 28585–28590.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. XDB20000000), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2018YFA0208600), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21872148) and the Youth Innovation Promotion Association of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. 2018339).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhai, R., Xiao, Y., Gu, Z. et al. Tunable chiroptical application by encapsulating achiral lanthanide complexes into chiral MOF thin films. Nano Res. 15, 1102–1108 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-021-3610-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-021-3610-x