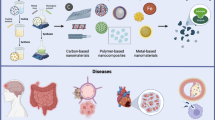
Abstract
Nanozymes are nanomaterials with enzyme-like properties that have attracted significant interest owing to their capability to address the limitations of traditional enzymes such as fragility, high cost, and impossible mass production. Over the past decade, a broad variety of nanomaterials have been found to mimic the enzyme-like activity by engineering the active centers of natural enzymes or developing multivalent elements within nanostructures. Carbon nanomaterials with well-defined electronic and geometric structures have served as favorable surrogates of traditional enzymes by mimicking the highly evolved catalytic center of natural enzymes. In particular, by combining the unique electronic, optical, thermal, and mechanical properties, carbon nanomaterials-based nanozymes can offer a variety of multifunctional platforms for biomedical applications. In this review, we will introduce the enzymatic characteristics and recent advances of carbon nanozymes, and summarize their significant applications in biomedicine.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gao, L. Z.; Zhuang, J.; Nie, L.; Zhang, J. B.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, N.; Wang, T. H.; Feng, J.; Yang, D. L.; Perrett, S. et al. Intrinsic peroxidase-like activity of ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 577–583.
Liang, M. M.; Yan, X. Y. Nanozymes: from new concepts, mechanisms, and standards to applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 2190–2200.
Wang, P. X.; Liu, S. L.; Hu, M. X.; Duan, D. M.; He, J. Y.; Hong, J. J.; Lv, R. Choi, H. S.; Yan, X. Y.; Liang, M. M. Peroxidase-like nanozymes induce a novel form of cell death and inhibit tumor growth in vivo. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2000647–2000656.
Jiang, B.; Duan, D. M.; Gao, L. Z.; Zhou, M. J.; Fan, K. L.; Tang, Y.; Xi, J. Q.; Bi, Y. H.; Tong, Z.; Gao, G. F.; Xie, N.; Tang, A. F.; Nie, G. H.; Liang, M. M.; Yan, X. Y. Standardized assays for determining the catalytic activity and kinetics of peroxidase-like nanozymes. Nat. Protoc. 2018, 13, 1506–1520.
Wei, H.; Wang, E. K. Nanomaterials with enzyme-like characteristics (nanozymes): Next-generation artificial enzymes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6060–6093.
McVey, C.; Logan, N.; Thanh, N. T. K.; Elliott, C.; Cao, C. Unusual switchable peroxidase-mimicking nanozyme for the determination of proteolytic biomarker. Nano Res. 2019, 12, 509–516.
Pardhi, V. P.; Verma, T.; Flora, S. J. S.; Chandasana, H.; Shukla, R. Nanocrystals: An overview of fabrication, characterization and therapeutic applications in drug delivery. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 5129–5146.
Wang, X. Y.; Hu, Y. H.; Wei, H. Nanozymes in bionanotechnology: From sensing to therapeutics and beyond. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2016, 3, 41–60.
Wang, Q. Q.; Wei, H.; Zhang, Z. Q.; Wang, E. K.; Dong, S. J. Nanozyme: An emerging alternative to natural enzyme for biosensing and immunoassay. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 105, 218–224.
Wang, W. S.; Li, B. L.; Yang, H. L.; Lin, Z. F.; Chen, L. L.; Li, Z.; Ge, J. Y.; Zhang, T.; Xia, H.; Li, L. H.; Lu, Y. Efficient elimination of multidrug-resistant bacteria using copper sulfide nanozymes anchored to graphene oxide nanosheets. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 2156–2160.
Sun, H. J.; Zhou, Y.; Ren, J. S.; Qu, X. G. Carbon nanozymes: Enzymatic properties, catalytic mechanism, and applications. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 9224–9237.
Hong, G. S.; Diao, S.; Antaris, A. L.; Dai, H. J. Carbon nanomaterials for biological imaging and nanomedicinal therapy. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 10816–10906.
Jariwala, D.; Sangwan, V. K.; Lauhon, L. J.; Marks, T. J.; Hersam, M. C. Carbon nanomaterials for electronics, optoelectronics, photo-voltaics, and sensing. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 2824–2860.
Xin, Q.; Jia, X. R.; Nawaz, A.; Xie, W. J.; Li, L. T.; Gong, J. R. Mimicking peroxidase active site microenvironment by functionalized graphene quantum dots. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 1427–1433.
Fan, K. L.; Xi, J. Q.; Fan, L.; Wang, P. X.; Zhu, C. H.; Tang, Y.; Xu, X. D.; Liang, M. M.; Jiang, B.; Yan, X. Y. et al. In vivo guiding nitrogen-doped carbon nanozyme for tumor catalytic therapy. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1440.
Cai, X.; Chen, H. L.; Wang, Z. X.; Sun, W. Q.; Shi, L. B.; Zhao, H. L.; Lan, M. B. 3D graphene-based foam induced by phytic acid: An effective enzyme-mimic catalyst for electrochemical detection of cell-released superoxide anion. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 123, 101–107.
Ren, C. X.; Hu, X. G.; Zhou, Q. X. Graphene oxide quantum dots reduce oxidative stress and inhibit neurotoxicity in vitro and in vivo through catalase—like activity and metabolic regulation. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1700595.
Nirala, N. R.; Abraham, S.; Kumar, V.; Bansal, A.; Srivastava, A.; Saxena, P. S. Colorimetric detection of cholesterol based on highly efficient peroxidase mimetic activity of graphene quantum dots. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2015, 218, 42–50.
Jalilov, A. S.; Nilewski, L. G.; Berka, V.; Zhang, C. H.; Yakovenko, A. A.; Wu, G.; Kent, T. A.; Tsai, A. L.; Tour, J. M. Perylene diimide as a precise graphene-like superoxide dismutase mimetic. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 2024–2032.
Wang, Y.; Wang, M. Q.; Lei, L. L.; Chen, Z. Y.; Liu, Y. S.; Bao, S. J. FePO4 embedded in nanofibers consisting of amorphous carbon and reduced graphene oxide as an enzyme mimetic for monitoring superoxide anions released by living cells. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 140.
Glorieux, C.; Calderon, P. B. Catalase, a remarkable enzyme: Targeting the oldest antioxidant enzyme to find a new cancer treatment approach. Biol. Chem. 2017, 398, 1095–1108.
Ali, M. E.; Rahman, M. M.; Sarkar, S. M.; Hamid, S. B. A. Heterogeneous metal catalysts for oxidation reactions. J. Nanomate. 2015, 2014, 209.
Chen, Q. M.; Liang, C. H.; Zhang, X. D.; Huang, Y. M. High oxidasemimic activity of Fe nanoparticles embedded in an N-rich porous carbon and their application for sensing of dopamine. Talanta 2018, 182, 476–485.
Li, S. Q.; Wang, L. T.; Zhang, X. D.; Chai, H. X.; Huang, Y. M. A Co,N co-doped hierarchically porous carbon hybrid as a highly efficient oxidase mimetic for glutathione detection. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2018, 264, 312–319.
Zhang, Q.; Chen, S.; Wang, H. Surface plasmon-enhanced nanozyme-based fenton process for visible-light-driven aqueous ammonia oxidation. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 4067–4074.
Ren, X. L.; Liu, J.; Ren, J.; Tang, F. Q.; Meng, X. W. One-pot synthesis of active copper-containing carbon dots with laccase-like activities. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 19641–19646.
Hernández-Ruiz, J.; Arnao, M. B.; Hiner, A. N. P.; García-Cánovas, F.; Acosta, M. Catalase-like activity of horseradish peroxidase: Relationship to enzyme inactivation by H2O2. Biochem. J. 2001, 354, 107–114.
Liu, S.; Tian, J. Q.; Wang, L.; Luo, Y. L.; Sun, X. P. A general strategy for the production of photoluminescent carbon nitride dots from organic amines and their application as novel peroxidase-like catalysts for colorimetric detection of H2O2 and glucose. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 411–413.
Mohammadpour, Z.; Safavi, A.; Shamsipur, M. A new label free colorimetric chemosensor for detection of mercury ion with tunable dynamic range using carbon nanodots as enzyme mimics. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 255, 1–7.
Song, Y. J.; Qu, K. G.; Zhao, C.; Ren, J. S.; Qu, X. G. Graphene oxide: Intrinsic peroxidase catalytic activity and its application to glucose detection. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 2206–2210.
Shi, W. B.; Wang, Q. L.; Long, Y. J.; Cheng, Z. L.; Chen, S. H.; Zhang, H. Z.; Huang, Y. M. Carbon nanodots as peroxidase mimetics and their applications to glucose detection. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 6695–6697.
Tran, H. V.; Nguyen, T. V.; Nguyen, N. D.; Piro, B.; Huynh, C. D. A nanocomposite prepared from FeOOH and N-doped carbon nanosheets as a peroxidase mimic, and its application to enzymatic sensing of glucose in human urine. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 270.
Yeh, M. H.; Lin, L. Y.; Sun, C. L.; Leu, Y. A.; Tsai, J. T.; Yeh, C. Y.; Vittal, R.; Ho, K. C. Multiwalled carbon nanotube@reduced graphene oxide nanoribbon as the counter electrode for dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 16626–16634.
Sang, Y. J.; Huang, Y. Y.; Li, W.; Ren, J. S.; Qu, X. G. Bioinspired design of Fe3+-doped mesoporous carbon nanospheres for enhanced nanozyme activity. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 7259–7263.
Gayathri, P.; Kumar, A. S. An iron impurity in multiwalled carbon nanotube complexes with chitosan that biomimics the heme-peroxidase function. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 17103–17112.
Huang, Y. Y.; Liu, C. Q.; Pu, F.; Liu, Z.; Ren, J. S.; Qu, X. G. A GO—Se nanocomposite as an antioxidant nanozyme for cytoprotection. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 3082–3085.
Azadmanesh, J.; Borgstahl, G. E. O. A review of the catalytic mechanism of human manganese superoxide dismutase. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 25.
Ali, S. S.; Hardt, J. I.; Quick, K. L.; Kim-Han, J. S.; Erlanger, B. F.; Huang, T. T.; Epstein, C. J.; Dugan, L. L. A biologically effective fullerene (C60) derivative with superoxide dismutase mimetic properties. Free Rad. Biol. Med. 2004, 37, 1191–1202.
Purich, D. L. Enzyme catalysis: A new definition accounting for noncovalent substrate- and product-like states. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2001, 26, 417–421.
Boutorine, A. S.; Takasugi, M.; Hélène, C.; Tokuyama, H.; Isobe, H.; Nakamura, E. Fullerene—oligonucleotide conjugates: Photoinduced sequence-specific DNA cleavage. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 1995, 33, 2462–2465.
He, X. X.; Zhang, F. Y.; Liu, J. F.; Fang, G. Z.; Wang, S. Homogenous graphene oxide-peptide nanofiber hybrid hydrogel as biomimetic polysaccharide hydrolase. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 18066–18074.
Zhang, Q.; He, X. X.; Han, A. L.; Tu, Q. X.; Fang, G. Z.; Liu, J. F.; Wang, S.; Li, H. B. Artificial hydrolase based on carbon nanotubes conjugated with peptides. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 16851–16856.
Ma, X. J.; Zhang, L.; Xia, M. F.; Li, S. Q.; Zhang, X. H.; Zhang, Y. D. Mimicking the active sites of organophosphorus hydrolase on the backbone of graphene oxide to destroy nerve agent simulants. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 21089–21093.
Zhang, P.; Sun, D. R.; Cho, A.; Weon, S.; Lee, S.; Lee, J.; Han, J. W.; Kim, D. P.; Choi, W. Modified carbon nitride nanozyme as bifunctional glucose oxidase-peroxidase for metal-free bioinspired cascade photocatalysis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 940.
Yang, H. K.; Xiao, J. Y.; Su, L.; Feng, T.; Lv, Q. Y.; Zhang, X. J. Oxidase-mimicking activity of the nitrogen-doped Fe3C@C composites. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 3882–3885.
Tang, D. S.; Liu, J. J.; Yan, X. M.; Kang, L. T. Graphene oxide derived graphene quantum dots with different photoluminescence properties and peroxidase-like catalytic activity. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 50609–50617.
Shan, X. Y.; Chai, L. J.; Ma, J. J.; Qian, Z. S.; Chen, J. R.; Feng, H. B-doped carbon quantum dots as a sensitive fluorescence probe for hydrogen peroxide and glucose detection. Analyst 2014, 139, 2322–2325.
Darabdhara, G.; Sharma, B.; Das, M. R.; Boukherroub, R.; Szunerits, S. Cu-Ag bimetallic nanoparticles on reduced graphene oxide nano-sheets as peroxidase mimic for glucose and ascorbic acid detection. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2017, 238, 842–851.
Yousefinejad, S.; Rasti, H.; Hajebi, M.; Kowsari, M.; Sadravi, S.; Honarasa, F. Design of C-dots/Fe3O4 magnetic nanocomposite as an efficient new nanozyme and its application for determination of H2O2 in nanomolar level. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2017, 247, 691–696.
Qiao, F. M.; Qi, Q. Q.; Wang, Z. Z.; Xu, K.; Ai, S. Y. MnSe-loaded g-C3N4 nanocomposite with synergistic peroxidase-like catalysis: Synthesis and application toward colorimetric biosensing of H2O2 and glucose. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2016, 229, 379–386.
Ding, P. H.; Di, J.; Chen, X. L.; Ji, M. X.; Gu, K. Z.; Yin, S.; Liu, Gao. P.; Zhang, F.; Xia, J. X.; Li, H. M. S, N codoped graphene quantum dots embedded in (BiO)2CO3: Incorporating enzymatic-like catalysis in photocatalysis. ASC Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 10229–10240.
Li, F.; Li, T. Y.; Sun, C. X.; Xia, J. H.; Jiao, Y.; Xu, H. P. Selenium-doped carbon quantum dots for free-radical scavenging. Angew. Chem, Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 9910–9914.
Hu, Y. H.; Gao, X. J.; Zhu, Y. Y.; Muhammad, F.; Tan, S. H.; Cao, W.; Lin, S. C.; Jin, Z.; Gao, X. F.; Wei, H. Nitrogen-doped carbon nanomaterials as highly active and specific peroxidase mimics. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 6431–6439.
Zeng, T.; Yu, M. D.; Zhang, H. Y.; He, Z. Q.; Chen, J. M.; Song, S. Fe/Fe3C@N-doped porous carbon hybrids derived from nano-scale MOFs: Robust and enhanced heterogeneous catalyst for peroxymonosulfate activation. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2017, 7, 396–404.
Chen, M. M.; Yang, B. C.; Zhu, J. L.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, X. W.; Liu, Q. Y. FePt nanoparticles-decorated graphene oxide nanosheets as enhanced peroxidase mimics for sensitive response to H2O2. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 90, 610–620.
Wang, H.; Chen, Q. W.; Zhou, S. Q. Carbon-based hybrid nanogels: A synergistic nanoplatform for combined biosensing, bioimaging, and responsive drug delivery. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 4198–4232.
Liu, L.; Du, B. J.; Shang, C. S.; Wang, J.; Wang, E. K. Construction of surface charge-controlled reduced graphene oxide-loaded Fe3O4 and Pt nanohybrid for peroxidase mimic with enhanced catalytic activity. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1014, 77–84.
Chen, S.; Quan, Y.; Yu, Y. L.; Wang, J. H. Graphene quantum dot/silver nanoparticle hybrids with oxidase activities for antibacterial application. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 313–321.
Wang, H.; Jiang, H.; Wang, S.; Shi, W. B.; He, J. C.; Liu, H.; Huang, Y. M. Fe3O4-MWCNT magnetic nanocomposites as efficient peroxidase mimic catalysts in a Fenton-like reaction for water purification without pH limitation. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 45809–45815.
Ma, Z.; Qiu, Y. F.; Yang, H. H.; Huang, Y. M.; Liu, J. J.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Hu, P. A. Effective synergistic effect of dipeptide-polyoxometalate-graphene oxide ternary hybrid materials on peroxidase-like mimics with enhanced performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 22036–22045.
Zheng, A. X.; Cong, Z. X.; Wang, J. R.; Li, J.; Yang, H. H.; Chen, G N. Highly-efficient peroxidase-like catalytic activity of graphene dots for biosensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 49, 519–524.
Fan, Z. T.; Zhou, S. X.; Garcia, C.; Fan, L. Z.; Zhou, J. B. pH-Responsive fluorescent graphene quantum dots for fluorescence-guided cancer surgery and diagnosis. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 4928–4933.
Lin, L. P.; Song, X. H.; Chen, Y. Y.; Rong, M. C.; Zhao, T. T.; Wang, Y. R.; Jiang, Y. Q.; Chen, X. Intrinsic peroxidase-like catalytic activity of nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots and their application in the colorimetric detection of H2O2 and glucose. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 869, 89–95.
Li, M.; Yang, X. J.; Ren, J. S.; Qu, K. G.; Qu, X. G. Using graphene oxide high near-infrared absorbance for photothermal treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1722–1728.
Chung, Y. H. Redox state control of a metalloprotein to generate multi-level signals for applications to bioelectronic devices. BioChip J. 2015, 9, 215–221.
Lang, J. D.; Berry, S. M.; Powers, G. L.; Beebe, D. J.; Alarid, E. T. Hormonally responsive breast cancer cells in a microfluidic co-culture model as a sensor of microenvironmental activity. Integr. Biol. 2013, 5, 807–816.
Cai, X.; Wang, Z. X.; Zhang, H. H.; Li, Y. F.; Chen, K. C.; Zhao, H. L.; Lan, M. B. Carbon-mediated synthesis of shape-controllable manganese phosphate as nanozymes for modulation of superoxide anions in HeLa cells. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 401–407.
Zhang, Y.; Wu, C. Y.; Zhou, X. J.; Wu, X. C.; Yang, Y. Q.; Wu, H. X.; Guo, S. W.; Zhang, J. Y. Graphenequantum dots/gold electrode and its application in living cell H2O2 detection. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 1816–1819.
Chen, X. M.; Su, B. Y.; Cai, Z. X.; Chen, X.; Oyama, M. PtPd nanodendrites supported on graphene nanosheets: A peroxidase-like catalyst for colorimetric detection of H2O2. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2014, 201, 286–292.
Qiu, N.; Liu, Y.; Xiang, M.; Lu, X. M.; Yang, Q.; Guo, R. A facile and stable colorimetric sensor based on three-dimensional graphene/mesoporous Fe3O4 nanohybrid for highly sensitive and selective detection of p-nitrophenol. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2018, 266, 86–94.
Tan, H. L.; Ma, C. J.; Gao, L.; Li, Q.; Song, Y. H.; Xu, F. G.; Wang, T.; Wang, L. Metal-organic framework-derived copper nanoparticle@carbon nanocomposites as peroxidase mimics for colorimetric sensing of ascorbic acid. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 16377–16383.
Zhong, M. X.; Chi, M. Q.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, C.; Lu, X. F. An efficient thin-walled Pd/polypyrrole hybrid nanotube biocatalyst for sensitive detection of ascorbic acid. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1056, 125–134.
Shamsipur, M.; Safavi, A.; Mohammadpour, Z. Indirect colorimetric detection of glutathione based on its radical restoration ability using carbon nanodots as nanozymes. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2014, 199, 463–469.
Singh, V. K.; Yadav, P. K.; Chandra, S.; Bano, D.; Talat, M.; Hasan, S. H. Peroxidase mimetic activity of fluorescent NS-carbon quantum dots and their application in colorimetric detection of H2O2 and glutathione in human blood serum. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 5256–5268.
Wang, Q. Q.; Zhang, X. P.; Huang, L.; Zhang, Z. Q.; Dong, S. J. One-pot synthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticle loaded 3D porous graphene nanocomposites with enhanced nanozyme activity for glucose detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 7465–7471.
Zhang, R. Z.; He, S. J.; Zhang, C. M.; Chen, W. Three-dimensional Fe- and N-incorporated carbon structures as peroxidase mimics for fluorescence detection of hydrogen peroxide and glucose. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 4146–4154.
Bao, Y. W.; Hua, X. W.; Ran, H. H.; Zeng, J.; Wu, F. G. Metal-doped carbon nanoparticles with intrinsic peroxidase-like activity for colorimetric detection of H2O2 and glucose. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 296–304.
Lin, X. Q.; Deng, H. H.; Wu, G. W.; Peng, H. P.; Liu, A. L.; Lin, X. H.; Xia, X. H.; Chen, W. Platinum nanoparticles/graphene-oxide hybrid with excellent peroxidase-like activity and its application for cysteine detection. Analyst 2015, 140, 5251–5256.
Yang, W. Q.; Huang, T. T.; Zhao, M. M.; Luo, F.; Weng, W.; Wei, Q. H.; Lin, Z. Y.; Chen, G. N. High peroxidase-like activity of iron and nitrogen co-doped carbon dots and its application in immunosorbent assay. Talanta 2017, 164, 1–6.
Song, Y. J.; Wang, X. H.; Zhao, C.; Qu, K. G.; Ren, J. S.; Qu, X. G. Label-free colorimetric detection of single nucleotide polymorphism by using single-walled carbon nanotube intrinsic peroxidase-like activity. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 3617–3621.
Wang, Q. B.; Lei, J. P.; Deng, S. Y.; Zhang, L.; Ju, H. X. Graphene-supported ferric porphyrin as a peroxidase mimic for electrochemical DNA biosensing. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 916–918.
Tao, Y.; Lin, Y. H.; Huang, Z. Z.; Ren, J. S.; Qu, X. G. Incorporating graphene oxide and gold nanoclusters: A synergistic catalyst with surprisingly high peroxidase-like activity over a broad pH range and its application for cancer cell detection. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 2510.
Tian, L.; Qi, J. X.; Qian, K.; Oderinde, O.; Cai, Y. Y.; Yao, C.; Song, W.; Wang, Y. H. An ultrasensitive electrochemical cytosensor based on the magnetic field assisted binanozymes synergistic catalysis of Fe3O4 nanozyme and reduced graphene oxide/molybdenum disulfide nanozyme. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2018, 260, 676–684.
Ding, H.; Cai, Y. J.; Gao, L. Z.; Liang, M. M.; Miao, B. P.; Wu, H. W.; Liu, Y.; Xie, N.; Tang, A. F.; Fan, K. L. et al. Exosome-like nanozyme vesicles for H2O2-responsive catalytic photoacoustic imaging of xenograft nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 203–209.
Sun, H. J.; Gao, N.; Dong, K.; Ren, J. S.; Qu, X. G. Graphene quantum dots-band-aids used for wound disinfection. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 6202–6210.
Samuel, E. L. G.; Duong, M. L. T.; Bitner, B. R.; Marcano, D. C.; Tour, J. M.; Kent, T. A. Hydrophilic carbon clusters as therapeutic, high-capacity antioxidants. Trends Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 501–505.
Dasarathy, S.; Brown, J. M. Alcoholic liver disease on the rise: Interorgan cross talk driving liver injury. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2017, 41, 880–882.
Sun, A. Q.; Mu, L.; Hu, X. G. Graphene oxide quantum dots as novel nanozymes for alcohol intoxication. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 12241–12252.
Maji, S. K.; Mandal, A. K.; Nguyen, K. T.; Borah, P.; Zhao, Y. L. Cancer cell detection and therapeutics using peroxidase-active nanohybrid of gold nanoparticle-loaded mesoporous silica-coated graphene. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 9807–9816.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Nos. 2019T120754 and 2018M633229), Sanming Project of Medicine in Shenzhen (No. SZSM201612031), Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province of China (Nos. 2018A030310665 and 2018A0303130295), Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Committee (Nos. ZDSYS201707281114196, JCYJ20170306091657539, JCYJ20170413162242627, JCYJ20190806163814395, JCYJ-20170306091452714, and GJHZ20170313172439851), Development and Reform Commission of Shenzhen Municipality (No. S2016005470013), National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2017YFA0205501), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81722024 and 81571728).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, H., Hu, B., Zhang, B. et al. Carbon-based nanozymes for biomedical applications. Nano Res. 14, 570–583 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-020-3053-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-020-3053-9