Abstract
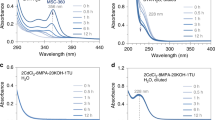
We report, for the first time, the synthesis of CdS magic-size clusters (MSCs) which exhibit a single sharp absorption peaking at ∼ 361 nm, along with sharp band edge photoemission at ∼ 377 nm and broad trap emission peaking at ∼ 490 nm. These MSCs are produced in a single-ensemble form without the contamination of conventional quantum dots (QDs) and/or other-bandgap clusters. They are denoted as MSC-361. We present the details of several controlled syntheses done in oleylamine (OLA), using Cd(NO3)2 or Cd(OAc)2 as a Cd source and thioacetamide (TAA) or elementary sulfur (S) as a S source. A high synthetic reproducibility of the reaction of Cd(NO3)2 and TAA to single-ensemble MSC-361 is achieved, the product of which is not contaminated by other bandgap clusters and/or QDs. In some cases, the reaction product exhibits an additional absorption peak at ∼ 322 nm. We demonstrate that the two peaks, at 361 and 322 nm, do not evolve synchronously. Therefore, the 322 nm peak is not a higher order electronic transition of MSC-361, but due to the presence of another ensemble, namely MSC-322. The present study suggests that there is an outstanding need for the development of a physical model to narrow the knowledge gap regarding the electronic structure in these colloidal semiconductor CdS MSCs.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang, H. T.; Hyun, B. R.; Wise, F. W.; Robinson, R. D. A generic method for rational scalable synthesis of monodisperse metal sulfide nanocrystals. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 5856–5860.
Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y; Buhro, W. E. Magic-size II–VI nanoclusters as synthons for flat colloidal nanocrystals. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 54, 1165–1177.
Nevers, D. R.; Williamson, C. B.; Hanrath, T.; Robinson, R. D. Surface chemistry of cadmium sulfide magic-sized clusters: A window into ligand-nanoparticle interactions. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 2866–2869.
Son, J. S.; Park, K.; Kwon, S. G.; Yang, J.; Choi, M. K.; Kim, J.; Yu, J. H.; Joo, J.; Hyeon, T. Dimension-controlled synthesis of CdS nanocrystals: From 0D quantum dots to 2D nanoplates. Small 2012, 8, 2394–2402.
Li, Z.; Qin, H. Y.; Guzun, D.; Benamara, M.; Salamo, G.; Peng, X. G. Uniform thickness and colloidal-stable CdS quantum disks with tunable thickness: Synthesis and properties. Nano Res. 2012, 5, 337–351.
Li, M. J.; Ouyang, J. Y.; Ratcliffe, C. I.; Pietri, L.; Wu, X. H.; Leek, D. M.; Moudrakovski, I.; Lin, Q.; Yang, B.; Yu, K. CdS magic-sized nanocrystals exhibiting bright band gap photoemission via thermodynamically driven formation. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 3832–3838.
Zhu, T. T.; Zhang, B. W.; Zhang, J.; Lu, J.; Fan, H. S.; Rowell, N.; Ripmeester, J. A.; Han, S.; Yu, K. Two-step nucleation of CdS magic-size nanocluster MSC-311. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 5727–5735.
Zhang, B. W.; Zhu, T. T.; Ou, M. Y.; Rowell, N.; Fan, H. S.; Han, J. T.; Tan, L.; Dove, M. T.; Ren, Y.; Zuo, X. B. et al. Thermally-induced reversible structural isomerization in colloidal semiconductor CdS magic-size clusters. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2499.
Zhang, J.; Hao, X. Y.; Rowell, N.; Kreouzis, T.; Han, S.; Fan, H. S.; Zhang, C. C.; Hu, C. W.; Zhang, M.; Yu, K. Individual pathways in the formation of magic-size clusters and conventional quantum dots. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 3660–3666.
Nevers, D. R.; Williamson, C. B.; Savitzky, B. H.; Hadar, I.; Banin, U.; Kourkoutis, L. F.; Hanrath, T.; Robinson, R. D. Mesophase formation stabilizes high-purity magic-sized clusters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 3652–3662.
Yu, W. W.; Peng X. G. Formation of high-quality CdS and other II–VI semiconductor nanocrystals in noncoordinating solvents: Tunable reactivity of monomers. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 2368–2371.
Pan, D. C.; Ji, X. L.; An, L. J.; Lu, Y. F. Observation of nucleation and growth of CdS nanocrystals in a two-phase system. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 3560–3566.
Ouyang, J. Y.; Kuijper, J.; Brot, S.; Kingston, D.; Wu, X. H.; Leek, D. M.; Hu, M. Z.; Ripmeester, J. A.; Yu, K. Photoluminescent colloidal CdS nano-crystals with high quality via noninjection one-pot synthesis in 1-octadecene. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 7579–7593.
Yu, Q. Y.; Liu, C. Y. Study of magic-size-cluster mediated formation of CdS nanocrystals: Properties of the magic-size clusters and mechanism implication. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 12766–12771.
Zanella, M.; Abbasi, A. Z.; Schaper, A. K.; Parak, W. J. Discontinuous growth of II–VI semiconductor nanocrystals from different materials. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 6205–6215.
Fojtik, A.; Weller, H.; Koch, U.; Henglein, A. Photo-chemistry of colloidal metal sulfides 8. photo-physics of extremely small CdS particles: Q-state CdS and magic agglomeration numbers. Ber. Bunsenges. Phys. Chem. 1984, 88, 969–977.
Vossmeyer, T.; Katsikas, L.; Giersig, M.; Popovic, I. G.; Diesner, K.; Chemseddine, A.; Eychmueller, A.; Weller, H. CdS nanoclusters: Synthesis, characterization, size dependent oscillator strength, temperature shift of the excitonic transition energy, and reversible absorbance shift. J. Phys. Chem. 1994, 98, 7665–7673.
Samanta, A; Deng, Z. T.; Liu, Y.; Yan, H. A perspective on functionalizing colloidal quantum dots with DNA. Nano Res. 2013, 6, 853–870.
Zhang, L. B.; Jean, S. R.; Ahmed, S.; Aldridge, P. M.; Li, X. Y.; Fan, F. J.; Sargent, E. H.; Kelley, S. O. Multifunctional quantum dot DNA hydrogels. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 381.
Luo, W. N.; Jiu, T. G.; Kuang, C. Y.; Li, B. R.; Lu, F. S.; Fang, J. F. Dithiol treatments enhancing the efficiency of hybrid solar cells based on PTB7 and CdSe nanorods. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 3045–3053.
Yang, Z. Y.; Fan, J. Z.; Proppe, A. H.; de Arquer, F. P. G.; Rossouw, D.; Voznyy, O.; Lan, X. Z.; Liu, M.; Walters, G.; Quintero-Bermudez, R. et al. Mixed-quantum-dot solar cells. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1325.
Empedocles, S A.; Neuhauser, R.; Shimizu, K. T.; Bawendi, M. G. Photoluminescence from single semiconductor nanostructures. Adv. Mater. 1999, 11, 1243–1256.
Cui, J.; Beyler, A. P.; Marshall, L. F.; Chen, O.; Harris, D. K.; Wanger, D. D.; Brokmann, X.; Bawendi, M. G. Direct probe of spectral inhomogeneity reveals synthetic tunability of single-nanocrystal spectral linewidths. Nat. Chem. 2013, 5, 602–606.
Kasuya, A.; Sivamohan, R.; Barnakov, Y. A.; Dmitruk, I. M.; Nirasawa, T.; Romanyuk, V. R.; Kumar, V.; Mamykin, S. V.; Tohji, K.; Jeyadevan, B. et al. Ultra-stable nanoparticles of CdSe revealed from mass spectrometry. Nat. Mater. 2004, 3, 99–102.
Beecher, A. N.; Yang, X. H.; Palmer, J. H.; LaGrassa, A. L.; Juhas, P.; Billinge, S. J. L.; Owen, J. S. Atomic structures and gram scale synthesis of three tetrahedral quantum dots. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 10645–10653.
Ekimov, A. I.; Hache, F.; Schanne-Klein, M. C.; Ricard, D.; Flytzanis, C.; Kudryavtsev, I. A.; Yazeva, T. V.; Rodina, A. V.; Efros, A. L. Absorption and intensity-dependent photoluminescence measurements on CdSe quantum dots: Assignment of the first electronic transitions. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 1993, 10, 100–107.
Norris, D. J.; Bawendi, M. G. Measurement and assignment of the size-dependent optical spectrum in CdSe quantum dots. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 53, 16338–16346.
Liu, M. Y.; Wang, K.; Wang, L. X.; Han, S.; Fan, H. S.; Rowell, N.; Ripmeester, J. A.; Renoud, R.; Bian, F. G.; Zeng, J. R. et al. Probing intermediates of the induction period prior to nucleation and growth of semiconductor quantum dots. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15467.
Wang, L. X.; Hui, J.; Tang, J. B.; Rowell, N.; Zhang, B. W.; Zhu, T. T.; Zhang, M.; Hao, X. Y.; Fan, H. S.; Zeng, J. R. et al. Precursor self-assembly identified as a general pathway for colloidal semiconductor magic-size clusters. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1800632.
LaMer, V. K.; Dinegar, R. H. Theory, production and mechanism of formation of monodispersed hydrosols. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1950, 72, 4847–4854.
van Embden, J.; Mulvaney, P. Nucleation and growth of CdSe nanocrystals in a binary ligand system. Langmuir 2005, 21, 10226–10233.
Steckel, J. S.; Yen, B. K. H.; Oertel, D. C.; Bawendi, M. G On the mechanism of lead chalcogenide nanocrystal formation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 13032–13033.
García-Rodríguez, R.; Hendricks, M. P.; Cossairt, B. M.; Liu, H. T.; Owen, J. S. Conversion reactions of cadmium chalcogenide nanocrystal precursors. Chem. Mater. 2013, 25, 1233–1249.
Yu, K.; Liu, X. Y.; Chen, Q. Y.; Yang, H. Q.; Yang, M. L.; Wang, X. Q.; Wang, X.; Cao, H.; Whitfield, D. M.; Hu, C. W. et al. Mechanistic study of the role of primary amines in precursor conversions to semiconductor nanocrystals at low temperature. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 6898–6904.
Yu, K.; Liu, X. Y.; Qi, T.; Yang, H. Q.; Whitfield, D. M.; Chen, Q. Y.; Huisman, E. J. C.; Hu, C. W. General low-temperature reaction pathway from precursors to monomers before nucleation of compound semiconductor nanocrystals. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12223.
Xie, L. S.; Shen, Y.; Franke, D.; Sebastián, V.; Bawendi, M. G.; Jensen, K. F. Characterization of indium phosphide quantum dot growth intermediates using MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 13469–13472.
Bowers, M. J.; McBride, J. R.; Rosenthal, S. J. White-light emission from magic-sized cadmium selenide nanocrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 15378–15379.
Cossairt, B. M.; Owen, J. S. CdSe clusters: At the interface of small molecules and quantum dots. Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 3114–3119.
Rosson, T. E.; Claiborne, S. M.; McBride, J. R.; Stratton, B. S.; Rosenthal, S. J. Bright white light emission from ultrasmall cadmium selenide nanocrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 8006–8009.
Dolai, S.; Nimmala, P. R.; Mandal, M.; Muhoberac, B. B.; Dria, K.; Dass, A.; Sardar, R. Isolation of bright blue light-emitting CdSe nanocrystals with 6.5 kDa core in gram scale: High photoluminescence efficiency controlled by surface ligand chemistry. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 1278–1285.
Yu, W. W.; Qu, L. H.; Guo, W. Z.; Peng, X. G. Experimental determination of the extinction coefficient of CdTe, CdSe, and CdS nanocrystals. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 2854–2860.
Jasieniak, J.; Smith, L.; van Embden, J.; Mulvaney, P. Re-examination of the size-dependent absorption properties of CdSe quantum dots. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 19468–19474.
Ouyang, J. Y.; Zaman, M. B.; Yan, F. J.; Johnston, D.; Li, G.; Wu, X. H.; Leek, D.; Ratcliffe, C. I.; Ripmeester, J. A.; Yu, K. Multiple families of magic-sized CdSe nanocrystals with strong bandgap photoluminescence via noninjection one-pot syntheses. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 13805–13811.
Yu, K.; Ouyang, J. Y.; Zaman, M. B.; Johnston, D.; Yan, F. J.; Li, G.; Ratcliffe, C. I.; Leek, D. M.; Wu, X. H.; Stupak, J. et al. Single-sized CdSe nanocrystals with bandgap photoemission via a noninjection one-pot approach. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 3390–3401.
Yu, K.; Hu, M. Z.; Wang, R. B.; Le Piolet, M.; Frotey, M.; Zaman, M. B.; Wu, X. H.; Leek, D. M.; Tao, Y.; Wilkinson, D. et al. Thermodynamic equilibrium-driven formation of single-sized nanocrystals: Reaction media tuning CdSe magic-sized versus regular quantum dots. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 3329–3339.
Liu, Y. H.; Wang, F. D.; Wang, Y. Y.; Gibbons, P. C.; Buhro, W. E. Lamellar assembly of cadmium selenide nanoclusters into quantum belts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 17005–17013.
Yu, K. CdSe magic-sized nuclei, magic-sized nanoclusters and regular nanocrystals: Monomer effects on nucleation and growth. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1123–1132.
Wang, Y. Y.; Liu, Y. H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, F. D.; Kowalski, P. J.; Rohrs, H. W.; Loomis, R. A.; Gross, M. L.; Buhro, W. E. Isolation of the magic-size CdSe nanoclusters [(CdSe)13(n-octylamine)13] and [(CdSe)13(oleylamine)13]. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 6154–6157.
Dolai, S.; Dutta, P.; Muhoberac, B. B.; Irving, C. D.; Sardar, R. Mechanistic study of the formation of bright white light-emitting ultrasmall CdSe nano-crystals: Role of phosphine free selenium precursors. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 1057–1070.
Zhu, D. K.; Hui, J.; Rowell, N.; Liu, Y. Y.; Chen, Q. Y.; Steegemans, T.; Fan, H. S.; Zhang, M.; Yu, K. Interpreting the ultraviolet absorption in the spectrum of 415 nm-bandgap CdSe magic-size clusters. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 2818–2824.
Hsieh, T. E.; Yang, T. W.; Hsieh, C. Y.; Huang, S. J.; Yeh, Y. Q.; Chen, C. H.; Li, E. Y.; Liu, Y. H. Unraveling the structure of magic-size (CdSe)13 cluster pairs. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 5468–5477.
Liu, Y. Y.; Willis, M.; Rowell, N.; Luo, W. Z.; Fan, H. S.; Han, S.; Yu, K. Effect of small molecule additives in the prenucleation stage of semiconductor CdSe quantum dots. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 6356–6363.
Wang, R. B.; Ouyang, J. Y.; Nikolaus, S.; Brestaz, L.; Zaman, M. B.; Wu, X. H.; Leek, D.; Ratcliffe, C. I.; Yu, K. Single-sized colloidal CdTe nanocrystals with strong bandgap photoluminescence. Chem. Commun. 2009, 962–964.
Acknowledgements
K. Y. acknowledges financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China(Nos. 21773162 and 21573155), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. SCU2015A002), the State Key Laboratory of Polymer Materials Engineering of Sichuan University (No. sklpme2018-2-08), and the Open Project of Key State Laboratory for Supramolecular Structures and Materials of Jilin University for SKLSSM 201830. H. F. and W. H. thank the National Major Scientific and Technological Special Project for “Significant New Drugs Development” (Nos. 2018ZX09201009-005-004 and 2018ZX09201009-005-001). We thank Sichuan Univ of Analytical & Testing Center. We are in debt to Dr. Shanling Wang (Analytical & Testing Center, Sichuan University) for TEM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, J., Hui, J., Zhang, M. et al. CdS magic-size clusters exhibiting one sharp ultraviolet absorption singlet peaking at 361 nm. Nano Res. 12, 1437–1444 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-019-2386-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-019-2386-8