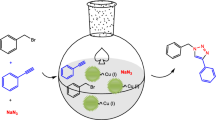
Abstract
Rh is an important catalyst that is widely used in a variety of organic reactions. In recent years, many efforts have focused on improving its catalytic efficiency by fabricating catalyst nanoparticles with controlled size and morphology. However, the frequently employed synthesis route using organic compounds either as the reaction medium or capping agent often results in residual molecules on the catalyst surface, which in turn drastically diminishes the catalytic performance. Herein, we report a facile, aqueous, surfactant-free synthesis of a novel Rh flowerlike structure obtained via hydrothermal reduction of Rh(acac)3 by formaldehyde. The unique Rh nanoflowers were constructed from ultrathin nanosheets, whose basal surfaces comprised {111} facets with an average thickness of ~1.1 nm. The specific surface area measured by CO stripping was 79.3 m2·g−1, which was much larger than that of commercial Rh black. More importantly, the Rh nanoflower catalyst exhibited excellent catalytic performance in the catalytic hydrogenation of phenol and cyclohexene, in contrast to the commercial Rh black and polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP)-capped Rh nanosheets exposed by similar {111} basal surfaces.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mu, X. D.; Meng, J. X.; Li, Z. C.; Kou, Y. Rhodium nanoparticles stabilized by ionic copolymers in ionic liquids: Long lifetime nanocluster catalysts for benzene hydrogenation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 9694–9695.
Dykeman, R. R.; Yan, N.; Scopelliti, R.; Dyson, P. J. Enhanced rate of arene hydrogenation with imidazolium functionalized bipyridine stabilized rhodium nanoparticle catalysts. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 717–719.
Park, K. H.; Jang, K.; Kim, H. J.; Uk Son, S. Nearmonodisperse tetrahedral rhodium nanoparticles on charcoal: The shape-dependent catalytic hydrogenation of arenes. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1152–1155.
Dahal, N.; García, S.; Zhou, J. P.; Humphrey, S. M. Beneficial effects of microwave-assisted heating versus conventional heating in noble metal nanoparticle synthesis. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 9433–9446.
Quek, X. Y.; Guan, Y. J.; Hensen, E. J. M. Structure sensitivity in the hydrogenation of unsaturated hydrocarbons over Rh nanoparticles. Catal. Today 2012, 183, 72–78.
Yoon, B.; Wai, C. M. Microemulsion-templated synthesis of carbon nanotube-supported Pd and Rh nanoparticles for catalytic applications. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 17174–17175.
Franke, R.; Selent, D.; Börner, A. Applied hydroformylation. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 5675–5732.
Hou, C.; Zhao, G. F.; Ji, Y. J.; Niu, Z. Q.; Wang, D. S.; Li, Y. D. Hydroformylation of alkenes over rhodium supported on the metal–organic framework ZIF-8. Nano Res. 2014, 7, 1364–1369.
Yuan, Y.; Yan, N.; Dyson, P. J. Advances in the rational design of rhodium nanoparticle catalysts: Control via manipulation of the nanoparticle core and stabilizer. ACS Catal. 2012, 2, 1057–1069.
Sun, Z.; Wang, Y. H.; Niu, M. M.; Yi, H. Q.; Jiang, J. Y.; Jin, Z. L. Poly(ethylene glycol)-stabilized Rh nanoparticles as efficient and recyclable catalysts for hydroformylation of olefins. Catal. Commun. 2012, 27, 78–82.
Zhang, Y. W.; Grass, M. E.; Huang, W. Y.; Somorjai, G. A. Seedless polyol synthesis and COoxidation activity of monodisperse (111)-and (100)-oriented rhodium nanocrystals in sub-10 nm sizes. Langmuir 2010, 26, 16463–16468.
Hou, C. P.; Zhu, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, X.; Kuang, Q.; Zheng, L. S. Formaldehyde-assisted synthesis of ultrathin Rh nanosheets for applications in COoxidation. CrystEngComm 2013, 15, 6127–6130.
Grass, M. E.; Zhang, Y. W.; Butcher, D. R.; Park, J. Y.; Li, Y. M.; Bluhm, H.; Bratlie, K. M.; Zhang, T. F.; Somorjai, G. A. A reactive oxide overlayer on rhodium nanoparticles during COoxidation and its size dependence studied by in situ ambient-pressure X-ray photoelectronspectroscopy. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 8893–8896.
Yu, N. F.; Tian, N.; Zhou, Z. Y.; Huang, L.; Xiao, J.; Wen, Y. H.; Sun, S. G. Electrochemical synthesis of tetrahexahedral rhodium nanocrystals with extraordinarily high surface energy and high electrocatalytic activity. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 5097–5101.
Muench, F.; Neetzel, C.; Kaserer, S.; Brötz, J.; Jaud, J. C.; Zhao-Karger, Z.; Lauterbach, S.; Kleebe, H. J.; Roth, C.; Ensinger, W. Fabrication of porous rhodium nanotube catalysts by electroless plating. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 12784–12791.
Li, Y. Y.; Dian, P.; Jin, T.; Sun, J. S.; Xu, D. Shapecontrolled electrodeposition of standing Rh nanoplates on indium tin oxide substrates and their electrocatalytic activity toward formic acid oxidation. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 83, 146–154.
Jia, Y. Y.; Jiang, Y. Q.; Zhang, J. W.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Q. L.; Xie, Z. X.; Zheng, L. Unique excavated rhombic dodecahedral PtCu3 alloy nanocrystals constructed with ultrathin nanosheets of high-energy {110} facets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 3748–3751.
Jia, Y. Y.; Cao, Z. M.; Chen, Q. L.; Jiang, Y. Q.; Xie, Z. X.; Zheng, L. S. Synthesis of composition-tunable octahedral Pt–Cu alloy nanocrystals by controlling reduction kinetics of metal precursors. Sci. Bull. 2015, 60, 1002–1008.
Zhang, Y. W.; Grass, M. E.; Kuhn, J. N.; Tao, F.; Habas, S. E.; Huang, W. Y.; Yang, P. D.; Somorjai, G. A. Highly selective synthesis of catalytically active monodisperse rhodium nanocubes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 5868–5869.
Wang, Y.; Chen, Y. G.; Nan, C. Y.; Li, L. L.; Wang, D. S.; Peng, Q.; Li, Y. D. Phase-transfer interface promoted corrosion from PtNi10 nanoctahedra to Pt4Ni nanoframes. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 140–155.
Tian, N.; Zhou, Z. Y.; Sun, S. G.; Ding, Y.; Wang, Z. L. Synthesis of tetrahexahedral platinum nanocrystals with high-index facets and high electro-oxidation activity. Science 2007, 316, 732–735.
Zhang, L.; Chen, D. Q.; Jiang, Z. Y.; Zhang, J. W.; Xie, S. F.; Kuang, Q.; Xie, Z. X.; Zheng, L. S. Facile syntheses and enhanced electrocatalytic activities of Pt nanocrystals with {hkk} high-index surfaces. Nano Res. 2012, 5, 181–189.
Zhang, J. W.; Hou, C. P.; Huang, H.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, Z. Y.; Chen, G. X.; Jia, Y. Y.; Kuang, Q.; Xie, Z. X.; Zheng, L. S. Surfactant-concentration-dependent shape evolution of Au-Pd alloy nanocrystals from rhombic dodecahedron to trisoctahedron and hexoctahedron. Small 2013, 9, 538–544.
Zhou, K. B.; Li, Y. D. Catalysis based on nanocrystals with well-defined facets. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 602–613.
Chen, Y. M.; Chen, Q.-S.; Peng, S.-Y.; Wang, Z.-Q.; Lu, G.; Guo, G.-C. Manipulating the concavity of rhodium nanocubes enclosed by high-index facets via site-selective etching. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 1662–1664.
Zhang, H.; Li, W. Y.; Jin, M. S.; Zeng, J.; Yu, T.; Yang, D. R.; Xia, Y. N. Controlling the morphology of rhodium nanocrystals by manipulating the growth kinetics with a syringe pump. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 898–903.
Huang, X.; Zeng, Z. Y.; Zhang, H. Metal dichalcogenide nanosheets: Preparation, properties and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 1934–1946.
Hu, C. Y.; Lin, K. Q.; Wang, X. L.; Liu, S. J.; Yi, J.; Tian, Y.; Wu, B. H.; Chen, G. X.; Yang, H. Y.; Dai, Y. et al. Electrostatic self-assembling formation of Pd superlattice nanowires from surfactant-free ultrathin Pd nanosheets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 12856–12859.
Huang, X.; Li, S. Z.; Huang, Y. Z.; Wu, S. X.; Zhou, X. Z.; Li, S. Z.; Gan, C. L.; Boey, F.; Mirkin, C. A.; Zhang, H. Synthesis of hexagonal close-packed gold nanostructures. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 292–297.
Yin, A. X.; Liu, W. C.; Ke, J.; Hu, W.; Gu, J.; Zhang, Y. W.; Yan, C. H. Ru nanocrystals with shape-dependent surfaceenhanced Raman spectra and catalytic properties: Controlled synthesis and DFT calculations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 20479–20489.
Huang, X. Q.; Tang, S. H.; Mu, X. L.; Dai, Y.; Chen, G. X.; Zhou, Z. Y.; Ruan, F. X.; Yang, Z. L.; Zheng, N. F. Freestanding palladium nanosheets with plasmonic and catalytic properties. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 28–32.
Nie, L. M.; Chen, M.; Sun, X. L.; Rong, P. F.; Zheng, N. F.; Chen, X. Y. Palladium nanosheets as highly stable and effective contrast agents for in vivo photoacoustic molecular imaging. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 1271–1276.
Duan, H. H.; Yan, N.; Yu, R.; Chang, C. R.; Zhou, G.; Hu, H. S.; Rong, H. P.; Niu, Z. Q.; Mao, J. J.; Asakura, H. et al. Ultrathin rhodium nanosheets. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3093.
Jang, K.; Kim, H. J.; Son, S. U. Low-temperature synthesis of ultrathin rhodium nanoplates via molecular orbital symmetry interaction between rhodium precursors. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 1273–1275.
Sathe, B. R. High aspect ratio rhodium nanostructures for tunable electrocatalytic performance. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 7866–7872.
Bratlie, K. M.; Lee, H.; Komvopoulos, K.; Yang, P. D.; Somorjai, G. A. Platinum nanoparticle shape effects on benzene hydrogenation selectivity. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 3097–3101.
Kuhn, J. N.; Tsung, C. K.; Huang, W. Y.; Somorjai, G. A. Effect of organic capping layers over monodisperse platinum nanoparticles upon activity for ethylene hydrogenation and carbon monoxide oxidation. J. Catal. 2009, 265, 209–215.
Li, Y.; El-Sayed, M. A. The effect of stabilizers on the catalytic activity and stability of Pd colloidal nanoparticles in the Suzuki reactions in aqueous solution. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 8938–8943.
Lee, H.; Kim, C.; Yang, S.; Han, J. W; Kim, J. Shapecontrolled nanocrystals for catalytic applications. Catal. Surv. Asia 2012, 16, 14–27.
Monzó, J.; Koper, M. T. M.; Rodriguez, P. Removing polyvinylpyrrolidone from catalytic Pt nanoparticles without modification of superficial order. ChemPhysChem 2012, 13, 709–715.
Lopez-Sanchez, J. A.; Dimitratos, N.; Hammond, C.; Brett, G. L.; Kesavan, L.; White, S.; Miedziak, P.; Tiruvalam, R.; Jenkins, R. L.; Carley, A. F. et al. Facile removal of stabilizer-ligands from supported gold nanoparticles. Nat. Chem. 2011, 3, 551–556.
Chen, Y.; Gu, X.; Nie, C. G.; Jiang, Z. Y.; Xie, Z. X.; Lin, C. J. Shape controlled growth of gold nanoparticles by a solution synthesis. Chem. Commun. 2005, (33), 4181–4183.
Pan, Y. T.; Yin, X.; Kwok, K. S.; Yang, H. Higher-order nanostructures of two-dimensional palladium nanosheets for fast hydrogen sensing. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 5953–5959.
Jin, R. C.; Cao, Y. W.; Mirkin, C. A.; Kelly, K. L.; Schatz, G. C.; Zheng, J. G. Photoinduced conversion of silver nanospheres to nanoprisms. Science 2001, 294, 1901–1903.
Germain, V.; Li, J.; Ingert, D.; Wang, Z. L.; Pileni, M. P.; Stacking faults in formation of silver nanodisks. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 8717–8720.
World Health Organization. Formaldehyde: Health and safety guide [Online]. IPCS International programme on chemical safety: Health and safety guide No. 57. http://www.inchem.org/documents/hsg/hsg/hsg057.htm (accessed Sep 14, 2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Y., Su, J., Yang, Y. et al. A facile surfactant-free synthesis of Rh flower-like nanostructures constructed from ultrathin nanosheets and their enhanced catalytic properties. Nano Res. 9, 849–856 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-015-0964-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-015-0964-y