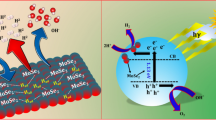
Abstract
Electron-hole separation is a critical step to achieving efficient photocatalysis, towards which use of co-catalysts has become a widely used strategy. Despite the tremendous efforts and demonstrated functions of noble metal co-catalysts, seeking noble metal-free co-catalysts will always be the goal when designing cost-effective, high-performance hybrid photocatalysts. In this work, we demonstrate that MoS2 nanosheets with 1T phase (i.e., octahedral phase) can function as a co-catalyst with multiple merits: (1) Noble-metal-free; (2) high mobility for charge transport; (3) high density of active sites for H2 evolution on basal planes; (4) good performance stability; (5) high light transparency. As demonstrated in both photocatalytic hydrogen production and Rhodamine B degradation, the developed hybrid structure with TiO2 exhibits excellent performance, in sharp contrast to bare TiO2 and the hybrid counterpart with 2H-MoS2.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Linsebigler, A. L.; Lu, G. Q.; Yates, J. T., Jr. Photocatalysis on TiO2 surfaces: Principles, mechanisms, and selected results. Chem. Rev. 1995, 95, 735–758.
Qu, Y. Q.; Duan, X. F. Progress, challenge and perspective of heterogeneous photocatalysts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 2568–2580.
Yang, J. H.; Wang, D. E.; Han, H. X.; Li, C. Roles of cocatalysts in photocatalysis and photoelectrocatalysis. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 1900–1909.
Trasatti, S. Work function, electronegativity, and electrochemical behaviour of metals. 3. Electrolytic hydrogen evolution in acid solutions. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1972, 39, 163–184.
Bao, N. Z.; Shen, L. M.; Takata, T.; Domen, K. Self-templated synthesis of nanoporous CdS nanostructures for highly efficient photocatalytic hydrogen production under visible light. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 110–117.
Xie, G. C.; Zhang, K.; Guo, B. D.; Liu, Q.; Fang, L.; Gong, J. R. Graphene-based materials for hydrogen generation from light-driven water splitting. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 3820–3839.
Zong. X.; Yan, H. J.; Wu, G. P.; Ma, G. J.; Wen, F. Y.; Wang, L.; Li, C. Enhancement of photocatalytic H2 evolution on CdS by loading MoS2 as cocatalyst under visible light irradiation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 7176–7177.
Bai, S.; Ge, J.; Wang, L. L.; Gong, M.; Deng, M. S.; Kong, Q.; Song, L.; Jiang. J.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, Y. et al. A unique semiconductor-metal-graphene stack design to harness charge flow for photocatalysis. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5689–5695.
Li, Y. G.; Wang, H. L.; Xie, L. M.; Liang, Y. Y.; Hong, G. S.; Dai, H. J. MoS2 nanoparticles grown on graphene: An advanced catalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 7296–7299.
Laursen, A. B.; Kegnæs, S.; Dahl, S.; Chorkendorff, I. Molybdenum sulfides—efficient and viable materials for electro- and photoelectrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 5577–5591.
Jaramillo, T. F.; Jorgensen, K. P.; Bonde, J.; Nielsen, J. H.; Horch, S.; Chorkendorff, I. Identification of active edge sites for electrochemical H2 evolution from MoS2 nanocatalysts. Science 2007, 317, 100–102.
Meng, F. K.; Li, J. T.; Cushing, S. K.; Zhi, M. J.; Wu, N. Q. Solar hydrogen generation by nanoscale p-n junction of p-type molybdenum disulfide/n-type nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 10286–10289.
Xie, J. F.; Zhang, J. J.; Li, S.; Grote, F.; Zhang, X. D.; Zhang, H.; Wang, R. X.; Lei, Y.; Pan. B. C.; Xie, Y. Controllable disorder engineering in oxygen-incorporated MoS2 ultrathin nanosheets for efficient hydrogen evolution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 17881–17888.
Xiang, Q. J.; Yu, J. G.; Jaroniec, M. Synergetic effect of MoS2 and graphene as cocatalysts for enhanced photocatalytic H2 production activity of TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 6575–6578.
Chang, K.; Mei. Z. W.; Wang, T.; Kang, Q.; Ouyang, S. X.; Ye, J. H. MoS2/graphene cocatalyst for efficient photocatalytic H2 evolution under visible light irradiation. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 7078–7087.
Eda, G.; Yamaguchi, H.; Voriy, D.; Fujita, T.; Chen, M. W.; Chhowalla, M. Photoluminescence from chemically exfoliated MoS2. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 5111–5116.
Voriy, D.; Salehi, M.; Silva, R.; Fujita, T.; Cheng, M. W.; Asefa, T.; Shenoy, V. B.; Eda, G.; Chhowalla, M. Conducting MoS2 nanosheets as catalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 6222–6227.
Lukowski, M. A.; Daniel, A. S.; Meng, F.; Forticaux, A.; Li, L. S.; Jin, S. Enhanced hydrogen evolution catalysis from chemically exfoliated metallic MoS2 nanosheets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 10274–10277.
Liang, Y. Y.; Wang, H. L.; Casalongue, H. S.; Chen, Z.; Dai, H. J. TiO2 nanocrystals grown on graphene as advanced photocatalytic hybrid materials. Nano Res. 2010, 3, 701–705.
Lin, Y. C.; Dumcenco, D. O.; Huang, Y. S.; Suenaga, K. Atomic mechanism of the semiconducting-to-metallic phase transition in single-layered MoS2. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 9, 391–396.
Yuwen, L. H.; Xu, F.; Xue, B.; Luo, Z. M.; Zhang, Q.; Bao, B. Q.; Su. S.; Weng, L. X.; Huang, W.; Wang, L. H. General synthesis of noble metal (Au, Ag, Pd, Pt) nanocrystals modified MoS2 nanosheets and enhanced catalytic activity of Pd-MoS2 for methanol oxidation. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 5762–5769.
Wang, H. T.; Lu, Z. Y.; Xu, S. C.; Kong, D. S.; Cha, J. J.; Zheng, G. Y.; Hsu, P. C.; Yan, K.; Bradshaw, D.; Prinz, F. B. et al. Electrochemical tuning of vertically aligned MoS2 nanofilms and its application in improving hydrogen evolution reaction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 19701–19706.
Yan, J. Q.; Wu, G. J.; Guan, N. J.; Li, L. D.; Li, Z. X.; Cao, X. Z. Understanding the effect of surface/bulk defects on the photocatalytic activity of TiO2: Anatase versus rutile. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 10978–10988.
King, L. A.; Zhao, W. J.; Chhowalla, M.; Riley, D. J.; Eda, G. Photoelectrochemical properties of chemically exfoliated MoS2. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 8935–8941.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, S., Wang, L., Chen, X. et al. Chemically exfoliated metallic MoS2 nanosheets: A promising supporting co-catalyst for enhancing the photocatalytic performance of TiO2 nanocrystals. Nano Res. 8, 175–183 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-014-0606-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-014-0606-9