Abstract
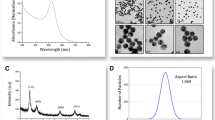
Protein coronas provide the biological identity of nanomaterials in vivo. Here we have used dynamic light scattering (DLS) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) to investigate the adsorption of serum proteins, including bovine serum albumin (BSA), transferrin (TRF) and fibrinogen (FIB), on gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) with different surface modifications (citrate, thioglycolic acid, cysteine, polyethylene glycol (PEG, M w = 2 k and 5 k)). AuNPs with PEG(5 k) surface modification showed no protein adsorption. AuNPs with non-PEG surface modifications showed aggregation with FIB. AuNPs with citrate and thioglycolic acid surface modifications showed 6–8 nm thick BSA and TRF coronas (corresponding to monolayer or bilayer proteins), in which the microscopic dissociation constants of BSA and TRF protein coronas are in the range of 10−8 to 10−6 M.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bruchez, M.; Moronne, M.; Gin, P.; Weiss, S.; Alivisatos, A. P. Semiconductor nanocrystals as fluorescent biological labels. Science 1998, 281, 2013–2016.
Hong, G. S.; Lee, J. C.; Robinson, J. T.; Raaz, U.; Xie, L. M.; Huang, N. F.; Cooke, J. P.; Dai, H. J. Multifunctional in vivo vascular imaging using near-infrared ii fluorescence. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1841–1846.
Petros, R. A.; DeSimone, J. M. Strategies in the design of nanoparticles for therapeutic applications. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 2010, 9, 615–627.
Huang, X. H.; El-Sayed, I. H.; Qian, W.; El-Sayed, M. A. Cancer cell imaging and photothermal therapy in the near-infrared region by using gold nanorods. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 2115–2120.
Liu, Z.; Robinson, J. T.; Tabakman, S. M.; Yang, K.; Dai, H. J. Carbon materials for drug delivery and cancer therapy. Mater. Today 2011, 14, 316–323.
Monopoli, M. P.; Aberg, C.; Salvati, A.; Dawson, K. A. Biomolecular coronas provide the biological identity of nanosized materials. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 779–786.
Tsai, D. H.; DelRio, F. W.; Keene, A. M.; Tyner, K. M.; MacCuspie, R. I.; Cho, T. J.; Zachariah, M. R.; Hackley, V. A. Adsorption and conformation of serum albumin protein on gold nanoparticles investigated using dimensional measurements and in situ spectroscopic methods. Langmuir 2011, 27, 2464–2477.
Casals, E.; Pfaller, T.; Duschl, A.; Oostingh, G. J.; Puntes, V. Time evolution of the nanoparticle protein corona. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 3623–3632.
Lacerda, S. H. D. P.; Park, J. J.; Meuse, C.; Pristinski, D.; Becker, M. L.; Karim, A.; Douglas, J. F. Interaction of gold nanoparticles with common human blood proteins. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 365–379.
Dominguez-Medina, S.; McDonough, S.; Swanglap, P.; Landes, C. F.; Link, S. In situ measurement of bovine serum albumin interaction with gold nanospheres. Langmuir 2012, 28, 9131–9139.
Deng, Z. J.; Liang, M. T.; Toth, I.; Monteiro, M. J.; Minchin, R. F. Molecular interaction of poly(acrylic acid) gold nanoparticles with human fibrinogen. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 8962–8969.
Röcker, C.; Pötzl, M.; Zhang, F.; Parak, W. J.; Nienhaus, G. U. A quantitative fluorescence study of protein monolayer formation on colloidal nanoparticles. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 577–580.
Shao, L. W.; Dong, C. Q.; Sang, F. M.; Qian, H. F.; Ren, J. C. Studies on interaction of CdTe quantum dots with bovine serum albumin using fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. J. Fluoresc. 2009, 19, 151–157.
Jiang, X.; Weise, S.; Hafner, M.; Röcker, C.; Zhang, F.; Parak, W. J.; Nienhaus, G. U. Quantitative analysis of the protein corona on FePt nanoparticles formed by transferrin binding. J. R. Soc. Interface 2010, 7, S5–S13.
Maffre, P.; Nienhaus, K.; Amin, F.; Parak, W. J.; Nienhaus, G. U. Characterization of protein adsorption onto FePt nanoparticles using dual-focus fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2011, 2, 374–383.
Milani, S.; Bombelli, F. B.; Pitek, A. S.; Dawson, K. A.; Rädler, J. Reversible versus irreversible binding of transferrin to polystyrene nanoparticles: Soft and hard corona. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 2532–2541.
Cedervall, T.; Lynch, I.; Lindman, S.; Berggård, T.; Thulin, E.; Nilsson, H.; Dawson, K. A.; Linse, S. Understanding the nanoparticle-protein corona using methods to quantify exchange rates and affinities of proteins for nanoparticles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 2050–2055.
Lundqvist, M.; Stigler, J.; Elia, G.; Lynch, I.; Cedervall, T.; Dawson, K. A. Nanoparticle size and surface properties determine the protein corona with possible implications for biological impacts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 14265–14270.
Zhang, H. Z.; Burnum, K. E.; Luna, M. L.; Petritis, B. O.; Kim, J. S.; Qian, W. J.; Moore, R. J.; Heredia-Langner, A.; Webb-Robertson, B. J. M.; Thrall, B. D. et al. Quantitative proteomics analysis of adsorbed plasma proteins classifies nanoparticles with different surface properties and size. Proteomics 2011, 11, 4569–4577.
Walkey, C. D.; Olsen, J. B.; Guo, H. B.; Emili, A.; Chan, W. C. W. Nanoparticle size and surface chemistry determine serum protein adsorption and macrophage uptake. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 2139–2147.
Zhu, T.; Vasilev, K.; Kreiter, M.; Mittler, S.; Knoll, W. Surface modification of citrate-reduced colloidal gold nanoparticles with 2-mercaptosuccinic acid. Langmuir 2003, 19, 9518–9525.
Rucareanu, S.; Gandubert, V. J.; Lennox, R. B. 4-(N,N-dimethylamino)pyridine-protected Au nanoparticles: Versatile precursors for water- and organic-soluble gold nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 4674–4680.
Wright, A. K.; Thompson, M. R. Hydrodynamic structure of bovine serum-albumin determined by transient electric birefringence. Biophys. J. 1975, 15, 137–141.
Armstrong, J. K.; Wenby, R. B.; Meiselman, H. J.; Fisher, T. C. The hydrodynamic radii of macromolecules and their effect on red blood cell aggregation. Biophys. J. 2004, 87, 4259–4270.
Weisel, J. W.; Litvinov, R. I. Mechanisms of fibrin polymerization and clinical implications. Blood 2013, 121, 1712–1719.
Bailey, S.; Evans, R. W.; Garratt, R. C.; Gorinsky, B.; Hasnain, S.; Horsburgh, C.; Jhoti, H.; Lindley, P. F.; Mydin, A.; Sarra, R. et al. Molecular structure of serum transferrin at 3.3-A resolution. Biochemistry 1988, 27, 5804–5812.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, M., Liu, R., Deng, Z. et al. Quantitative study of protein coronas on gold nanoparticles with different surface modifications. Nano Res. 7, 345–352 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-013-0400-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-013-0400-0