Abstract
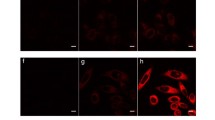
Polymer-coated nanoparticles are widely used for drug delivery in cancer therapy. However, it is not clear whether the polymer coating is disrupted in the lipid bilayer or intracellular space. Our current work suggests that the polymer coating of inorganic nanoparticles is disrupted after internalization by cancer cells. Single dispersed red quantum dots (QDs) labeled with 5-carboxyfluorescein (5-FAM) (green) (diameter = 28 nm) were incubated with cancer cells (PC-3) and imaged via fluorescence microscopy. Initially the 5-FAM-labeled polymer coating was attached to the QD and its green fluorescence was quenched when the nanoparticles were internalized after 4 h incubation, but the 5-FAM-labeled polymer became separated from the QD once inside the lysosomes of cells and its fluorescence becomes visible after 8 h. The fluorescence ratio (5-FAM/QDs) was increased 29-fold after 8 h incubation compared to 2 h. The fluorescence quenching effect of PEG-5-FAM after conjugation in solution (quenched by 44%) was compared to free poly(ethylene glycol)-5-FAM (PEG-5-FAM) mixing with QDs, which only exhibited slight (6.9%) quenching of 5-FAM. In addition, the intracellular dissociation of polymer coating from QD loaded micelles (diameter = 300 nm) was also observed. Furthermore, amphiphilic polymer labeled with the hydrophobic dye 6-((4,4-difluoro-1,3-dimethyl-5-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-bora-3a,4a-diaza-s-indacene-2-propionyl)amino)hexanoic acid (BODIPY® TMR) (red) was applied to encapsulate hydrophobic iron oxide nanoparticles (IONPs). The BODIPY dye was quenched by both the encapsulated IONPs and the hydrophobic region inside the micelles, while an 8-fold fluorescence enhancement was observed after polymeric micelle dissociation. Our in vitro results also reveal the polymeric dissociation after internalization by cancer cells as the dye signal becomes detectable after 24 h incubation. These results suggest that the polymer coating is stable in the lipid bilayer and becomes dissociated from nanoparticles in the lysosome of cancer cells. These data will provide guidance for intracellular drug delivery using polymer coated nanoparticles.
Graphical abstract

Similar content being viewed by others

References
Nie, S. M.; Gao, X. H.; Yang, L. L.; Petros, J. A.; Marshal, F. F.; Simons, J. W. In vivo molecular and cellular imaging with quantum dots. Curr. Opin. Biotech. 2005, 16, 63–72.
Geidel, C.; Schmachtel, S.; Riedinger, A.; Pfeiffer, C., Mullen, K.; Klapper, M.; Parak, W. J. A General synthetic approach for obtaining cationic and anionic inorganic nanoparticles via encapsulation in amphiphilic copolymers. Small 2011, 7, 2929–2934.
Liu, G. Y.; Liu, X. S.; Wang, S. S.; Chen, C. J.; Ji, J. Biomimetic polymersomes as carriers for hydrophilic quantum dots. Langmuir 2012, 28, 557–562.
Wang, T. X.; Sridhar, R.; Korotcov, A.; Ting, A. H.; Francis, K.; Mitchell, J.; Wang, P. C. Synthesis of amphiphilic triblock copolymers as multidentate ligands for biocompatible coating of quantum dots. Colloid Surface A 2011, 375, 147–155.
Ning, Y.; Zhang, H.; Han, J. S.; Yang, C. H.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, D.; Yang, B. Versatile fabrication of water-dispersible nanoparticle-amphiphilic copolymer composite microspheres with specific functionalities. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 6837–6843.
Tagit, O.; Janczewski, D.; Tomczak, N.; Han, M. Y.; Herek, J. L.; Vancso, G. J. Nanostructured thermoresponsive quantum dot/PNIPAM assemblies. Eur. Polym. J. 2010, 46, 1397–1403.
Chen, H. W.; Wu, X. Y.; Duan, H. W.; Wang, Y. A.; Wang, L. Y.; Zhang, M. M.; Mao, H. Biocompatible polysiloxane-containing diblock copolymer PEO-b-PγMPS for coating magnetic nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 2009, 1, 2134–2140.
Chen, K.; Xie, J.; Xu, H. Y.; Behera, D.; Michalski, M. H.; Biswal, S.; Wang, A.; Chen, X. Y. Triblock copolymer coated iron oxide nanoparticle conjugate for tumor integrin targeting. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 6912–6919.
Duan, H. W.; Kuang, M.; Wang, X. X.; Wang, Y. A.; Mao, H.; Nie, S. M. Reexamining the effects of particle size and surface chemistry on the magnetic properties of iron oxide nanocrystals: New insights into spin disorder and proton relaxivity. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 8127–8131.
Tong, S.; Hou, S. J.; Ren, B. B.; Zheng, Z. L.; Bao, G. Self-assembly of phospholipid-PEG coating on nanoparticles through dual solvent exchange. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 3720–3726.
Yang, M.; Chen, T.; Lau, W. S.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Chen, H. Development of polymer-encapsulated metal nanoparticles as surface-enhanced Raman scattering probes. Small 2009, 5, 198–202.
Mandal, S.; Ghatak, C.; Rao, V. G.; Ghosh, S.; Sarkar, N. Pluronic micellar aggregates loaded with gold nanoparticles (Au NPs) and fluorescent dyes: A study of controlled nanometal surface energy transfer. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 5585–5597.
Chen, H. Y.; Abraham, S.; Mendenhall, J.; Delamarre, S. C.; Smith, K.; Kim, I.; Batt, C. A. Encapsulation of single small gold nanoparticles by diblock copolymers. ChemPhysChem 2008, 9, 388–392.
Ashley, C. E.; Carnes, E. C.; Phillips, G. K.; Padilla, D.; Durfee, P. N.; Brown, P. A.; Hanna, T. N.; Liu, J. W.; Phillips, B.; Carter, M. B., et al. The targeted delivery of multi-component cargos to cancer cells by nanoporous particle-supported lipid bilayers. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 389–397.
Zou, P.; Yu, Y. K.; Wang, Y. A.; Zhong, Y. Q.; Welton, A.; Galban, C.; Wang, S. M.; Sun, D. X. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanotheranostics for targeted cancer cell imaging and pH-dependent intracellular drug release. Mol. Pharmaceut. 2010, 7, 1974–1984.
Qi, L. F.; Gao, X. H. Quantum dot-amphipol nanocomplex for intracellular delivery and real-time imaging of siRNA. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 1403–1410.
Yezhelyev, M. V.; Qi, L. F.; O’Regan, R. M.; Nie, S.; Gao, X. H. Proton-sponge coated quantum dots for siRNA delivery and intracellular imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 9006–9012.
Conner, S. D.; Schmid, S. L. Regulated portals of entry into the cell. Nature 2003, 422, 37–44.
Aaron, J.; Travis, K.; Harrison, N.; Sokolov, K. Dynamic imaging of molecular assemblies in live cells based on nanoparticle plasmon resonance coupling. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 3612–3618.
Kneipp, J.; Kneipp, H.; McLaughlin, M.; Brown, D.; Kneipp, K. In vivo molecular probing of cellular compartments with gold nanoparticles and nanoaggregates. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 2225–2231.
El-Sayed, I. H.; Huang, X. H.; El-Sayed, M. A. Surface plasmon resonance scattering and absorption of anti-EGFR antibody conjugated gold nanoparticles in cancer diagnostics: Applications in oral cancer. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 829–834.
Mallidi, S.; Larson, T.; Tam, J.; Joshi, P. P.; Karpiouk, A.; Sokolov, K.; Emelianov, S. Multiwavelength photoacoustic imaging and plasmon resonance coupling of gold nano-particles for selective detection of cancer. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 2825–2831.
Chen, H. T.; Kim, S. W.; Li, L.; Wang, S. Y.; Park, K.; Cheng, J. X. Release of hydrophobic molecules from polymer micelles into cell membranes revealed by Förster resonance energy transfer imaging. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 6596–6601.
Kim, S.; Shi, Y. Z.; Kim, J. Y.; Park, K.; Cheng, J. X. Overcoming the barriers in micellar drug delivery: Loading efficiency, in vivo stability, and micelle-cell interaction. Expert. Opin. Drug Del. 2010, 7, 49–62.
Jain, T. K.; Foy, S. P.; Erokwu, B.; Dimitrijevic, S.; Flask, C. A.; Labhasetwar, V. Magnetic resonance imaging of multifunctional pluronic stabilized iron-oxide nanoparticles in tumor-bearing mice. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 6748–6756.
Yang, H. M.; Lee, H. J.; Jang, K. S.; Park, C. W.; Yang, H. W.; Heo, W.; Kim, J. D. Poly(amino acid)-coated iron oxide nanoparticles as ultra-small magnetic resonance probes. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 4566–4574.
Gao, X. H.; Cui, Y. Y.; Levenson, R. M.; Chung, L. W. K.; Nie, S. M. In vivo cancer targeting and imaging with semiconductor quantum dots. Nat. Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 969–976.
Sperling, R. A.; Pellegrino, T.; Li, J. K.; Chang, W. H.; Parak, W. J. Electrophoretic separation of nanoparticles with a discrete number of functional groups. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2006, 16, 943–948.
Jaiswal, J. K.; Mattoussi, H.; Mauro, J. M.; Simon, S. M. Long-term multiple color imaging of live cells using quantum dot bioconjugates. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 47–51.
Zhang, L. W.; Monteiro-Riviere, N. A. Mechanisms of quantum dot nanoparticle cellular uptake. Toxicol. Sci. 2009, 110, 138–155.
Xiao, Y.; Forry, S. P.; Gao, X.; Holbrook, R. D.; Telford, W. G.; Tona, A. Dynamics and mechanisms of quantum dot nanoparticle cellular uptake. J. Nanobiotechnology 2010, 8, 13.
Nabiev, I.; Mitchell, S.; Davies, A.; Williams, Y.; Kelleher, D.; Moore, R.; Gun’ko, Y. K.; Byrne, S.; Rakovich, Y. P.; Donegan, J. F., et al. Nonfunctionalized nanocrystals can exploit a cell’s active transport machinery delivering them to specific nuclear and cytoplasmic compartments. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 3452–3461.
Ritter, S. C.; Milanick, M. A.; Meissner, K. E. Encapsulation of FITC to monitor extracellular pH: A step towards the development of red blood cells as circulating blood analyte biosensors. Biomed. Opt. Express 2011, 2, 2012–2021.
Wang, F.; Wang, Y. C.; Dou, S.; Xiong, M. H.; Sun, T. M.; Wang, J. Doxorubicin-tethered responsive gold nanoparticles facilitate intracellular drug delivery for overcoming multidrug resistance in cancer cells. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 3679–3692.
Chen, Y.; O’Donoghue, M. B.; Huang, Y. F.; Kang, H. Z.; Phillips, J. A.; Chen, X. L.; Estevez, M. C.; Yang, C. Y. J.; Tan, W. H. A surface energy transfer nanoruler for measuring binding site distances on live cell surfaces. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 16559–16570.
Zhou, K. J.; Wang, Y. G.; Huang, X. N.; Luby-Phelps, K.; Sumer, B. D.; Gao, J. M. Tunable, ultrasensitive pH-responsive nanoparticles targeting specific endocytic organelles in living cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2011, 50, 6109–6114.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Zou, P., Connarn, J. et al. Intracellular dissociation of a polymer coating from nanoparticles. Nano Res. 5, 815–825 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-012-0265-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-012-0265-7