Abstract
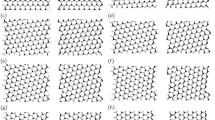
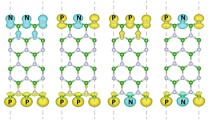
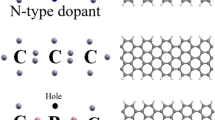
First-principles investigations of the edge energies and edge stresses of single-layer hexagonal boron nitride (BN) are presented. The armchair edges of BN nanoribbons (BNNRs) are more stable in energy than zigzag ones. Armchair BNNRs are under compressive edge stress while zigzag BNNRs are under tensile edge stress, due to the edge reconstruction effect and edge coulomb repulsion effect. The intrinsic spin-polarization and edge saturation play important roles in modulating the edge stability of BNNRs. The edge energy difference between BN and graphene can be used to guide the design of specific hybrid BNC structures as the hybrid BNC systems prefer the low-energy edge configurations: In an armchair BNC nanoribbon (BNCNR), BN domains are expected to grow outside of C domains, while the opposite occurs in a zigzag BNCNR. More importantly, armchair BNCNRs can reproduce unique electronic properties of armchair graphene nanoribbons (GNRs), which are expected to be robust against edge functionalization or disorder. Within a certain range of C/BN ratios, zigzag BNCNRs may exhibit intrinsic half-metallicity without any external constraints. These diverse electronic properties of BNCNRs may offer unique opportunities to develop nanoscale electronics and spintronics beyond individual graphene and BN. More generally, these principles for designing BNC can also be extended to other hybrid nanostructures.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Corso, M.; Auwarter, W.; Muntwiler, M.; Tamai, A.; Greber, T.; Osterwalder, J. Boron Nitride nanomesh. Science 2004, 303, 217–220.
Nagashima, A.; Tejima, N.; Gamou, Y.; Kawai, T.; Oshima, C. Electronic-structure of monolayer hexagonal boron-nitride physisorbed on metal-surfaces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1995, 75, 3918–3921.
Jin, C. H.; Lin, F.; Suenaga, K.; Iijima, S. Fabrication of a freestanding boron nitride single layer and its defect assignments. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 195505.
Meyer, J. C.; Chuvilin, A.; Algara-Siller, G.; Biskupek, J.; Kaiser, U. Selective sputtering and atomic resolution imaging of atomically thin boron nitride membranes. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 2683–2689.
Han, M. Y.; Ozyilmaz, B.; Zhang, Y. B.; Kim, P. Energy band-gap engineering of graphene nanoribbons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 98, 206805.
Chen, Z.; Lin, Y. M.; Rooks, M. J.; Avouris, P. Graphene nano-ribbon electronics. Physica E 2007, 40, 228–232.
Tapaszto, L.; Dobrik, G.; Lambin, P.; Biro, L. P. Tailoring the atomic structure of graphene nanoribbons by scanning tunnelling microscope lithography. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 397–401.
Castro Neto, A. H.; Guinea, F.; Peres, N. M. R.; Novoselov, K. S.; Geim, A. K. The electronic properties of graphene. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2009, 81, 109–162.
Son, Y.W.; Cohen, M. L.; Louie, S. G. Energy gaps in graphene nanoribbons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 216803.
Wang, X. R.; Ouyang, Y. J.; Li, X. L.; Wang, H. L.; Guo, J.; Dai, H. J. Room-temperature all-semiconducting sub-10-nm graphene nanoribbon field-effect transistors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 206803.
Park, C. H.; Louie, S. G. Energy gaps and Stark effect in boron nitride nanoribbons. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 2200–2203.
Zheng, F. W.; Zhou, G.; Liu, Z. R.; Wu, J.; Duan, W. H.; Gu, B.L.; Zhang, S. B. Half metallicity along the edge of zigzag boron nitride nanoribbons. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 78, 205415.
Barone, V.; Peralta, J. E. Magnetic boron nitride nanoribbons with tunable electronic properties. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 2210–2214.
Meyer, J. C.; Geim, A. K.; Katsnelson, M. I.; Novoselov, K. S.; Booth, T. J.; Roth, S. The structure of suspended graphene sheets. Nature 2007, 446, 60–63.
Gass, M. H.; Bangert, U.; Bleloch, A. L.; Wang, P.; Nair, R. R.; Geim, A. K. Free-standing graphene at atomic resolution. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 676–681.
Liu, Z.; Suenaga, K.; Harris, P. J. F.; Iijima, S. Open and closed edges of graphene layers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 015501.
Huang, J. Y.; Ding, F.; Yakobson, B. I.; Lu, P.; Qi, L.; Li, J. In situ observation of graphene sublimation and multi-layer edge reconstructions. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 10103–10108.
Shenoy, V. B.; Reddy, C. D.; Ramasubramaniam, A.; Zhang, Y. W. Edge-stress-induced warping of graphene sheets and nanoribbons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 101, 245501.
Bets, K. V.; Yakobson, B. I. Spontaneous twist and intrinsic instabilities of pristine graphene nanoribbons. Nano Res. 2009, 2, 161–166.
Huang, B.; Liu, M.; Su, N. H.; Wu, J.; Duan, W. H.; Gu, B. L.; Liu, F. Quantum manifestations of graphene edge stress and edge instability: A first-principles study. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 166404.
Jun S. Density-functional study of edge stress in graphene. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 78, 073405.
Mukherjee, R.; Bhowmick, S. Edge stabilities of hexagonal boron nitride nanoribbons: A first-principles study. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2011, 7, 720–724.
Jun, S.; Li, X. B.; Meng, F. C.; Ciobanu, C. V. Elastic properties of edges in BN and SiC nanoribbons and of boundaries in C-BN superlattices: A density functional theory study. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 83, 153407.
Xiang, H. J.; Yang, J. L.; Hou, J. G.; Zhu, Q. S. First-principles study of small-radius single-walled BN nanotubes. Phys. Rev. B 2003, 68, 035427.
Ci, L.; Song, L.; Jin, C. H..; Jariwala, D.; Wu, D. X.; Li, Y. J.; Srivastava, A.; Wang, Z. F.; Storr, K.; Balicas, L.; Liu, F.; Ajayan, P. M. Atomic layers of hybridized boron nitride and graphene domains. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 430–435.
Perdew, J. P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865–3868.
Kresse, G.; Furthmüller, J. Efficiency of ab-initio total energy calculations for metals and semiconductors using a plane-wave basis set. Comp. Mater. Sci. 1996, 6, 15–50.
Kresse, G.; Joubert, D. From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 59, 1758–1775.
Nielsen, O. H.; Martin, R. M. Quantum-mechanical theory of stress and force. Phys. Rev. B 1985, 32, 3780–3791.
Wu, M. H.; Wu, X. J.; Pei, Y.; Zeng, X. C. Inorganic nanoribbons with unpassivated zigzag edges: Half metallicity and edge reconstruction. Nano Res. 2011, 4, 233–239.
Koskinen, P.; Malola, S.; Hakkinen, H. Self-passivating edge reconstructions of graphene. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 101, 115502.
Yuge, K. Phase stability of boron carbon nitride in a heterographene structure: A first-principles study. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 79, 144109.
Krivanek, O. L.; Chisholm, M. F.; Nicolosi, V.; Pennycook, T. J.; Corbin, G. J.; Dellby, N.; Murfitt, M. F.; Own, C. S.; Szilagyi, Z. S.; Oxley, M. P. et al. Atom-by-atom structural and chemical analysis by annular dark-field electron microscopy. Nature 2010, 464, 571–574.
Yan, Q. M.; Huang, B.; Yu, J.; Zheng, F. W.; Zang, J.; Wu, J.; Gu, B. L.; Liu, F.; Duan, W. H. Intrinsic current-voltage characteristics of graphene nanoribbon transistors and effect of edge doping. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 1469–1473.
Singh, A. K.; Yakobson, B. I. Electronics and magnetism of patterned graphene nanoroads. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 1540–1543.
Xiang, H. J.; Kan, E. J.; Wei, S.H.; Whangbo, M.H.; Yang, J. L. “Narrow” graphene nanoribbons made easier by partial hydrogenation. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 4025–4030.
Nakada, K.; Fujita, M.; Dresselhaus, G.; Dresselhaus, M. S. Edge state in graphene ribbons: Nanometer size effect and edge shape dependence. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 54, 17954–17961.
Son, Y. -W.; Cohen, M. L.; Louie, S. G. Half-metallic graphene nanoribbons. Nature 2006, 444, 347–349.
Kan, E. J.; Li, Z. Y.; Yang, J. L.; Hou, J. G. Half-metallicity in edge-modified zigzag graphene nanoribbons. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 4224–4225.
Kim, W. Y.; Kim, K. S. Prediction of very large values of magnetoresistance in a graphene nanoribbon device. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 408–412.
Munoz-Rojas, F.; Fernandez-Rossier, J.; Palacios, J. J. Giant magnetoresistance in ultrasmall graphene based devices. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 136810.
Seol, G.; Guo, J. Bandgap opening in boron nitride confined armchair graphene nanoribbon. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 143107.
Du, A. J.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, Z. H.; Lu, G. Q.; Smith, S. C. C-BN single-walled nanotubes from hybrid connection of BN/C nanoribbons: Prediction by ab initio density functional calculations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 1682–1683.
Huang, B.; Si, C.; Lee, H.; Zhao, L.; Wu, J.; Gu, B.L.; Duan, W. H. Intrinsic half-metallic BN-C nanotubes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 043115.
Huang, B.; Yan, Q. M.; Zhou, G.; Wu, J.; Gu, B.L.; Duan, W. H.; Liu, F. Making a field effect transistor on a single graphene nanoribbon by selective doping. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 253122.
Huang, B.; Liu, F.; Wu, J.; Gu, B.L.; Duan, W. H. Suppression of spin polarization in graphene nanoribbons by edge defects and impurities. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 77, 153411.
Huang, B.; Li, Z. Y.; Liu, Z. R.; Zhou, G.; Hao, S. G.; Wu, J.; Gu, B.L.; Duan, W. H. Adsorption of gas molecules on graphene nanoribbons and its implication for nanoscale molecule sensor. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 13442–13446.
Li, J.; Li, Z. Y.; Zhou, G.; Liu, Z. R.; Wu, J. A.; Gu, B.L.; Ihm, J. S.; Duan, W. H. Spontaneous edge-defect formation and defect-induced conductance suppression in graphene nanoribbons. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 82, 115410.
Li, X. L.; Wang, X. R.; Zhang, L.; Lee, S. W.; Dai, H. J. Chemically derived, ultrasmooth graphene nanoribbon semiconductors. Science 2008, 319, 1229–1232.
Cervantes-Sodi, F.; Csanyi, G.; Piscanec, S.; Ferrari, A. C. Edge-functionalized and substitutionally doped graphene nanoribbons: Electronic and spin properties. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 77, 165427.
Chen, Y.; Zou, J.; Campbell, S. J.; Le Caer, G. Boron nitride nanotubes: Pronounced resistance to oxidation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 84, 2430–2432.
Wu, X. J.; An, W.; Zeng, X. C. Chemical functionalization of boron-nitride nanotubes with NH3 and amino functional groups. J.Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 12001–12006.
Kan, E. J.; Wu, X. J.; Li, Z. Y.; Zeng, X. C.; Yang, J. L.; Hou, J. G. Half-metallicity in hybrid BCN nanoribbons. J. Chem. Phys. 2008, 129, 084712.
Li, J.; Zhou, G.; Chen, Y.; Gu, B.L.; Duan, W. H. Magnetism of C adatoms on BN nanostructures: Implications for functional nanodevices. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 1796–1801.
Dutta, S.; Manna, A. K.; Pati, S. K. Intrinsic half-metallicity in modified graphene nanoribbons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 096601.
Pruneda, J. M. Origin of half-semimetallicity induced at interfaces of C-BN heterostructures. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 81, 161409.
Liu, Y. L.; Wu, X. J.; Zhao, Y.; Zeng, X. C.; Yang, J. L. Half-metallicity in hybrid graphene/boron nitride nanoribbons with dihydrogenated edges. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 9442–9450.
He, J.; Chen, K. Q.; Fan, Z. Q.; Tang, L. M.; Hu, W. P. Transition from insulator to metal induced by hybridized connection of graphene and boron nitride nanoribbons. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 193305.
Du, A. J.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, Z. H.; Amal, R.; Lu, G. Q.; Smith, S. C. Dots versus antidots: Computational exploration of structure, magnetism, and half-metallicity in boron-nitride nanostructures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 17354–17359.
Zhang, Z. H.; Guo, W. L. Tunable ferromagnetic spin ordering in boron nitride nanotubes with topological fluorine adsorption. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 6874–6879.
Chen, W.; Li, Y. F.; Yu, G. T.; Li, C. Z.; Zhang, S. B. B.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, Z. F. Hydrogenation: A simple approach to realize semiconductor-half-metal-metal transition in boron nitride nanoribbons. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 1699–1705.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, B., Lee, H., Gu, BL. et al. Edge stability of boron nitride nanoribbons and its application in designing hybrid BNC structures. Nano Res. 5, 62–72 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-011-0185-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-011-0185-y