Abstract
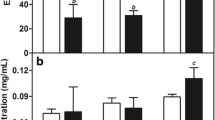
The CD44 receptor, which is upregulated in many cancer cells, provides a selective cellular surface for targeted drug delivery systems. We developed a hybrid nanocarrier for the CD44-targeted delivery of ibuprofen (IBU) and paclitaxel (PTX). The solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) were prepared by a hot-melt oil/water emulsion technique and then coated with hyaluronic acid (HA) by electrostatic interactions. The final SLN were spherical with a hydrodynamic diameter (Z) of 72.16 ± 2.9 nm, polydispersity index (PDI) of 0.276 ± 0.009, and zeta potential (ZP) of 28.20 ± 0.69 mV. Similarly, SLN coated with HA (SLN-HA) exhibited acceptable physical properties (Z 169.3 ± 0.55 nm, PDI 0.285 ± 0.004, and ZP − 10.5 ± 0.15 mV). Cell viability assays showed that the combination of IBU, a chemopreventive agent, and PTX exerted a synergistic inhibitory effect on the proliferation of cancer cells (CI < 1.0). Additionally, our observations indicated that both SLN and SLN-HA enhanced apoptosis and cellular uptake compared to the cocktail of free drugs. HA indicated its affinity for cancer cells through the improvement of cellular uptake and induction of apoptosis. These results clearly indicated that these nanoparticle systems hold great promise for drug delivery in breast cancer treatment.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arpicco S, Lerda C, Dalla Pozza E, Costanzo C, Tsapis N, Stella B, Donadelli M, Dando I, Fattal E, Cattel L (2013) Hyaluronic acid-coated liposomes for active targeting of gemcitabine. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 85:373–380
Basakran NS (2015) CD44 as a potential diagnostic tumor marker. Saudi Med J 36:273–279
Chou TC (2006) Theoretical basis, experimental design, and computerized simulation of synergism and antagonism in drug combination studies. Pharmacol Rev 58:621–681
Chou TC, Talalay P (1981) Generalized equations for the analysis of inhibitions of Michaelis–Menten and higher-order kinetic systems with two or more mutually exclusive and nonexclusive inhibitors. Eur J Biochem 115:207–216
Chou T-C, Talalay P (1984) Quantitative analysis of dose–effect relationships: the combined effects of multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv Enzym Regul 22:27–55
Cuzick J, Otto F, Baron JA, Brown PH, Burn J, Greenwald P, Jankowski J, La Vecchia C, Meyskens F, Senn HJ (2009) Aspirin and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for cancer prevention: an international consensus statement. Lancet Oncol 10:501–507
Danhier F, Lecouturier N, Vroman B, Jérôme C, Marchand-Brynaert J, Feron O, Préat V (2009) Paclitaxel-loaded PEGylated PLGA-based nanoparticles: in vitro and in vivo evaluation. J Control Release 133:11–17
Endo H, Yano M, Okumura Y, Kido H (2014) Ibuprofen enhances the anticancer activity of cisplatin in lung cancer cells by inhibiting the heat shock protein 70. Cell Death Dis 5:e1027
Esposito G, Geninatti Crich S, Aime S (2008) Efficient cellular labeling by CD44 receptor-mediated uptake of cationic liposomes functionalized with hyaluronic acid and loaded with MRI contrast agents. ChemMedChem 3:1858–1862
Fonseca C, Simoes S, Gaspar R (2002) Paclitaxel-loaded PLGA nanoparticles: preparation, physicochemical characterization and in vitro anti-tumoral activity. J Control Release 83:273–286
Garud A, Singh D, Garud N (2012) Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN): method, characterization and applications. Int Curr Pharm J 1:384–393
Götte M, Yip GW (2006) Heparanase, hyaluronan, and CD44 in cancers: a breast carcinoma perspective. Cancer Res 66:10233–10237
Harris RE, Alshafie GA, Abou-Issa H, Seibert K (2000) Chemoprevention of breast cancer in rats by celecoxib, a cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitor. Cancer Res 60:2101–2103
Hayward SL, Wilson CL, Kidambi S (2016) Hyaluronic acid-conjugated liposome nanoparticles for targeted delivery to CD44 overexpressing glioblastoma cells. Oncotarget 7:34158
Jin J, Krishnamachary B, Mironchik Y, Kobayashi H, Bhujwalla ZM (2016) Phototheranostics of CD44-positive cell populations in triple negative breast cancer. Sci Rep 6:27871
Mero A, Campisi M (2014) Hyaluronic acid bioconjugates for the delivery of bioactive molecules. Polymers 6:346–369
Mueller RH, Maeder K, Gohla S (2000) Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) for controlled drug delivery—a review of the state of the art. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 50:161–177
Murohashi M, Hinohara K, Kuroda M, Isagawa T, Tsuji S, Kobayashi S, Umezawa K, Tojo A, Aburatani H, Gotoh N (2010) Gene set enrichment analysis provides insight into novel signalling pathways in breast cancer stem cells. Br J Cancer 102:206–212
Naseri N, Valizadeh H, Zakeri-Milani P (2015) Solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers: structure, preparation and application. Adv Pharm Bull 5:305–313
Nguyen HT, Tran TH, Kim JO, Yong CS, Nguyen CN (2015) Enhancing the in vitro anti-cancer efficacy of artesunate by loading into poly-d, l-lactide-co-glycolide (PLGA) nanoparticles. Arch Pharm Res 38:716–724
Nguyen HT, Tran TH, Thapa RK, Pham TT, Jeong J-H, Youn YS, Choi H-G, Yong CS, Kim JO (2017) Incorporation of chemotherapeutic agent and photosensitizer in a low temperature-sensitive liposome for effective chemo-hyperthermic anticancer activity. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 14:155–164
Ouakrim DA, Dashti SG, Chau R, Buchanan DD, Clendenning M, Rosty C, Winship IM, Young JP, Giles GG, Leggett B (2015) Aspirin, ibuprofen, and the risk for colorectal cancer in Lynch syndrome. J Natl Cancer Inst. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djv170
Panyam J, Labhasetwar V (2003) Dynamics of endocytosis and exocytosis of poly (d, l-lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles in vascular smooth muscle cells. Pharm Res 20:212–220
Ponta H, Sherman L, Herrlich PA (2003) CD44: from adhesion molecules to signalling regulators. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4:33–45
Potta SG, Minemi S, Nukala RK, Peinado C, Lamprou DA, Urquhart A, Douroumis D (2011) Preparation and characterization of ibuprofen solid lipid nanoparticles with enhanced solubility. J Microencapsul 28:74–81
Pradhan R, Ramasamy T, Choi JY, Kim JH, Poudel BK, Tak JW, Nukolova N, Choi H-G, Yong CS, Kim JO (2015) Hyaluronic acid-decorated poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles for combined delivery of docetaxel and tanespimycin. Carbohydr Polym 123:313–323
Ravar F, Saadat E, Gholami M, Dehghankelishadi P, Mahdavi M, Azami S, Dorkoosh FA (2016) Hyaluronic acid-coated liposomes for targeted delivery of paclitaxel, in vitro characterization and in vivo evaluation. J Control Release 229:10–22
Segura T, Anderson BC, Chung PH, Webber RE, Shull KR, Shea LD (2005) Crosslinked hyaluronic acid hydrogels: a strategy to functionalize and pattern. Biomaterials 26:359–371
Sheridan C, Kishimoto H, Fuchs RK, Mehrotra S, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Turner CH, Goulet R Jr, Badve S, Nakshatri H (2006) CD44+/CD24− breast cancer cells exhibit enhanced invasive properties: an early step necessary for metastasis. Breast Cancer Res 8:R59
Sherman L, Sleeman J, Herrlich P, Ponta H (1994) Hyaluronate receptors: key players in growth, differentiation, migration and tumor progression. Curr Opin Cell Biol 6:726–733
Smalley WE, DuBois RN (1997) Colorectal cancer and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Adv Pharmacol 39:1–20
Sutaria D, Grandhi BK, Thakkar A, Wang J, Prabhu S (2012) Chemoprevention of pancreatic cancer using solid-lipid nanoparticulate delivery of a novel aspirin, curcumin and sulforaphane drug combination regimen. Int J Oncol 41:2260–2268
Taketo MM (1998a) Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors in tumorigenesis (part I). J Natl Cancer Inst 90:1529–1536
Taketo MM (1998b) Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors in tumorigenesis (Part II). J Natl Cancer Inst 90:1609–1620
Thakkar A, Chenreddy S, Wang J, Prabhu S (2015) Evaluation of ibuprofen loaded solid lipid nanoparticles and its combination regimens for pancreatic cancer chemoprevention. Int J Oncol 46:1827–1834
Thapa RK, Choi JY, Poudel BK, Hiep TT, Pathak S, Gupta B, Choi H-G, Yong CS, Kim JO (2015) Multilayer-coated liquid crystalline nanoparticles for effective sorafenib delivery to hepatocellular carcinoma. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:20360–20368
Thapa RK, Nguyen HT, Jeong J-H, Shin BS, Ku SK, Choi H-G, Yong CS, Kim JO (2017) Synergistic anticancer activity of combined histone deacetylase and proteasomal inhibitor-loaded zein nanoparticles in metastatic prostate cancers. Nanomed Nanotechnol Biol Med 13:885–896
Toole BP (2009) Hyaluronan–CD44 interactions in cancer: paradoxes and possibilities. Clin Cancer Res 15:7462–7468
Tran TH, Choi JY, Ramasamy T, Truong DH, Nguyen CN, Choi H-G, Yong CS, Kim JO (2014) Hyaluronic acid-coated solid lipid nanoparticles for targeted delivery of vorinostat to CD44 overexpressing cancer cells. Carbohydr Polym 114:407–415
Tran TH, Nguyen HT, Pham TT, Choi JY, Choi H-G, Yong CS, Kim JO (2015) Development of a graphene oxide nanocarrier for dual-drug chemo-phototherapy to overcome drug resistance in cancer. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:28647–28655
Tran TH, Nguyen TD, Van Nguyen H, Nguyen HT, Kim JO, Yong CS, Nguyen CN (2016) Targeted and controlled drug delivery system loading artesunate for effective chemotherapy on CD44 overexpressing cancer cells. Arch Pharmacal Res 39:687–694
Tran TH, Nguyen HT, Phuong Tran TT, Ku SK, Jeong JH, Choi HG, Yong CS, Kim JO (2017) Combined photothermal and photodynamic therapy by hyaluronic acid-decorated polypyrrole nanoparticles. Nanomedicine (Lond) 12:1511–1523
Watanabe O, Kinoshita J, Shimizu T, Imamura H, Hirano A, Okabe T, Aiba M, Ogawa K (2005) Expression of a CD44 variant and VEGF-C and the implications for lymphatic metastasis and long-term prognosis of human breast cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res CR 24:75–82
Wood PL, Khan MA, Smith T, Goodenowe DB (2011) Cellular diamine levels in cancer chemoprevention: modulation by ibuprofen and membrane plasmalogens. Lipids Health Dis 10:214–222
Wu L, Zhang J, Watanabe W (2011) Physical and chemical stability of drug nanoparticles. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 63:456–469
Yao M, Zhou W, Sangha S, Albert A, Chang AJ, Liu TC, Wolfe MM (2005) Effects of nonselective cyclooxygenase inhibition with low-dose ibuprofen on tumor growth, angiogenesis, metastasis, and survival in a mouse model of colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res 11:1618–1628
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tran, B.N., Nguyen, H.T., Kim, J.O. et al. Combination of a chemopreventive agent and paclitaxel in CD44-targeted hybrid nanoparticles for breast cancer treatment. Arch. Pharm. Res. 40, 1420–1432 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-017-0968-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-017-0968-0