Abstract
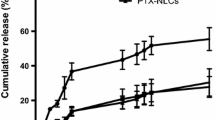
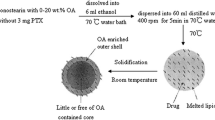
Paclitaxel (PTX) is a well-known antitumor drug, widely utilized in the treatment of breast, ovarian, head, and neck tumors, among others. The low aqueous solubility (< 1.0 μg/mL; log P = 3.96) limits its use by intravenous route, and alternatives found for the marketed products are associated with high toxicity. Incorporation of PTX into lipid nanocarriers has been considered an interesting nontoxic alternative for this route, but drug loading is usually low. This study aimed to analyze the influence of the lipid composition and three different lipid nanosystems—solid lipid nanoparticles, nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs), and nanoemulsion—in PTX encapsulation and its biological response. The three proposed systems were prepared by hot melt homogenization followed by ultrasonication. Among the blank formulations first prepared, NLC had the smallest size (74 ± 1 nm), with negative zeta potential (− 11.4 ± 0.1 mV). The incorporation of 0.10 mg/mL PTX into this NLC formulation yielded high and stable encapsulation (0.089 ± 0.003 mg/mL), also supported by polarized light microscopy and differential scanning calorimetry curves. NLC-PTX was very effective against MCF-7 (IC50 25.33 ± 3.17 nM) and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell lines (IC50 2.13 ± 0.21 nM), compared to free PTX (IC50 > 500 nM). In addition, no significant cytotoxicity was found against fibroblast cells. Taken together, these results demonstrated that PTX was successfully incorporated into NLC with appropriate physicochemical characteristics for intravenous administration, suggesting that the use of NLC as vehicle to incorporate PTX may be a promising strategy in the treatment of breast cancer.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aburahma MH, Badr-Eldin SM (2014) Compritol 888 ATO: a multifunctional lipid excipient in drug delivery systems and nanopharmaceuticals. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 11:1865–1883. https://doi.org/10.1517/17425247.2014.935335
Baek JS, So JW, Shin SC, Cho CW (2012) Solid lipid nanoparticles of paclitaxel strengthened by hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin as an oral delivery system. Int J Mol Med 30:953–959. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2012.1086
Baker MT, Naguib M (2005) Propofol: the challenges of formulation. Anesthesiology 103:860–876
Banerjee I, De K, Mukherjee D, Dey G, Chattopadhyay S, Mukherjee M, Mandal M, Bandyopadhyay AK, Gupta A, Ganguly S, Misra M (2016) Paclitaxel-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles modified with Tyr-3-octreotide for enhanced anti-angiogenic and anti-glioma therapy. Acta Biomater 38:69–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2016.04.026
Barbosa MV, Monteiro LO, Carneiro G, Malagutti AR, Vilela JM, Andrade MS, Oliveira MC, Carvalho-Junior AD, Leite EA (2015) Experimental design of a liposomal lipid system: a potential strategy for paclitaxel-based breast cancer treatment. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 136:553–561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2015.09.055
Bruxel F, Laux M, Wild LB, Fraga M, Koester LS, Teixeira HF (2012) Nanoemulsions as parenteral drug delivery systems. Quim Nova 35:1827–1840. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-40422012000900023
Carneiro G, Silva EL, Pacheco LA, de Souza-Fagundes EM, Correa NC, de Goes AM, Oliveira MC, Ferreira LAM (2012) Formation of ion pairing as an alternative to improve encapsulation and anticancer activity of all-trans retinoic acid loaded in solid lipid nanoparticles. Int J Nanomedicine 7:6011–6020. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S38953
Castro GA, Coelho AL, Oliveira CA, Mahecha GA, Orefice RL, Ferreira LA (2009) Formation of ion pairing as an alternative to improve encapsulation and stability and to reduce skin irritation of retinoic acid loaded in solid lipid nanoparticles. Int J Pharm 381:77–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2009.07.025
Das S, Ng WK, Tan RB (2012) Are nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) better than solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs): development, characterizations and comparative evaluations of clotrimazole-loaded SLNs and NLCs? Eur J Pharm Sci 47:139–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2012.05.010
Donyai P, Sewell GJ (2006) Physical and chemical stability of paclitaxel infusions in different container types. J Oncol Pharm Pract 12:211–222. https://doi.org/10.1177/1078155206073589
Feng SS, Mu L, Win KY, Huang G (2004) Nanoparticles of biodegradable polymers for clinical administration of paclitaxel. Curr Med Chem 11:413–424. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867043455909
Gaucher G, Poreba M, Ravenelle F, Leroux JC (2007) Poly(N-vinyl-pyrrolidone)-block-poly(D,L-lactide) as polymeric emulsifier for the preparation of biodegradable nanoparticles. J Pharm Sci 96:1763–1775. https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.20833
Gelderblom H, Verweij J, Nooter K, Sparreboom A (2001) Cremophor EL: the drawbacks and advantages of vehicle selection for drug formulation. Eur J Cancer 37:1590–1598. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0959-8049(01)00171-X
Gibson JD, Khanal BP, Zubarev ER (2007) Paclitaxel-functionalized gold nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 129:11653–11661. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja075181k
Green MR, Manikhas GM, Orlov S, Afanasyev B, Makhson AM, Bhar P, Hawkins MJ (2006) Abraxane, a novel Cremophor-free, albumin-bound particle form of paclitaxel for the treatment of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol 17:1263–1268. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdl104
Hamaguchi T, Matsumura Y, Suzuki M, Shimizu K, Goda R, Nakamura I, Nakatomi I, Yokoyama M, Kataoka K, Kakizoe T (2005) NK105, a paclitaxel-incorporating micellar nanoparticle formulation, can extend in vivo antitumour activity and reduce the neurotoxicity of paclitaxel. Br J Cancer 92:1240–1246. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6602479
Hua MY, Yang HW, Chuang CK, Tsai RY, Chen WJ, Chuang KL, Chang YH, Chuang HC, Pang ST (2010) Magnetic-nanoparticle-modified paclitaxel for targeted therapy for prostate cancer. Biomaterials 31:7355–7363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.05.061
ISO 10993–5 (2009) Biological evaluation of medical devices-part 5. Tests for Cytotoxicity: In vitro Methods. ISO, Geneve
Jain V, Swarnakar NK, Mishra PR, Verma A, Kaul A, Mishra AK, Jain NK (2012) Paclitaxel loaded PEGylated glecerylmonooleate based nanoparticulate carriers in chemotherapy. Biomaterials 33:7206–7220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.06.056
Jenning V, Mader K, Gohla SH (2000) Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) based on binary mixtures of liquid and solid lipids: a (1)H-NMR study. Int J Pharm 205:15–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-5173(00)00462-2
Jing J, Szarpak-Jankowska A, Guillot R, Pignot-Paintrand I, Picart C, Auzély-Velty R (2013) Cyclodextrin/paclitaxel complex in biodegradable capsules for breast cancer treatment. Chem Mater 25:3867–3873. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm4019925
Kataoka K, Kwon GS, Yokoyama M, Okano T, Sakurai Y (1993) Block copolymer micelles as vehicles for drug delivery. J Control Release 24:119–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-3659(93)90172-2
Miao J, Du Y, Yuan H, Zhang X, Li Q, Rao Y, Zhao M, Hu F (2015) Improved cytotoxicity of paclitaxel loaded in nanosized lipid carriers by intracellular delivery. J Nanopart Res 17:10–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-014-2852-x
Mitri K, Shegokar R, Gohla S, Anselmi C, Muller RH (2011) Lipid nanocarriers for dermal delivery of lutein: preparation, characterization, stability and performance. Int J Pharm 414:267–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2011.05.008
Mohanraj V, Chen Y (2006) Nanoparticles—a review. Trop J Pharm Res 5:561–573. https://doi.org/10.4314/tjpr.v5i1.14634
Muller RH, Mader K, Gohla S (2000) Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) for controlled drug delivery—a review of the state of the art. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 50:161–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0939-6411(00)00087-4
Naahidi S, Jafari M, Edalat F, Raymond K, Khademhosseini A, Chen P (2013) Biocompatibility of engineered nanoparticles for drug delivery. J Control Release 166:182–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2012.12.013
Schedle A, Samorapoompichit P, Rausch-Fan XH, Franz A, Fureder W, Sperr WR, Sperr W, Ellinger A, Slavicek R, Boltz-Nitulescu G, Valent P (1995) Response of L-929 fibroblasts, human gingival fibroblasts, and human tissue mast cells to various metal cations. J Dent Res 74:1513–1520. https://doi.org/10.1177/00220345950740081301
Selvamuthukumar S, Velmurugan R (2012) Nanostructured lipid carriers: a potential drug carrier for cancer chemotherapy. Lipids Health Dis 11:159–166. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-511X-11-159
Shao Z, Shao J, Tan B, Guan S, Liu Z, Zhao Z, He F, Zhao J (2015) Targeted lung cancer therapy: preparation and optimization of transferrin-decorated nanostructured lipid carriers as novel nanomedicine for co-delivery of anticancer drugs and DNA. Int J Nanomedicine 10:1223–1233. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S77837
Sharma US, Balasubramanian SV, Straubinger RM (1995) Pharmaceutical and physical properties of paclitaxel (Taxol) complexes with cyclodextrins. J Pharm Sci 84:1223–1230. https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.2600841015
Swidan SA, Ghonaim HM, Samy AM, Ghorab MM (2016) Comparative study of solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers for in vitro Paclitaxel delivery. J Chem Pharm Res 8:482–493
Tosta FV, Andrade LM, Mendes LP, Anjos JLV, Alonso A, Marreto RN, Lima EM, Taveir SF (2014) Paclitaxel-loaded lipid nanoparticles for topical application: the influence of oil content on lipid dynamic behavior, stability, and drug skin penetration. J Nanopart Res 16:2782–2793. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-014-2782-7
Tran TH, Ramasamy T, Truong DH, Choi HG, Yong CS, Kim JO (2014) Preparation and characterization of fenofibrate-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers for oral bioavailability enhancement. AAPS PharmSciTech 15:1509–1515. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-014-0175-y
Trickler WJ, Nagvekar AA, Dash AK (2008) A novel nanoparticle formulation for sustained paclitaxel delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech 9:486–493. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-008-9063-7
USP 36-NF 34 (2016) The United States Pharmacopeia and National Formulary. United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Rockville
Videira M, Almeida AJ, Fabra À (2012) Preclinical evaluation of a pulmonary delivered paclitaxel-loaded lipid nanocarrier antitumor effect. Nanomedicine 8:1208–1215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2011.12.007
Wang Y, Zhang H, Hao J, Li B, Li M, Xiuwen W (2016) Lung cancer combination therapy: co-delivery of paclitaxel and doxorubicin by nanostructured lipid carriers for synergistic effect. Drug Deliv 23:1398–1403. https://doi.org/10.3109/10717544.2015.1055619
Weber S, Zimmer A, Pardeike J (2014) Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) and nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) for pulmonary application: a review of the state of the art. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 86:7–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2013.08.013
Wissing SA, Kayser O, Muller RH (2004) Solid lipid nanoparticles for parenteral drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 56:1257–1272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2003.12.002
Wu L, Tang C, Yin C (2010) Folate-mediated solid-liquid lipid nanoparticles for paclitaxel-coated poly(ethylene glycol). Drug Dev Ind Pharm 36:439–448. https://doi.org/10.3109/03639040903244472
Xu W, Lee M-K (2015) Development and evaluation of lipid nanoparticles for paclitaxel delivery: a comparison between solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers. J Pharm Investig 45:675–680. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-015-0224-x
Yang Y, Corona A 3rd, Schubert B, Reeder R, Henson MA (2014) The effect of oil type on the aggregation stability of nanostructured lipid carriers. J Colloid Interface Sci 418:261–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2013.12.024
Yu S, Zhang Y, Wang X, Zhen X, Zhang Z, Wu W, Jiang X (2013) Synthesis of paclitaxel-conjugated beta-cyclodextrin polyrotaxane and its antitumor activity. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 52:7272-7277. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201301397
Zhang XG, Miao J, Dai YQ, Du YZ, Yuan H, Hu FQ (2008) Reversal activity of nanostructured lipid carriers loading cytotoxic drug in multi-drug resistant cancer cells. Int J Pharm 361:239-244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2008.06.002
Zhang W, Shi Y, Chen Y, Hao J, Sha X, Fang X (2011) The potential of Pluronic polymeric micelles encapsulated with paclitaxel for the treatment of melanoma using subcutaneous and pulmonary metastatic mice models. Biomaterials 32:5934-5944. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.04.075
Zhao S, Yang X, Garamus VM, Handge UA, Berengere L, Zhao L, Salamon G, Willumeit R, Zou A, Fan S (2014) Mixture of nonionic/ionic surfactants for the formulation of nanostructured lipid carriers: effects on physical properties. Langmuir 30:6920-6928 https"//doi.org/10.1021/la501141m
Zheng N, Gao Y, Ji H, Wu L, Qi X, Liu X, Tang J (2016) Vitamin E derivative-based multifunctional nanoemulsions for overcoming multidrug resistance in cancer. J Drug Target 24:663-669 https://doi.org/10.3109/1061186X.2015.1135335
Funding
The authors would like to thank Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Minas Gerais (FAPEMIG-Brazil), Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq-Brazil), and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES-Brazil) for their financial support and scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Sousa Marcial, S.P., Carneiro, G. & Leite, E.A. Lipid-based nanoparticles as drug delivery system for paclitaxel in breast cancer treatment. J Nanopart Res 19, 340 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-017-4042-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-017-4042-0