Abstract
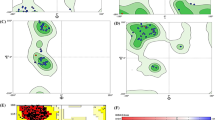
Bruton tyrosine kinase (Btk) is a non-receptor tyrosine kinase. It is a crucial component in BCR pathway and expressed only in hematopoietic cells except T cells and Natural killer cells. BTK is a promising target because of its involvement in signaling pathways and B cell diseases such as autoimmune disorders and lymphoma. In this work, a combined molecular modeling study of molecular docking, 3D-QSAR and molecular dynamic (MD) simulation were performed on a series of 2,5-diaminopyrimidine compounds as inhibitors targeting Btk kinase to understand the interaction and key residues involved in the inhibition. A structure based CoMFA (q 2 = 0.675, NOC = 5, r 2 = 0.961) and COMSIA (q 2 = 0.704, NOC = 6, r 2 = 0.962) models were developed from the conformation obtained by docking. The developed models were subjected to various validation techniques such as leave-five-out, external test set, bootstrapping, progressive sampling and rm 2 metrics and found to have a good predictive ability in both internal and external validation. Our docking results showed the important residues that interacts in the active site residues in inhibition of Btk kinase. Furthermore, molecular dynamics simulation was employed to study the stability of the docked conformation and to investigate the binding interactions in detail. The MD simulation analyses identified several important hydrogen bonds with Btk, including the gatekeeper residue Thr474 and Met477 at the hinge region. Hydrogen bond with active site residues Leu408 and Arg525 were also recognized. A good correlation between the MD results, docking studies and the contour map analysis are observed. This indicates that the developed models are reliable. Our results from this study can provide insights in the designing and development of more potent Btk kinase inhibitors.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aalipour A, Advani RH (2013) Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitors: a promising novel targeted treatment for B cell lymphomas. Br J Haematol 163:436–443
Arnold LD, Calderwood DJ, Dixon RW, Johnston DN, Kamens JS, Munschauer R, Rafferty P, Ratnofsky SE (2000) Pyrrolo [2, 3-d] pyrimidines containing an extended 5-substituent as potent and selective inhibitors of lck I. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 10:2167–2170
Berendsen HJ, Postma JPM, Van Gunsteren WF, Dinola A, Haak J (1984) Molecular dynamics with coupling to an external bath. J Chem Phys 81:3684–3690
Carter TA, Wodicka LM, Shah NP, Velasco AM, Fabian MA, Treiber DK, Milanov ZV, Atteridge CE, Biggs WH, Edeen PT (2005) Inhibition of drug-resistant mutants of ABL, KIT, and EGF receptor kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:11011–11016
Cramer RD, Patterson DE, Bunce JD (1988) Comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA). 1. Effect of shape on binding of steroids to carrier proteins. J Am Chem Soc 110:5959–5967
Da Silva AWS, Vranken WF (2012) ACPYPE-antechamber python parser interface. BMC Res Notes 5:367
Davis RE, Ngo VN, Lenz G, Tolar P, Young RM, Romesser PB, Kohlhammer H, Lamy L, Zhao H, Yang Y (2010) Chronic active B-cell-receptor signalling in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Nature 463:88–92
De Gorter DJ, Beuling EA, Kersseboom R, Middendorp S, Van Gils JM, Hendriks RW, Pals ST, Spaargaren M (2007) Bruton’s tyrosine kinase and phospholipase Cγ2 mediate chemokine-controlled B cell migration and homing. Immunity 26:93–104
De Rooij MF, Kuil A, Geest CR, Eldering E, Chang BY, Buggy JJ, Pals ST, Spaargaren M (2012) The clinically active BTK inhibitor PCI-32765 targets B-cell receptor–and chemokine-controlled adhesion and migration in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 119:2590–2594
Essmann U, Perera L, Berkowitz ML, Darden T, Lee H, Pedersen LG (1995) A smooth particle mesh Ewald method. J Chem Phys 103:8577–8593
Eswar N, Webb B, Marti‐Renom MA, Madhusudhan M, Eramian D, Shen MY, Pieper U, Sali A (2006) Comparative protein structure modeling using modeller. Curr Protoc Bioinf Unit 5.6:1–5
Fiser A, Do RKG, Šali A (2000) Modeling of loops in protein structures. Protein Sci 9:1753–1773
Gadhe CG, Kothandan G, Cho SJ (2012) Large variation in electrostatic contours upon addition of steric parameters and the effect of charge calculation schemes in CoMFA on mutagenicity of MX analogues. Mol Simul 38:861–871
Genevier HC, Hinshelwood S, Gaspar HB, Rigley KP, Brown D, Saeland S, Rousset F, Levinsky RJ, Callard RE, Kinnon C (1994) Expression of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase protein within the B cell lineage. Eur J Immunol 24:3100–3105
Gomez-Rodriguez J, Readinger JA, Viorritto IC, Mueller KL, Houghtling RA, Schwartzberg PL (2007) Tec kinases, actin, and cell adhesion. Immunol Rev 218:45–64
Herman SE, Gordon AL, Hertlein E, Ramanunni A, Zhang X, Jaglowski S, Flynn J, Jones J, Blum KA, Buggy JJ (2011) Bruton tyrosine kinase represents a promising therapeutic target for treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia and is effectively targeted by PCI-32765. Blood 117:6287–6296
Hess B (2008) P-LINCS: a parallel linear constraint solver for molecular simulation. J Chem Theory Comput 4:116–122
Hornak V, Abel R, Okur A, Strockbine B, Roitberg A, Simmerling C (2006) Comparison of multiple Amber force fields and development of improved protein backbone parameters. Proteins 65:712–725
Hu R, Barbault F, Delamar M, Zhang R (2009) Receptor-and ligand-based 3D-QSAR study for a series of non-nucleoside HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem 17:2400–2409
Huey R, Morris GM, Olson AJ, Goodsell DS (2007) A semiempirical free energy force field with charge-based desolvation. J Comput Chem 28:1145–1152
Klebe G, Abraham U, Mietzner T (1994) Molecular similarity indices in a comparative analysis (CoMSIA) of drug molecules to correlate and predict their biological activity. J Med Chem 37:4130–4146
Kurosaki T (1997) Molecular mechanisms in B cell antigen receptor signaling. Curr Opin Immunol 9:309–318
Li Y-P, Weng X, Ning F-X, Ou J-B, Hou J-Q, Luo H-B, Li D, Huang Z-S, Huang S-L, Gu L-Q (2013) 3D-QSAR studies of azaoxoisoaporphine, oxoaporphine, and oxoisoaporphine derivatives as anti-AChE and anti-AD agents by the CoMFA method. J Mol Graph Model 41:61–67
Li X, Zuo Y, Tang G, Wang Y, Zhou Y, Wang X, Guo T, Xia M, Ding N, Pan Z (2014) Discovery of a series of 2, 5-diaminopyrimidine covalent irreversible inhibitors of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase with in vivo antitumor activity. J Med Chem 57:5112–5128
Mahajan S, Ghosh S, Sudbeck EA, Zheng Y, Downs S, Hupke M, Uckun FM (1999) Rational design and synthesis of a novel anti-leukemic agent targeting Bruton′ s tyrosine kinase (BTK), LFM-A13 [α-cyano-β-hydroxy-β-methyl-N-(2,5-dibromophenyl) propenamide]. J Biol Chem 274:9587–9599
Mao C, Zhou M, Uckun FM (2001) Crystal structure of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase domain suggests a novel pathway for activation and provides insights into the molecular basis of X-linked agammaglobulinemia. J Biol Chem 276:41435–41443
Marcotte DJ, Liu YT, Arduini RM, Hession CA, Miatkowski K, Wildes CP, Cullen PF, Hong V, Hopkins BT, Mertsching E (2010) Structures of human Bruton’s tyrosine kinase in active and inactive conformations suggest a mechanism of activation for TEC family kinases. Protein Sci 19:429–439
Martí-Renom MA, Stuart AC, Fiser A, Sánchez R, Melo F, Šali A (2000) Comparative protein structure modeling of genes and genomes. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 29:291–325
Melo F, Sánchez R, Sali A (2002) Statistical potentials for fold assessment. Protein Sci 11:430–448
Mohamed AJ, Yu L, Bäckesjö CM, Vargas L, Faryal R, Aints A, Christensson B, Berglöf A, Vihinen M, Nore BF (2009) Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (Btk): function, regulation, and transformation with special emphasis on the PH domain. Immunol Rev 228:58–73
Morris GM, Goodsell DS, Halliday RS, Huey R, Hart WE, Belew RK, Olson AJ (1998) Automated docking using a Lamarckian genetic algorithm and an empirical binding free energy function. J Comput Chem 19:1639–1662
Ortolano S, Hwang IY, Han SB, Kehrl JH (2006) Roles for phosphoinositide 3-kinases, Bruton’s tyrosine kinase, and Jun kinases in B lymphocyte chemotaxis and homing. Eur J Immunol 36:1285–1295
Petro JB, Rahman SJ, Ballard DW, Khan WN (2000) Bruton’s tyrosine kinase is required for activation of IκB kinase and nuclear factor κB in response to B cell receptor engagement. J Exp Med 191:1745–1754
Ponader S, Chen S-S, Buggy JJ, Balakrishnan K, Gandhi V, Wierda WG, Keating MJ, O’brien S, Chiorazzi N, Burger JA (2012) The Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor PCI-32765 thwarts chronic lymphocytic leukemia cell survival and tissue homing in vitro and in vivo. Blood 119:1182–1189
Pronk S, Páll S, Schulz R, Larsson P, Bjelkmar P, Apostolov R, Shirts MR, Smith JC, Kasson PM, Van Der Spoel D (2013) GROMACS 4.5: a high-throughput and highly parallel open source molecular simulation toolkit. Bioinformatics 29:845–854
Rawlings DJ, Witte ON (1994) Bruton’s tyrosine kinase is a key regulator in B-cell development. Immunol Rev 138:105–119
Roy K, Chakraborty P, Mitra I, Ojha PK, Kar S, Das RN (2013) Some case studies on application of “rm2” metrics for judging quality of quantitative structure–activity relationship predictions: emphasis on scaling of response data. J Comput Chem 34:1071–1082
Shen MY, Sali A (2006) Statistical potential for assessment and prediction of protein structures. Protein Sci 15:2507–2524
Smith C, Baskin B, Humire-Greiff P, Zhou J-N, Olsson P, Maniar H, Kjellen P, Lambris J, Christensson B, Hammarström L (1994) Expression of Bruton’s agammaglobulinemia tyrosine kinase gene, BTK, is selectively down-regulated in T lymphocytes and plasma cells. J Immunol 152:557–565
Smith C, Islam TC, Mattsson PT, Mohamed AJ, Nore BF, Vihinen M (2001) The Tec family of cytoplasmic tyrosine kinases: mammalian Btk, Bmx, Itk, Tec, Txk and homologs in other species. BioEssays 23:436–446
Spaargaren M, Beuling EA, Rurup ML, Meijer HP, Klok MD, Middendorp S, Hendriks RW, Pals ST (2003) The B cell antigen receptor controls integrin activity through Btk and PLCγ2. J Exp Med 198:1539–1550
SYBYL-X 2.1, Tripos International, 1699 South Hanley Rd., St. Louis, Missouri, 63144, USA
Tsukada S, Witte ON (1994) X-linked agammaglobulinemia and Bruton’s tyrosine kinase. Mechanisms of lymphocyte activation and immune regulation V. Springer, New York, pp 233–238
Uckun FM (1998) Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) as a dual-function regulator of apoptosis. Biochem Pharmacol 56:683–691
Vetrie D, Vořechovský I, Sideras P, Holland J, Davies A, Flinter F, Hammarström L, Kinnon C, Levinsky R, Bobrow M (1993) The gene involved in X-linked agammaglobulinaemia is a member of the src family of protein-tyrosine kinases. Nature 361:226–233
Wang J, Wolf RM, Caldwell JW, Kollman PA, Case DA (2004) Development and testing of a general amber force field. J Comput Chem 25:1157–1174
Webb B, Sali A (2014) Protein structure modeling with MODELLER. Protein structure prediction. Springer, New York, pp 1–15
Wiestner A (2013) Targeting B-Cell receptor signaling for anticancer therapy: the Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor ibrutinib induces impressive responses in B-cell malignancies. J Clin Oncol 31:128–130
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea grant (MRC, 2015-009070) funded by the Korea government (MSIP).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Authors have not declared any conflicts of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balasubramanian, P.K., Balupuri, A. & Cho, S.J. Molecular modeling studies on series of Btk inhibitors using docking, structure-based 3D-QSAR and molecular dynamics simulation: a combined approach. Arch. Pharm. Res. 39, 328–339 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-015-0698-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-015-0698-0