Abstract
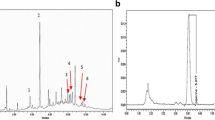
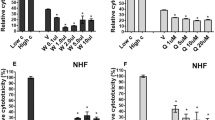
The leaves and stems of Asteraceae Artemisia iwayomogi (Ai) for a long time have been known to inhibit inflammatory cytokine production and allergic reactions, and have been used to treat liver diseases. It needs to be elucidated in terms of global gene expression whether Ai has an influence as an anti-inflammatory agent on the cultured human gingival fibroblast stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS). This study investigated the anti-inflammatory changes of the genes by Ai using the Affymetrix genechip human gene 1.0 ST array when the cultured human gingival fibroblast was treated with LPS. It was observed that the inflammation- and immune response-related genes were activated by LPS challenge in the cultured human gingival fibroblast. The array analysis showed that 65 of the 344 genes up-regulated by LPS stimulation, when compared to the control, were down-regulated by the Ai treatment. A number of inflammation- and immune response-related genes of the 65 genes were found. In addition, 78 of the 164 genes down-regulated by the LPS, when compared to the control, were up-regulated by the Ai treatment. The regulatory patterns of the representative genes were correlated with the real-time RT-PCR analysis. The Ai extract and its specific components, scopolin and scopoletin, significantly hindered the production of inflammatory mediators such as IL-6, TNF-α and nitrite in the LPS-challenged fibroblast. This study suggests that Ai can comprehensively inhibit the activation of the inflammation- and immune response-related genes and the inflammatory mediators in the human gingival fibroblast.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn, H., Kim, J. Y., Lee, H. J., Kim, Y. K., and Ryu, J. H., Inhibitors of inducible nitric oxide synthase expression from Artemisia iwayomogi. Arch. Pharm. Res., 26, 301–305 (2003).
An, J. H., Lee, S. Y., Jeon, J. Y., Cho, K. G., Kim, S. U., and Lee, M. A., Identification of gliotropic factors that induce human stem cell migration to malignant tumor. J. Proteome Res., 8, 2873–2881 (2009).
Bachvarov, D. R., Hess, J. F., Menke, J. G., Larrivée, J. F., and Marceau, F., Structure and genomic organization of the human B1 receptor gene for kinins (BDKRB1). Genomics, 33, 374–381 (1996).
Bauer, A. K., Dixon, D., DeGraff, L. M., Cho, H. Y., Walker, C. R., Malkinson, A. M., and Kleeberger, S. R., Toll-like receptor 4 in butylated hydroxytoluene-induced mouse pulmonary inflammation and tumorigenesis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst., 97, 1778–1781 (2005).
Bauer, A. K., Fostel, J., Degraff, L. M., Rondini, E. A., Walker, C., Grissom, S. F., Foley, J., and Kleeberger, S. R., Transcriptomic analysis of pathways regulated by tolllike receptor 4 in a murine model of chronic pulmonary inflammation and carcinogenesis. Mol. Cancer, 8, 107 (2009).
Beikler, T., Peters, U., Prior, K., Eisenacher, M., and Flemmig, T. F., Gene expression in periodontal tissues following treatment. BMC Med. Genomics, 1, 30 (2008).
Bissonnette, E. Y., Tremblay, G. M., Turmel, V., Pirotte, B., and Reboud-Ravaux, M., Coumarinic derivatives show anti-inflammatory effects on alveolar macrophages, but their anti-elastase activity is essential to reduce lung inflammation in vivo. Int. Immunopharmacol., 9, 49–54 (2009).
Cao, W., Tang, S., Yuan, H., Wang, H., Zhao, X., and Lu, H., Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigen Wag31 induces expression of C-chemokine XCL2 in macrophages. Curr. Microbiol., 57, 189–194 (2008).
Deiteren, K., Hendriks, D., Scharpé, S., and Lambeir, A. M., Carboxypeptidase M: Multiple alliances and unknown partners. Clin. Chim. Acta, 399, 24–39 (2009).
Ding, Y., Liang, C., Yang, S. Y., Ra, J. C., Choi, E. M., Kim, J. A., and Kim, Y. H., Phenolic compounds from Artemisia iwayomogi and their effects on osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull., 33, 1448–1453 (2010).
Grimshaw, M. J., Wilson, J. L., and Balkwill, F. R., Endothelin-2 is a macrophage chemoattractant: implications for macrophage distribution in tumors. Eur. J. Immunol., 32, 2393–2400 (2002).
Han, X. and Amar, S., Identification of genes differentially expressed in cultured human periodontal ligament fibroblasts vs. human gingival fibroblasts by DNA microarray analysis. J. Dent. Res., 81, 399–405 (2002).
Hwang, J. S., Ji, H. J., Koo, K. A., Lee, N. H., Yeo, H. K., Cheong, S. W., Park, J. H., Oh, G. S., Yoon, C. S., and Youn, H. J., AIP1, a water-soluble fraction from Artemisia iwayomogi, suppresses thymocyte apoptosis in vitro and down-regulates the expression of Fas gene. Biol. Pharm. Bull., 28, 921–924 (2005).
Hwang, S. H., Choi, Y. G., Jeong, M. Y., Hong, Y. M., Lee, J. H., and Lim, S., Microarray analysis of gene expression profile by treatment of Cinnamomi Ramulus in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated BV-2 cells. Gene, 443, 83–90 (2009).
Jeong, M. Y., Kim, Y. H., Lee, N. K., Lee, J. Y., Herr, Y., Lee, J. H., and Lim, S., Antimicrobial effect on the periodontal pathogens and anti-inflammatory effect of Eriobotryae Folium. J. Korean Orient. Med., 29, 182–192 (2008).
Kim, A. R., Zou, Y. N., Park, T. H., Shim, K. H., Kim, M. S., Kim, N. D., Kim, J. D., Bae, S. J., Choi, J. S., and Chung, H. Y., Active components from Artemisia iwayomogi displaying ONOO(−) scavenging activity. Phytother. Res., 18, 1–7 (2004).
Kim, S. H., Choi, C. H., Kim, S. Y., Eun, J. S., and Shin, T. Y., Anti-allergic effects of Artemisia iwayomogi on mast cell-mediated allergy model. Exp. Biol. Med., 230, 82–88 (2005).
Krayer, J. W., Leite, R. S., and Kirkwood, K. L., Non-surgical chemotherapeutic treatment strategies for the management of periodontal diseases. Dent. Clin. North Am., 54, 13–33 (2010).
Lang, R., Hammer, M., and Mages, J., DUSP meet immunology: dual specificity MAPK phosphatases in control of the inflammatory response. J. Immunol., 177, 7497–7504 (2006).
Lee, J. A., Sung, H. N., Jeon, C. H., Gill, B. C., Oh, G. S., Youn, H. J., and Park, J. H., A carbohydrate fraction, AIP1 from Artemisia iwayomogi suppresses pulmonary eosinophilia and Th2-type cytokine production in an ovalbumin-induced allergic asthma. Down-regulation of TNF-α expression in the lung. Int. Immunopharmacol., 8, 117–125 (2008a).
Lee, J. A., Sung, H. N., Jeon, C. H., Gill, B. C., Oh, G. S., Youn, H. J., and Park, J. H., AIP1, a carbohydrate fraction from Artemisia iwayomogi, modulates the functional differentiation of bone marrow-derived dendritic cells. Int. Immunopharmacol., 8, 534–541 (2008b).
Muschietti, L., Gorzalczany, S., Ferraro, G., Acevedo, C., and Martino, V., Phenolic compounds with anti-inflammatory activity from Eupatorium buniifolium. Planta Med., 67, 743–744 (2001).
Pan, R., Dai, Y., Gao, X., and Xia, Y., Scopolin isolated from Erycibe obtusifolia Benth stems suppresses adjuvantinduced rat arthritis by inhibiting inflammation and angiogenesis. Int. Immunopharmacol., 9, 859–869 (2009).
Proudfoot, A. E., de Souza, A. L., and Muzio, V., The use of chemokine antagonists in EAE models. J. Neuroimmunol., 198, 27–30 (2008).
Ryu, J. H., Ahn, H., Kim, J. Y., and Kim, Y. K., Inhibitory activity of plant extracts on nitric oxide synthesis in LPSactivated macrophages. Phytother. Res., 17, 485–489 (2003).
Schulze-Topphoff, U., Prat, A., Prozorovski, T., Siffrin, V., Paterka, M., Herz, J., Bendix, I., Ifergan, I., Schadock, I., Mori, M. A., Van Horssen, J., Schröter, F., Smorodchenko, A., Han, M. H., Bader, M., Steinman, L., Aktas, O., and Zipp, F., Activation of kinin receptor B1 limits encephalitogenic T lymphocyte recruitment to the central nervous system. Nat. Med., 15, 788–793 (2009).
Shin, K. M., Kim, I. T., Park, Y. M., Ha, J., Choi, J. W., Park, H. J., Lee, Y. S., and Lee, K. T., Anti-inflammatory effect of caffeic acid methyl ester and its mode of action through the inhibition of prostaglandin E2, nitric oxide and tumor necrosis factor-alpha production. Biochem. Pharmacol., 68, 2327–2336 (2004).
Shin, T. Y., Park, J. S., and Kim, S. H., Artemisia iwayomogi inhibits immediate-type allergic reaction and inflammatory cytokine secretion. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol., 28, 421–430 (2006).
Stievano, L., Piovan, E., and Amadori, A., C and CX3C chemokines: cell sources and physiopathological implications. Crit. Rev. Immunol., 24, 205–228 (2004).
Taillé, C., Guénégou, A., Almolki, A., Piperaud, M., Leynaert, B., Vuillaumier, S., Neukirch, F., Boczkowski, J., Aubier, M., Benessiano, J., and Crestani, B., ETB receptor polymorphism is associated with airway obstruction. BMC Pulm. Med., 7, 5 (2007).
Wang, H. W., Lin, C. P., Chiu, J. H., Chow, K. C., Kuo, K. T., Lin, C. S., and Wang, L. S., Reversal of inflammation-associated dihydrodiol dehydrogenases (AKR1C1 and AKR1C2) overexpression and drug resistance in nonsmall cell lung cancer cells by wogonin and chrysin. Int. J. Cancer, 120, 2019–2027 (2007).
Wang, P. L., Ohura, K., Fujii, T., Oido-Mori, M., Kowashi, Y., Kikuchi, M., Suetsugu, Y., and Tanaka, J., DNA microarray analysis of human gingival fibroblasts from healthy and inflammatory gingival tissues. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 305, 970–973 (2003).
Yang, M. D., Wu, C. C., Chiou, S. H., Chiu, C. F., Lin, T. Y., Chiang, I. P., and Chow, K. C., Reduction of dihydrodiol dehydrogenase expression in resected hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Rep., 10, 271–276 (2003).
Yoshida, T., Imai, T., Kakizaki, M., Nishimura, M., Takagi, S., and Yoshie, O., Identification of single C motif-1/lymphotactin receptor XCR1. J. Biol. Chem., 273, 16551–16554 (1998).
Zhang, X., Tan, F., Zhang, Y., and Skidgel, R. A., Carboxypeptidase M and kinin B1 receptors interact to facilitate efficient b1 signaling from B2 agonists. J. Biol. Chem., 283, 7994–8004 (2008).
Zhang, Y., Blattman, J. N., Kennedy, N. J., Duong, J., Nguyen, T., Wang, Y., Davis, R. J., Greenberg, P. D., Flavell, R. A., and Dong, C., Regulation of innate and adaptive immune responses by MAP kinase phosphatase 5. Nature, 430, 793–797 (2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, YG., Yeo, S., Kim, SH. et al. Anti-inflammatory changes of gene expression by Artemisia iwayomogi in the LPS-stimulated human gingival fibroblast: Microarray analysis. Arch. Pharm. Res. 35, 549–563 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-012-0319-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-012-0319-0