Abstract
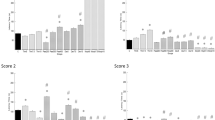
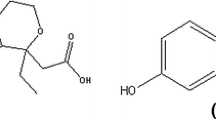
Some endogenous hormones (epinephrine and cortisol) can change an individual’s pain threshold. Propranolol is a non-selective β adrenergic receptor blocker which antagonises the anti-inflammatory effect of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs via the β1 and β2 adrenergic receptors. The roles of epinephrine and cortisol were investigated in the analgesic activity of metyrosine in rats with reduced epinephrine levels induced by metyrosine. Pain threshold measurement was performed using an analgesimeter with different doses and the single or combined usage of metyrosine, prednisolone, metyrapone and propranolol in rats. Epinephrine and corticosterone levels were measured by high-performance liquid chromatography in metyrosineadministered rats. Metyrosine reduces the epinephrine levels without affecting the corticosterone levels, thereby creating an analgesic effect. It was determined that prednisolone did not have an analgesic effect in rats with normal epinephrine levels, but its analgesic activity increased with a parallel decrease in the epinephrine levels. Similarly, the combined use of prednisolone and metyrosine provided a stronger analgesic effect than that rendered by metyrosine alone. The strongest analgesic effect, however, was observed in the group of rats with the lowest epinephrine level in whom the metyrosine + prednisolone combination was administered. The findings of this study may be useful in severe pain cases in which the available analgesics are unable to relieve the individual’s pain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albayrak, A., Polat, B., Cadirci, E., Hacimuftuoglu, A., Halici, Z., Gulapoglu, M., Albayrak, F., and Suleyman, H., Gastric anti-ulcerative and anti-inflammatory activity of metyrosine in rats. Pharmacol. Rep., 62, 113–119 (2010).
Bodnar, R. J., Sharpless, N. S., Kordower, J. H., Potegal, M., and Barr, G. A., Analgesic responses following adrenal demedullation and peripheral catecholamine depletion. Physiol. Behav., 29, 1105–1109 (1982).
Botting, R. M., Inhibitors of cyclooxygenases: mechanisms, selectivity and uses. J. Physiol. Pharmacol., 57Suppl 5, 113–124 (2006).
Burke, A., Smyth, E., and FitzGerald, G. A., Analgesicantipyretic agents; pharmacotherapy of gout. In Brunton, L. L. (Ed.), Goodman&Gilman’s The Pharmalogical Basis of Therapeutics. The McGraw-Hill Companies, USA, pp. 695–696, (2006).
Burtis, C. A. and Ashwood, E. R., Tietz textbook of clinical Chemistry, 3rd. W.B. Saunders Company, Phidelphia (1999).
Czyrak, A., Fijal, K., Mackowiak, M., Zajaczkowski, W., and Wedzony, K., Metyrapone, an inhibitor of corticosterone synthesis, blocks the kainic acid-induced expression of HSP 70. Synapse, 38, 144–150 (2000).
Filaretov, A. A., Bogdanov, A. I., and Yarushkina, N. I., Stress-induced analgesia. The role of hormones produced by the hypophyseal-adrenocortical system. Neurosci. Behav. Physiol., 26, 572–578 (1996).
Fukuda, T., Nishimoto, C., Miyabe, M., and Toyooka, H., Unilateral adrenalectomy attenuates hemorrhagic shock-induced analgesia in rats. J. Anesth., 21, 348–353 (2007).
Guay, J., Bateman, K., Gordon, R., Mancini, J., and Riendeau, D., Carrageenan-induced paw edema in rat elicits a predominant prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) response in the central nervous system associated with the induction of microsomal PGE2 synthase-1. J. Biol. Chem., 279, 24866–24872 (2004).
Guedj, D. and Weinberger, A., Effect of weather conditions on rheumatic patients. Ann. Rheum. Dis., 49, 158–159 (1990).
Hoffman, B. B., Theraphy of hypertension. In Brunton, L. L. (Ed.), Goodman Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. McGraw-Hill, New-York, pp. 845–897, (2006).
Howe, J. R., Wang, J. Y., and Yaksh, T. L., Selective antagonism of the antinociceptive effect of intrathecally applied alpha adrenergic agonists by intrathecal prazosin and intrathecal yohimbine. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 224, 552–558 (1983).
Ling, S. and Jamali, F., Effect of cannulation surgery and restraint stress on the plasma corticosterone concentration in the rat: application of an improved corticosterone HPLC assay. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci., 6, 246–251 (2003).
Livingston, A., Mechanism of action of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Vet. Clin. North Am. Small Anim. Pract., 30, 773–781 (2000).
Payan, D. G., Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs; Nonopioid Analgesics; Drugs Used in Gout. In Katzung, B. G. (Ed.), Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. Mc Graw-Hill, New-York, pp. 806–849, (2004).
Schoneshofer, M., Schefzig, B., and Arabin, S., Short-term kinetics of serum adrenal steroids and plasma ACTH after a single dose of metyrapone in man. J. Endocrinol. Invest., 3, 229–236 (1980).
Suleyman, H., Halici, Z., Cadirci, E., Hacimuftuoglu, A., Keles, S., and Gocer, F., Indirect role of alpha2-adrenoreceptors in anti-ulcer effect mechanism of nimesulide in rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol., 375, 189–198 (2007).
Suleyman, H., Halici, Z., Cadirci, E., Hacimuftuoglu, A., and Bilen, H., Indirect role of beta2-adrenergic receptors in the mechanism of anti-inflammatory action of NSAIDS. J. Physiol. Pharmacol., 59, 661–672 (2008).
Suleyman, H., Cadirci, E., Albayrak, A., Halici, Z., Polat, B., Hacimuftuoglu, A., and Alp, H. H., Reason for the aggravation of diseases caused by inflammation and the ineffectiveness of NSAIDs on these diseases in rainy weather. Pharmacol. Rep., 61, 514–519 (2009a).
Suleyman, H., Dursun, H., Bilici, M., Cadirci, E., Halici, Z., Gulaboglu, M., and Albayrak, F., Relation of adrenergic receptors, which have roles in gastroprotective and antiinflammatory effect of adrenal gland hormones, with cyclooxygenase enzyme levels in rats. J. Physiol. Pharmacol., 60, 129–134 (2009b).
Sutton, L. C., Fleshner, M., Mazzeo, R., Maier, S. F., and Watkins, L. R., A permissive role of corticosterone in an opioid form of stress-induced analgesia: blockade of opiate analgesia is not due to stress-induced hormone release. Brain Res., 663, 19–29 (1994).
Vane, J. and Botting, R., Inflammation and the mechanism of action of anti-inflammatory drugs. FASEB J., 1, 89–96 (1987).
Vane, J. R., Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis as a mechanism of action for aspirin-like drugs. Nat. New Biol., 231, 232–235 (1971).
Verges, J., Montell, E., Tomas, E., Cumelles, G., Castaneda, G., Marti, N., and Moller, I., Weather conditions can influence rheumatic diseases. Proc. West Pharmacol. Soc., 47, 134–136 (2004).
Yokoro, C. M., Tatsuo, M. A., Pereira, L. S., Alves, D. L., and Francischi, J. N., Role of endogenous glucocorticoids in hyperalgesia and edema in old arthritic rats. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res., 36, 77–83 (2003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Albayrak, Y., Saglam, M.B., Yildirim, K. et al. Effects of epinephrine and cortisol on the analgesic activity of metyrosine in rats. Arch. Pharm. Res. 34, 1519–1525 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-011-0914-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-011-0914-5