Abstract
Purpose
To assess the importance of the pituitary adrenal axis in producing stress-induced analgesia (SIA) after hemorrhagic shock, we performed formalin tests after hemorrhage and reinfusion in unilaterally adrenalectomized or sham-operated rats.
Methods
Fifty-two adult Sprague-Dawley rats were divided into seven groups: sham-operation normotensive (n = 8), sham-operation shock (n = 8), adrenalectomy normotensive (n = 7), adrenalectomy shock (n = 7), sham-operation shock + yohimbine (n = 7), sham-operation normotensive + corticosterone (n = 7), and adrenalectomy shock + corticosterone (n = 8). The left adrenal gland was cauterized 24 h before the experiment. The mean blood pressure in the shock groups was kept at 50–60 mmHg for 30 min by draining arterial blood. After the blood-reinfusion or observation period, 10% formalin was injected into the rear paw. Nociceptive behaviors and locomotion were observed and rated for 1 h, using the criteria of Dubuisson and Dennis. In 12 other sham-operated and adrenalectomized rats, plasma adrenalin, noradrenalin, and corticosterone concentrations were measured before and after hemorrhagic shock.
Results
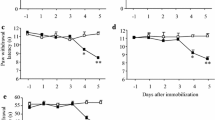
Although the sham-operation shock group showed a lower pain score, the adrenalectomy shock group showed nociceptive behavior similar to that in the normotensive groups. Yohimbine did not affect the SIA; however, corticosterone administration reversed the effects of the adrenalectomy on the SIA. The plasma corticosterone levels in the unilaterally adrenalectomized rats were lower than those in the sham-operated rats and did not increase after hemorrhagic shock.
Conclusion
These results suggest that adrenocortical systems play an important role in hemorrhagic shock-induced SIA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
HK Beecher (1946) ArticleTitlePain in man wounded in battle Ann Surg 123 96–105 Occurrence Handle17858731 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00000658-194601000-00008 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD2srktlyjsw%3D%3D
RJ Bodnar DD Kelly M Brutus M Glusman (1980) ArticleTitleStress-induced analgesia: neural and hormonal determinants Neurosci Biobehav Rev 4 87–100 Occurrence Handle6995874 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0149-7634(80)90028-7 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3cXkt1eiu7g%3D
GW Terman Y Shavit JW Lewis JT Cannon JC Liebeskind (1984) ArticleTitleIntrinsic mechanisms of pain inhibition: activation by stress Science 226 1270–1277 Occurrence Handle6505691 Occurrence Handle10.1126/science.6505691 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiqD28rnslY%3D
T Fukuda Nishimoto Ch M Miyabe H Toyooka (2001) ArticleTitleThe residual effects of hemorrhagic shock on pain reaction and c-fos expression in rats Anesth Analg 93 424–429 Occurrence Handle11473874 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00000539-200108000-00038 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3MvislSktQ%3D%3D
T Fukuda Ch Nishimoto H Toyooka (2005) ArticleTitleEffects of naloxone on stress-induced analgesia following hemorrhagic shock Reg Anesth Pain Med 30 339–343 Occurrence Handle16032585 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.rapm.2005.03.013 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXmsVOkurg%3D
S Mousa CH Miller D Couri (1981) ArticleTitleCorticosteroid modulation and stress-induced analgesia in rats Neuroendocrinology 33 317–319 Occurrence Handle7301053 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL38XhsFChug%3D%3D
RJ Bodnar NS Sharpless JH Kordower M Potegal GA Barr (1982) ArticleTitleAnalgesia responses following adrenal demedullation and peripheral catecholamine depletion Physiol Behav 29 1105–1109 Occurrence Handle6819590 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0031-9384(82)90305-5 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3sXislylsw%3D%3D
DD Kelly AJ Silverman M Glusman RJ Bodnar (1993) ArticleTitleCharacterization of pituitary mediation of stress-induced antinociception in rats Physiol Behav 53 769–775 Occurrence Handle8511184 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0031-9384(93)90187-K Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByyB1cfnt1M%3D
LC Sutton M Fleshner R Mazzeo SF Maier LR Watkins (1994) ArticleTitleA permissive role of corticosterone in an opioid form of stress-induced analgesia: blockade of opiate analgesia is not due to stress-induced hormone release Brain Res 663 19–29 Occurrence Handle7850467 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0006-8993(94)90458-8 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXitFOnsLw%3D
AA Filaretov AI Bogdanov NI Yarushkina (1996) ArticleTitleStress-induced analgesia. The role of hormones produced by the hypophyseal-adrenocortical system Neurosci Behav Physiol 26 572–578 Occurrence Handle9121636 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF02359502 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByiC2szovVc%3D
F Sierralta D Naquira G Pinardi HF Miranda (1996) ArticleTitleα-Adrenoceptor and opioid receptor modulation of clonidine-induced antinociception Br J Pharmacol 119 551–554 Occurrence Handle8894177 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XmtFyru7Y%3D
HB Lee MD Blaufox (1985) ArticleTitleBlood volume in the rat J Nucl Med 25 72–76
D Dubuisson SG Dennis (1977) ArticleTitleThe formalin test: a quantitative study of the analgesic effects of morphine, meperidine, and brain stem stimulation in rats and cats Pain 4 161–174 Occurrence Handle564014 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0304-3959(77)90130-0 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE1cXhsVGrt7s%3D
R Guillemin T Vargo J Rossier S Minick N Ling C Rivier W Vale F Bloom (1977) ArticleTitleβ-Endorphin and adrenocorticotropin are secreted concomitantly by the pituitary gland Science 197 1367–1369 Occurrence Handle197601 Occurrence Handle10.1126/science.197601 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE2sXlvVWnt7w%3D
AM Aloisi ME Albonetti M Muscettola F Facchinetti C Tanganelli G Carli (1995) ArticleTitleEffects of formalin-induced pain on ACTH, beta-endorphin, corticosterone and interleukin-6 plasma levels in rats Neuroendocrinology 62 13–18 Occurrence Handle7566433 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXnt1Sltb8%3D
BK Taylor SF Akana MA Peterson MF Dallman AI Basbaum (1998) ArticleTitlePituitary-adrenocortical responses to persistent noxious stimuli in the awake rat: endogenous corticosterone does not reduce nociception in the formalin test Endocrinology 139 2407–2413 Occurrence Handle9564852 Occurrence Handle10.1210/en.139.5.2407 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXivFShtbw%3D
TJ Coderre ME Fundytus JE McKenna S Dalal R Melzack (1993) ArticleTitleThe formalin test: a validation of the weighted-scores method of behavioural pain rating Pain 54 43–50 Occurrence Handle8378102 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0304-3959(93)90098-A Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByyA1M%2FpvVU%3D
FV Abott KBJ Franklin RF Westbrook (1995) ArticleTitleThe formalin test: scoring properties of the first and second phases of the pain response in rats Pain 60 91–102 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0304-3959(94)00095-V
M Jhanwar-Uniyal KJ Renner MT Bailo VN Luine SF Leibowitz (1989) ArticleTitleCorticosterone-dependent alterations in utilization of catecholamines in discrete areas of rat brain Brain Res 500 247–255 Occurrence Handle2605494 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0006-8993(89)90320-X Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3cXjtVOltA%3D%3D
G Telegdy I Vermes (1975) ArticleTitleEffect of adrenocortical hormones on activity of the serotoninergic system in limbic structures in rats Neuroendocrinology 18 16–26 Occurrence Handle1143627 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE2MXlsFygsrY%3D
A Cintra K Fuxe V Solfrini LF Agnati B Tinner AC Wikstrom W Staines S Okret JA Gustafsson (1991) ArticleTitleCentral peptidergic neurons as targets for glucocorticoid action. Evidence for the presence of glucocorticoid receptor immunoreactivity in various types of classes of peptidergic neurons J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 40 93–103 Occurrence Handle1683565 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0960-0760(91)90172-2 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XjsVOltA%3D%3D
BS McEwen ER DeKloet W Rostene (1986) ArticleTitleAdrenal steroid receptors and actions in the nervous system Physiol Rev 66 1121–1188 Occurrence Handle3532143 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2sXmsFI%3D
NI Iarushkina AI Bogdanov (1998) ArticleTitleThe role of corticosteroids in analgesic effect caused by stimulation of the periaqueductal gray matter of the midbrain in rats Ross Fiziol Zh Im I M Sechenova 84 642–650 Occurrence Handle9805776 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M%2Fit1Kiug%3D%3D
AA Filaretov AI Bogdanov NI Yarushkina (1990) ArticleTitleAntinociceptive effect of midbrain periaqueductal gray matter (PAG) stimulation and pituitary-adrenocortical system (PACS) Neuroendocrinol Lett 12 326
ZY Hu E Bourreau I Jung-Testas P Robel EE Baulieu (1987) ArticleTitleNeurosteroids: oligodendrocyte mitochondria convert cholesterol to pregnenolone Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84 8215–8219 Occurrence Handle3479785 Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.84.23.8215 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BieD28fls1A%3D
I Jung-Testas ZY Hu EE Baulieu P Robel (1989) ArticleTitleNeurosteroids: biosynthesis of pregnenolone and progesterone in primary cultures of rat glial cells Endocrinology 93 1157–1162
O Zinder DE Dar (1999) ArticleTitleNeuroactive steroids: their mechanism of action and their function in the stress response Acta Physiol Scand 167 181–188 Occurrence Handle10606819 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-201x.1999.00579.x Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXhslWlug%3D%3D
MD Majewska NL Harrison RD Schwartz JL Barker SM Paul (1986) ArticleTitleSteroid hormone metabolites are barbiturate-like modulators of the GABA receptor Science 232 1004–1007 Occurrence Handle2422758 Occurrence Handle10.1126/science.2422758 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL28XktVSqsr0%3D
ML Barbaccia G Roscetti M Trabucchi MC Mostallino A Concas RH Purdy G Biggio (1996) ArticleTitleTime-dependent changes in rat brain neuroactive steroid concentrations and GABAa receptor function after acute stress Neuroendocrinology 63 166–172 Occurrence Handle9053781 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XitVaitrg%3D
RH Purdy AL Morrow PH Moore SM Paul (1991) ArticleTitleStress-induced elevations of γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptor-active steroids in the rat brain Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88 4553–4557 Occurrence Handle1852011 Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.88.10.4553 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXkvVGqt7g%3D
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Fukuda, T., Nishimoto, C., Miyabe, M. et al. Unilateral adrenalectomy attenuates hemorrhagic shock-induced analgesia in rats. J Anesth 21, 348–353 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-007-0521-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-007-0521-2