Abstract
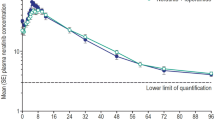
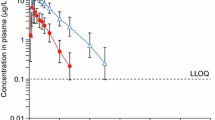
The present study aims to investigate the effects of prednisolone on the pharmacokinetics of orally and intravenously administered loratadine in rats. A single dose of loratadine was administered orally (4 mg/kg) and intravenously (1 mg/kg) in the presence or absence of prednisolone (0.2 or 0.8 mg/kg). Compared to the oral control group, prednisolone (0.2 mg/kg, p < 0.05; 0.8 mg/kg, p < 0.01) significantly increased the area under the plasma concentrationtime curve of orally administered loratadine by 54.0–96.4%. After oral administration, the peak plasma concentration of loratadine was significantly (0.2 mg/kg, p < 0.05; 0.8 mg/kg, p < 0.01) increased by 20.9–65.3% in the presence of prednisolone. Consequently, the relative bioavailability of loratadine was increased by 1.54- to 1.96-fold. Compared to the intravenous control group, the presence of prednisolone significantly (0.8 mg/kg, p < 0.05) increased the area under the plasma concentration-time curve of loratadine. Prednisolone enhanced the oral bioavailability of loratadine in this study. The enhanced bioavailability of loratadine may be due to inhibition both cytochrome P450 3A4-mediated metabolism and the efflux pump P-glycoprotein (P-gp) in the intestine and/or liver by the presence of prednisolone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amini, H. and Ahmadiani, A., Rapid determination of loratadine in small volume plasma samples by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci., 809, 227–230 (2004).
Bradley, C. M. and Nicholson, A. N., Studies on the central effects of the H1-antagonist, loratadine. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol., 32, 419–421 (1987).
Carr, R. A., Edmonds, A., Shi, H., Locke, C. S., Gustavson, L. E., Craft, J. C., Harris, S. I., and Palmer, R., Steady-state pharmacokinetics and electrocardiographic pharmacodynamics of clarithromycin and loratadine after individual or concomitant administration. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 42, 1176–1180 (1998).
Clissold, S. P., Sorkin, E. M., and Goa, K. L., Loratadine, a preliminary review of its pharmacodynamic properties and therapeutic efficacy. Drugs, 37, 42–57 (1989).
Cummins, C. L., Jacobsen, W., and Benet, L. Z., Unmasking the dynamic interplay between intestinal P-glycoprotein and CYP3A4. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 300, 1036–1045 (2002).
Frey, B. M. and Frey, F. J., Clinical pharmacokinetics of prednisone and prednisolone. Clin. Pharmacokinet., 19, 126–146 (1990).
Frey, F. J. and Frey, B. M., Urinary 6b-hydroxyprednisolone excretion indicates enhanced prednisolone catabolism. J. Lab. Clin. Med., 101, 593–604 (1983).
Henz, B. M., The pharmacologic profile of desloratadine: a review. Allergy, 56Suppl 65, 7–13 (2001).
Hilbert, J., Radwanski, E., Weglein, R., Luc, V., Perentesis, G., Symchowicz, S., and Zampaglione, N., Pharmacokinetics and dose proportionality of loratadine. J. Clin. Pharmacol., 27, 694–698 (1987).
Ito, K., Kusuhara, H., and Sugiyama, Y., Effects of intestinal CYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein on oral drug absorption; theoretical approach. Pharm. Res., 16, 225–231 (1999).
Kaminsky, L. S. and Fasco, M. J., Small intestinal cytochromes P450. Crit. Rev. Toxocol., 21, 407–422 (1991).
Karssen, A. M., Meijer, O. C., van der Sandt, I. C., De Boer, A. G., De Lange, E. C., and De Kloet, E. R., The role of the efflux transporter P-glycoprotein in brain penetration of prednisolone. J. Endocrinol., 175, 251–260 (2002).
Kay, G. G., Berman, B., Mockoviak, S. H., Morris, C. E., Reeves, D., Starbuck, V., Su-kenik, E., and Harris, A. G., Initial and steady-state effects of diphenhydramine and loratadine on sedation, cognition, mood, and psychomotor performance. Arch. Intern. Med., 157, 2350–2356 (1997).
Kosoglou, T., Salfi, M., Lim, J. M., Batra, V. K., Cayen, M. N., and Affrime, M. B., Evaluation of the pharmacokinetics and electrocardiographic pharmacodynamics of loratadine with concomitant administration of ketoconazole or cimetidine. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol., 50, 581–589 (2000).
Kreutner, W., Hey, J. A., Anthes, J., Barnett, A., Young, S., and Tozzi, S., Preclinical pharmacology of desloratadine, a selective and nonsedating histamine H1 receptor antagonist. 1st communication: Receptor selectivity, antihistaminic activity, and antiallergenic effects. Arzneimittelforschung, 50, 345–352 (2000).
Madsbad, S., Bjerregaard, B., Henriksen, J. H., Juhl, E., and Kehlet, H., Impaired conversion of prednisone to prednisolone in patients with liver cirrhosis. Gut, 21, 52–56 (1980).
Nakayama, A., Eguchi, O., Hatakeyama, M., Saitoh, H., and Takada, M., Different absorption behaviors among steroid hormones due to possible interaction with P-glycoprotein in the rat small intestine. Biol. Pharm. Bull., 22, 535–538 (1999).
Philpot, E. E., Safety of second generation antihistamines. Allergy Asthma Proc., 21, 15–19 (2000).
Pichard, L., Gillet, G., Fabre, I., Dalet-Beluche, I., Bonfils, C., Thenot, J. P., and Maurel, P., Identification of the rabbit and human cytochromes P-450IIIA as the major enzymes involved in the N-demethylation of diltiazem. Drug Metab. Dispos., 18, 711–719 (1990).
Pichard, L., Fabre, I., Daujat, M., Domergue, J., Joyeux, H., and Maurel, P., Effect of corticosteroids on the expression of cytochromes P450 and on cyclosporin A oxidase activity in primary cultures of human hepatocytes. Mol. Pharmacol., 41, 1047–1055 (1992).
Prenner, B. M., Capano, D., and Harris, A. G., Efficacy and tolerability of loratadine versus fexofenadine in the treatment of seasonal allergic rhinitis: A-double-blind comparison with crossover treatment of nonresponders. Clin. Ther., 22, 760–769 (2000).
Ramaekers, J. G., Uiterwijk, M. M., and O’Hanlon, J. F., Effects of loratadine and cetirizine on actual driving and psychometric test performance, and EEG during driving. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol., 42, 363–369 (1992).
Wacher, V. J., Silverman, J. A., Zhang, Y., and Benet, L. Z., Role of P-glycoprotein and cytochrome P450 3A in limiting oral absorption of peptides and peptidomimetics. J. Pharm. Sci., 87, 1322–1330 (1998).
Wang, E. J., Casciano, C. N., Clement, R. P., and Johnson, W. W., Evaluation of the interaction of loratadine and desloratadine with P-glycoprotein. Drug Metab. Dispos., 29, 1080–1083 (2001).
Waxman, D. J., Attisano, C., Guengerich, F. P., and Lapenson, D. P., Human liver microsomal steroid metabolism: identification of the major microsomal steroid hormone 6bhydroxylase cyto-chrome P-450 enzyme. Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 263, 424–436 (1988).
Wolozin, B., Kellman, W., Ruosseau, P., Celesia, G. G., and Siegel, G., Decreased prevalence of Alzheimer disease associated with 3-hydroxy-3-methyglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitors. Arch. Neurol., 10, 1439–1443 (2000).
Yates, C. R., Chang, C., Kearbey, J. D., Yasuda, K., Schuetz, E. G., Miller, D. D., Dalton, J. T., and Swaan, P. W., Structural determinants of P-glycoprotein-mediated transport of glucocorticoids. Pharm Res., 20, 1794–1803 (2003).
Yin, O. Q., Shi, X., and Chow, M. S., Reliable and specific high-performance liquid chromatographic method for simultaneous determination of loratadine and its metabolite in human plasma. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci., 796, 165–172 (2003).
Yumibe, N., Huie, K., Chen, K. J., Snow, M., Clement, R. P., and Cayen, M. N., Identification of human liver cytochrome P450 enzymes that metabolize the nonsedating antihistamine loratadine. Formation of descarboethoxyloratadine by CYP3A4 and CYP2D6. Biochem. Pharmacol., 51, 165–172 (1996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, C., Kim, M. & Choi, JS. Effects of prednisolone on the pharmacokinetics of loratadine after oral and intravenous administration of loratadine in rats. Arch. Pharm. Res. 33, 1395–1400 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-010-0913-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-010-0913-y