Abstract
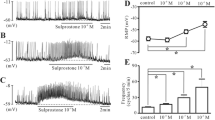
The aim of this study was to clarify if phentolamine has proven effects on the pacemaker activities of interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC) from the mouse small intestine involving the ATPsensitive K+ channels and adrenergic receptor. The actions of phentolamine on pacemaker activities were investigated using whole-cell patch-clamp technique and intracellular Ca2+ analysis at 30°C in cultured mouse intestinal ICC. ICC generated spontaneous pacemaker currents at a holding potential of −70 mV. Treatment with phentolamine reduced the frequency and amplitude of the pacemaker currents and increased the resting outward currents. Moreover, under current clamping (I = 0), phentolamine hyperpolarized the ICC membrane and decreased the amplitude of the pacemaker potentials. We also observed that phentolamine inhibited spontaneous [Ca2+]i oscillations in ICC. The alpha-adrenergic drugs prazosin, yohimbine, methoxamine, and clonidine had no effect on ICC intestinal pacemaker activity and did not block phentolamine-induced effects. Phentolamine-induced effects on the pacemaker currents and the pacemaker potentials were significantly inhibited by ATP sensitive K+ channel blocker glibenclamide, but not by TEA, apamin, or 4-aminopyridine. In addition, the NO synthase inhibitor, L-NAME and the guanylate cyclase inhibitor, ODQ were incapable of blocking the phentolamine-induced effects. These results demonstrate that phentolamine regulates the pacemaker activity of ICC via ATP-sensitive K+ channel activation. Phentolamine could act through an adrenergic receptor- and also through NO-independent mechanism that involves intracellular Ca2+ signaling.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brayden, J. E., Clinical roles of KATP channels in vascular smooth muscle. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol., 29, 312–316 (2002).
Choi, S., Chang, I. Y., Yeum, C. H., You, H. J., Park, J. S., Jeong, H. S., So, I., Kim, K. W., and Jun, J. Y., Activating of ATP-dependent K+ channels comprised of Kir 6.2 and SUR2B by PGE2 through EP2 receptor in cultured interstitial cells of Cajal from murine small intestine. Cell. Physiol. Biochem., 18, 187–198 (2006).
Deka, D. K. and Brading, A. F., Nitric oxide activates glibenclamide-sensitive K+ channels in urinary bladder myocytes through a c-GMP-dependent mechanism. Eur. J. Pharmacol., 492, 13–19 (2004).
Dunne, M. J., Block of ATP-regulated potassium channels by phentolamine and other alpha-adrenoceptor antagonists. Br. J. Pharmacol., 103, 1847–1850 (1991).
Epperson, A., Hatton, W. J., Callaghan, B., Doherty, P., Walker, R. L., Sanders, K. M., Ward, S. M., and Horowitz, B., Molecular components expressed in cultured and freshly isolated interstitial cells of Cajal. Am. J. Physiol., Cell Physiol., 279, C529–C539 (2000).
Hoffmann, B. B. and Lefkowitz, R. J., The pharmacological basis of therapeutics. Pergamon Press, New York, Chapter 10, (1991).
Hoy, M., Bokvist, K., Xiao-Gang, W., Hansen, J., Juhl, K., Berggren, P. O., Buschard, K., and Gromada, J., Phentolamine inhibits exocytosis of glucagons by Gi2 proteindependent activation of calcineurin in rat pancreatic α-cells. J. Biol. Chem., 276, 924–930 (2001).
Huizinga, J. D., Thunberg, L., Kluppel, M., Malysz, J., Mikkelsen, H. B., and Bernstein, A., W/kit gene required for interstitial cells of Cajal for intestinal pacemaker activity. Nature, 373, 347–349 (1995).
Jonas, J. C., Plant, T. D., and Henquin, J. C., Imidazoline antagonists of α2-adrenoceptors increase insulin release in vitro by inhibiting ATP-sensitive K+ channels in pancreatic β-cells. Br. J. Pharmacol., 107, 8–14 (1992).
Jun, J. Y., Kong, I. D., Koh, S. D., Wang, X. U., Perrino, B. A., Ward, S. M., and Sanders, K. M., Regulation of ATP-sensitive K+ channels by protein kinase C in murine colonic myocytes. Am. J. Physiol., Cell Physiol., 281, C857–C864 (2001).
Jun, J. Y., Choi, S., Yeum, C. H., Chang, I. Y., Park, C. K., Kim, M. Y., Kong, I. D., So, I., Kim, K. W., and You, H. J., Noradrenaline inhibits pacemaker currents through stimulation of beta 1-drenoceptors in cultured interstitial cells of Cajal from murine small intestine. Br. J. Pharmacol., 141, 670–677 (2004).
Jun, J. Y., Choi, S., Chang, I. Y., Yoon, C. K., Jeong, H. G., Kong, I. D., So, I., Kim, K. W., and You, H. J., Deoxycholic acid inhibits pacemaker currents by activating ATP-dependent K+ channels through prostaglandin E2 in interstitial cells of Cajal from the murine small intestine. Br. J. Pharmacol., 144, 242–251 (2005).
Kito, Y., Ward, S. M., and Sanders, K. M., Pacemaker potentials generated by interstitial cells of Cajal in the murine intestine. Am. J. Physiol., 288, C710–C720 (2005).
Kubo, M., Quayle, J. M., and Standen, N. B., Angiotensin II inhibition of ATP-sensitive K+ currents in rat arterial smooth muscle cells through protein kinase C. J. Physiol., 503, 489–496 (1997).
Mannhold, R., KATP channel openers: Structure-activity relationships and therapeutic potential. Med. Res. Rev., 24, 213–266 (2004).
Murphy, M. E. and Brayden, J. E., Nitric oxide hyperpolarizes rabbit mesenteric arteries via ATP-sensitive potassium channels. J. Physiol., 486, 47–58 (1995).
Park, C. G., Kim, M. Y., Kim, J. S., Choi, S., Yeum, C. H., Parajuli, S. P., Park, J. S., Jeong, H. S., So, I., Kim, K. W., and Jun, J. Y., Inhibition of pacemaker currents by nitric oxide via activation of ATP-sensitive K+ channels in cultured interstitial cells of Cajal from mouse small intestine. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol., 376, 175–184 (2007).
Plant, T. D. and Henquin, J. C., Phentolamine and yohimbine inhibit ATP-sensitive K+ channels in mouse pancreatic β-cells. Br. J. Pharmacol., 101, 115–120 (1990).
Plant, T. D., Jonas, J. C., and Henquin, J. C., Clonidine inhibits ATP-sensitive K+ channels in mouse pancreatic β-cells. Br. J. Pharmacol., 104, 385–390 (1991).
Proks, P. and Ashcroft, F. M., Phentolamine block of KATP channels is mediated by Kir 6.2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 94, 11716–11720 (1997).
Quayle, J. M., Bonev, A. D., Brayden, J. E., and Nelson, M. T., Calcitonin gene-related peptide activated ATP-sensitive K+ currents in rabbit arterial smooth muscle via protein kinase A. J. Physiol., 475, 9–13 (1994).
Rodrigo, G. C. and Standen, N. G., ATP-sensitive potassium channels. Curr. Pharm. Des., 11, 1915–1940 (2005).
Rustenbeck, I., Kowalewski, R., Herrmann, C., Dickel, C., Ratzka, P., and Hasselblatt, A., Effects of imidazoline compounds on cytoplasmic Ca2+ concentration and ATPsensitive K+ channels in pancreatic β-cells. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes, 103, 42–45 (1995.).
Sanders, K. M., Koh, S. D., and Ward, S. M., Interstitial cells of Cajal as pacemakers in the gastrointestinal tract. Annu. Rev. Physiol., 68, 307–343 (2006).
Schwietert, R., Wilhelm, D., Wilffert, B., and Van Zwieten, P. A., The effect of some alpha-adrenoceptor antagonists on spontaneous myogenic activity in the rat portal vein and the putative involvement of ATP-sensitive K+ channels. Eur. J. Pharmacol., 211, 87–95 (1992).
Shepherd, R. M., Hashmi, M. N., Kane C., Squires, P. E., and Dunne, M. J., Elevation of cytosolic calcium by imidazolines in mouse islets of Langerhans: implications for stimulus-response coupling of insulin release. Br. J. Pharmacol., 119, 911–916 (1996).
Silva, L. F. G., Nascimento, N. R., Fonteles, M. C., de Nucci, G., Moraes, M. E., Vasconcelos, P. R., and Moraes, M. O., Phentolamine relaxes human corpus cavernosum by a nonadrenergic mechanism activating ATP-sensitive K+ channel. Int. J. Impot. Res., 17, 27–32 (2005).
Small, R. C., Berry, J. L., and Foster, R. W., Potassium channel opening drugs and the airways. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res., 25, 983–998 (1992).
Suzuki, H., Takano, H., Yamamoto, Y., Komuro, T., Saito, M., Kato, K., and Mikoshiba, K., Properties of gastric smooth muscles obtained from mice which lack inositol triphosphate receptor. J. Physiol., 525, 105–111 (2000).
Vemulapalli, S. and Kurowski, S., Phentolamine mesylate relaxes rabbit corpus cavernosum by a nonadrenergic, noncholinergic mechanism. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol., 15, 1–7 (2001).
Ward, S. M., Burns, A. J., Torihashi, S., and Sanders, K. M., Mutation of the proto-oncogene c-kit blocks development of interstitial cells and electrical rhythmicity in murine intestine. J. Physiol., 480, 91–97 (1994).
Ward, S. M. and Sanders, K. M., Involvement of intramus cular interstitial cells of Cajal in neuroeffector transmission in the gastrointestinal tract. J. Physiol., 576, 675–682 (2006).
Wilde, A. A., Veldkamp, M. W., van Ginneken, A. C., and Opthof, T., Phentolamine blocks ATP sensitive potassium channels in cardiac ventricular cells. Cardiovasc. Res., 28, 847–850 (1994).
Zhang, L., Bonev, A. D., Mawe, G. M., and Nelson, M. T., Protein kinase A mediates activation of ATP-sensitive K+ currents by CGRP in gallbladder smooth muscle. Am. J. Physiol., 267, G494–G499 (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahn, S.W., Kim, S.H., Kim, J.H. et al. Phentolamine inhibits the pacemaker activity of mouse interstitial cells of Cajal by activating ATP-sensitive K+ channels. Arch. Pharm. Res. 33, 479–489 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-010-0319-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-010-0319-x