Abstract
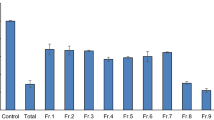
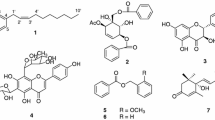
Fourteen diterpenes were isolated from the n-hexane fraction of the roots of Aralia cordata (syn. = A. continentalis). Through spectroscopy, the chemical structures were determined as: ent-pimara-8(14),15-diene-19-oic acid (1); ent-kaur-16-en-19-oic-acid (2); 18-nor-ent-pimara-8(14),15-diene-4β-ol (3); 18-nor-ent-kaur-16-ene-4β-ol (4); ent-pimara-8(14),15-diene-19-ol (5); 7α-hydroxy-ent-pimara-8(14),15-diene-19-oic acid (6); 7β-hydroxy-ent-pimara-8(14),15-diene-19-oic acid (7); ent-pimar-15-en-8α,19-diol (8); 7-oxo-ent-pimara-8(14),15-diene-19-oic acid (9); 16α-hydroxy-17-isovaleroyloxy-ent-kauran-19-oic acid (10); 17-hydroxy-ent-kaur-15-en-19-oic acid (11); 15α,16α-epoxy-17-hydroxy-ent-kauran-19-oic acid (12); 16α,17-dihydroxy-ent-kauran-19-oic acid (13); and 16α-methoxy-17-hydroxy-ent-kauran-19-oic acid (14). Compounds 4, 5, 8, 12, and 14 were first isolated from this plant. The anti-Alzheimer and antioxidant effects of ent-pimarane-type diterpenes 1, 3, 5, 8, and 9, as well as ent-kaurane-type diterpenes 2, 4, and 10∼13, were evaluated via β-site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme 1 (BACE1), acetylcholinesterase (AChE), butyrylcholinesterase (BChE), peroxynitrite (ONOO−), and nitric oxide (NO·) assays. Of the compounds tested, 8 exerted the most effective BChE inhibition with an IC50 value of 7.58 µM, followed by 3, 13, 11, 2, and 10. Compounds 9∼11 exhibited good BACE1 inhibitory activities with IC50 values of 18.58∼24.10 µM. However, 11 showed marginal AChE inhibitory effect, and all compounds tested showed no scavenging activities on ONOO− and NO· at a concentration of 100 µM.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambrosio, S. R., Furtado, N. A., de Oliveira, D. C., da Costa, F. B., Martins, C. H., de Carvalho, T. C., Porto, T. S., and Veneziani, R. C., Antimicrobial activity of kaurane diterpenes against oral pathogens. Z. Naturforsch. [C], 63, 326–330 (2008).
Ambrosio, S. R., Tirapelli, C. R., da Costa, F. B., and de Oliveira, A. M., Kaurane and pimarane-type diterpenes from the Viguiera species inhibit vascular smooth muscle contractility. Life Sci., 79, 925–933 (2006).
Bae, K. W., Medicinal Plants of Korea, Kyohak Publishing Co. Ltd., Seoul, p. 363 (2000).
Bohlmann, F., Suding, H., Cuatrecasas, J., King, R. M., and Robinson, H., Neue diterpene aus der subtribus espeletiinae. Phytochemistry, 19, 267–271 (1980).
Dang, N. H., Zhang, X., Zheng, M., Son, K. H., Chang, H. W., Kim, H. P., Bae, K., and Kang, S. S., Inhibitory constituents against cyclooxygenases from Aralia cordata Thunb. Arch. Pharm. Res., 28, 28–33 (2005).
Ellman, G. L., Courtney, K. D., Andres, V. Jr., and Featherstone, R. M., A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholineserase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol., 7, 88–95 (1961).
Ertaş, A., Öztürk, M., Boða, M., and Topçu, G., Antioxidant and anticholinesterase activity evaluation of ent-kaurane diterpenoids from Sideritis arguta (perpendicular). J. Nat. Prod., 72, 500–502 (2009).
Han, B. H., Han, Y. N., Han, K. A., Park, M. H., and Lee, E. O., Studies on the anti-inflammatory activity of Aralia continentalis (I). Characterization of continentalic acid and its anti-inflammatory activity. Arch. Pharm. Res., 6, 17–23 (1983).
Han, B. H., Woo, E. R., Park, M. H., and Han, Y. N., Studies on the anti-inflammatory activity of Aralia continentalis (III). Anti-inflammatory activity of (−)-kaur-16-en-19-oic acid. Arch. Pharm. Res., 8, 59–65 (1985).
Herz, W., Kulanthaivel, P., and Watanabe, K., ent-Kauranes and other constituents of three Helianthus species, Phytochemistry, 22, 2021–2025 (1983).
Jeong, S. I., Han, W. S., Yun, Y. H., and Kim, K. J., Continentalic acid from Aralia continentalis shows activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Phytother. Res., 20, 511–514 (2006).
Kang, S. S., Chemistry and biological activity of the constituents from Aralia species. Ann. Rept. Nat. Prod. Sci., 5, 1–26 (1997).
Kim, J. Y., Jung, K. J., Choi, J. S., and Chung, H. Y., Hesperetin: a potent antioxidant against peroxynitrite. Free Radic. Res., 38, 761–769 (2004).
Kim, S., Na, M., Oh, H., Jang, J., Sohn, C. B., Kim, B. Y., Oh, W. K., and Ahn, J. S., PTP1B inhibitory activity of kaurane diterpenes isolated from Siegesbeckia glabrescens. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem., 21, 379–383 (2006).
Ko, H. H., Chang, W. -L., and Lu, T. -M., Antityrosinase and antioxidant effects of ent-kaurane diterpenes from leaves of Broussonetia papyrifera. J. Nat. Prod., 71, 1930–1933 (2008).
Kooy, N. W., Royall, J. A., Ischiropoulos, H., and Beckman, J. S., Peroxynitrite-mediated oxidation of dihydrorhodamine 123. Free Radic. Biol. Med., 16, 149–156 (1994).
Lee, I. S., Jin, W., Zhang, X., Hung, T. M., Song, K. S., Seong, Y. H., and Bae, K., Cytotoxic and COX-2 inhibitory constituents from the aerial parts of Aralia cordata. Arch. Pharm. Res., 29, 548–555 (2006).
Lee, W. T., Lineamenta Flora Koreae, Academy, Seoul, pp. 771–772 (1996).
Lee, Y. N., Flora of Korea, Kyohak Publishing Co. Ltd., Seoul, p. 541 (2002).
Matsuo, A., Uto, S., Nakayama, M., Hayashi, S., Yamasaki, K., Kasai, R., and Tanaka, O., (−)-Thermarol, a new entpimarane-class diterpene diol from Jungermannia thermarum (Liverwort). Tetrahedron Lett., 2451–2454 (1976).
Mihashi, S., Yanagisawa, I., Tanaka, O., and Shibata, S., Further study on the diterpenes of Aralia spp. Tetrahedron Lett., 1683–1686 (1969).
Na, M., Oh, W. K., Kim, Y. H., Cai, X. F., Kim, S., Kim, B. Y., and Ahn, J. S., Inhibition of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B by diterpenoids isolated from Acanthopanax koreanum. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 16, 3061–3064 (2006).
Nakazawa, Y., Hamada, C., Ishino, A., Tajima, M., and Fujimoto, Y., Hair preparation and skin prepartions containing kaurene derivatives. Jpn. Kokai Tokkyo Koho, JP 2002037716 (2002).
Okuyama, E., Nishimura, S., and Yamazaki, M., Analgesic principles from Aralia cordata THUNB. Chem. Pharm. Bull., 39, 405–407 (1991).
Perry, L. M., Medicinal Plants of East and Southeast Asia: Attributed Properties and Uses, The MIT press, Cambridge, p. 41 (1980).
Porto, T. S., Rangel, R., Furtado, N. A., de Carvalho, T. C., Martins, C. H., Veneziani, R. C., Da Costa, F. B., Vinholis, A. H., Cunha, W. R., Heleno, V. C., and Ambrosio, S. R., Pimarane-type diterpenes: antimicrobial activity against oral pathogens. Molecules, 14, 191–199 (2009).
Rao, A. A., Sridhar, G. R., and Das, U. N., Elevated butyrylcholinesterase and acetylcholinesterase may predict the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus and Alzheimer’s disease. Med. Hypotheses, 69, 1272–1276 (2007).
Ryu, S. Y., Ahn, J. W., Han, Y. N., Han, B. H., and Kim, S. H., In vitro antitumor activity of diterpenes from Aralia cordata. Arch. Pharm. Res., 19, 77–78 (1996).
Seo, C. S., Li, G., Kim, C. H., Lee, C. S., Jahng, Y., Chang, H. W., and Son, J. K., Cytotoxic and DNA topoisomerases I and II inhibitory constituents from the roots of Aralia cordata. Arch. Pharm. Res., 30, 1404–1409 (2007).
Shibata, S., Mihashi, S., and Tanaka, O., The occurrence of (−)pimarane-type diterpene in Aralia cordata THUNB. Tetrahedron Lett., 51, 5241–5243 (1967).
Tanaka, O., Mihashi, S., Yanagisawa, I., Nikaido, T., and Shibata, S., Chemical studies of oriental plant drugs. XXXIV. Diterpenes of Aralia cordata. Oxidative transformation of 4-axial aldehyde of some diterpenes and a note to the naturally occurring 4-hydroxy-18(or 19)-norditerpenes. Tetrahedron, 28, 4523–4537 (1972).
Thirugnanasampandan, R., Jayakumar, R., Narmatha Bai, V., Martin, E., and Rajendra Prasad, K. J., Antiacetylcholinesterase and antioxidant ent-kaurene diterpenoid, melissoidesin from Isodon wightii (Bentham) H. Hara. Nat. Prod. Res., 22, 681–688 (2008).
Tirapelli, C. R., Ambrosio, S. R., Coutinho, S. T., de Oliveira, D. C., da Costa, F. B., and de Oliveira, A. M., Pharmacological comparison of the vasorelaxant action displayed by kaurenoic acid and pimaradienoic acid. J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 57, 997–1004 (2005).
Vassar, R., β-Secretase (BACE) as a drug target for alzheimer’s disease. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev., 54, 1589–1602 (2002).
Wu, Y. C., Hung, Y. C., Chang, F. R., Cosentino, M., Wang, H. K., and Lee, K. H., Identification of ent-16β,17-dihydroxykauran-19-oic acid as an anti-HIV principle and isolation of the new diterpenoids annosquamosins A and B from Annona squamosa. J. Nat. Prod., 59, 635–637 (1996).
Yahara, S., Ishida, M., Yamasaki, K., Tanaka, O., and Mihashi, S., Minor diterpenes of Aralia cordata THUNB: 17-Hydroxy-ent-kaur-15-en-19-oic acid and grandifloric acid. Chem. Pharm. Bull., 22, 1629–1631 (1974).
Yan, R., Bienkowski, M. J., Shuck, M. E., Miao, H., Tory, M. C., Pauley, A. M., Brashier, J. R., Stratman, N. C., Mathews, W. R., Buhl, A. E., Carter, D. B., Tomasselli, A. G.., Parodi, L. A., Heinrikson, R. L., and Gurney, M. E., Membrane-anchored aspartyl protease with Alzheimer’s disease β-secretase activity. Nature, 402, 533–537 (1999).
Zhang, Y. M., Yang, J. S., and Xu, X. D., A new kaurane derivative from Aralia fargesii. Chin. Chem. Lett., 10, 673–674 (1999).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jung, H.A., Lee, E.J., Kim, J.S. et al. Cholinesterase and BACE1 inhibitory diterpenoids from Aralia cordata . Arch. Pharm. Res. 32, 1399–1408 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-009-2009-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-009-2009-0