Abstract
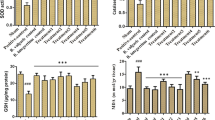
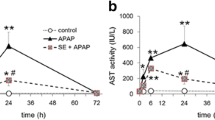
The present study has been conducted to evaluate the curative effect of propolis extract, a honey bee-hive product, against acetaminophen (APAP) induced oxidative stress and dysfunction in liver and kidney. Animals were challenged with APAP (2 g/kg, p.o.) followed by treatment of propolis extract (100 and 200 mg/kg, p.o.) once only after 24 h. Release of transaminases, alkaline phosphatase, lactate dehydrogenase, and serum bilirubin were increased, whereas hemoglobin and blood sugar were decreased after APAP administration. Antioxidant status in both the liver and kidney tissues were estimated by determining the glutathione, malondialdehyde content and activities of the CYP enzymes, which showed significant alterations after APAP intoxication. In addition, activities of adenosine triphosphatase, acid phosphatase, alkaline phosphatase, and major cell contents (total protein, glycogen and cholesterol) were also altered due to APAP poisoning. Propolis extract successfully reversed the alterations of these biochemical variables at higher dose. Improvements in hepatorenal histoarchitecture were also consistent with biochemical observations. The results indicated that ethanolic extract of propolis has ability to reverse APAP-induced hepatorenal biochemical and histopathological alterations probably by increasing the antioxidative defense activities due to various phenolic compounds present in it.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asatoor, A. M., and King, E., Simplified colorimetric blood sugar method. Process. Biochem., (325 Meeting) 56, xliv (1954).
Aso, K., Kanno, G., Tadano, T., Satoh, S., and Ishikawa, M., Inhibitory effect of propolis on the growth of human leukemia U937. Biol. Pharm. Bull., 27, 727–730 (2004).
Banerjee, A., Linscheer, W. G., Chiji, H., Murthy, U. K., Cho, C., Nandi, J., and Chan, S. H., Induction of an ATPase inhibitor protein by propylthiouracil and protection against paracetamol (acetaminophen) hepatotoxicity in the rat. Br. J. Pharmacol., 124, 1041–1047 (1998).
Bhadauria, M., Nirala, S. K., and Shukla, S., Propolis protects CYP2E1 enzymatic activities and oxidative stress induced by carbon tetrachloride. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 302, 215–224 (2007a).
Bhadauria, M., Nirala, S. K., and Shukla, S., Duration dependent hepatoprotective effect of propolis extract against carbon tetrachloride induced acute damage in rats. Adv. Ther., 24, 1134–1143 (2007b).
Boyanova, L., Gergova, G., Nikolov, R., Derejian, S., Lazarova, E., Katsarov, N., Mitov, I., and Krastev, Z., Activity of Bulgarian propolis against 94 Helicobacter pylori strains in vitro by agar-well diffusion, agar dilution and disc diffusion methods. J. Med. Microbiol., 54, 481–483 (2005).
Bratter, C., Tregel, M., Liebenthal, C., and Volk, H. D., Prophylactic effectiveness of propolis for immunostimulation: a clinical pilot study. Forsch Komplementarmed., 6, 256–260 (1999).
Breger, J., Fuchs, B. B., Aperis, G., Moy, T. I., Ausubel, F. M., and Mylonakis, E., Antifungal chemical compounds identified using a C. elegans pathogenicity assay. PLoS Pathogens, 3, 168–177 (2007).
Brehe, J. E. and Burch, H. B., Enzymatic assay for glutathione. Anal. Biochem., 74, 189–197 (1976).
Chattopadhyay, R. R., Sarkar, S. K., Ganguly, S., Madda, C., and Baru, T. K., Hepatoprotective activity of Ocimum sanctum leaf extract against paracetamol induced hepatic damage in rats. Indian J. Pharmacol., 24, 163–165 (1992).
Chen, W., Shockcor, J. P., Tonge, R., Hunter, A., Gartner, C., and Nelson, S. D., Protein and nonprotein cysteinyl thiol modification by N-acetyl-p-benzoquinoneimine via a novel ipso adduct. Biochem., 38, 8159–8166 (1999).
Claus, R., Kinscherf, R., Gehrke, C., Bonaterra, G., Basnet, P., Metz, J., and Deigner, H. P., Antiapoptotic effect of propolis extract and propol on human macrophages exposed to minimally modified low density lipoprotein. Arzneimittelforschung, 50, 373–379 (2000).
Cochin, J. and Axelrod, J., Biochemical Pharmacological changes in the rats following chronic administration of morphine. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 125, 105–110 (1959).
Cohen, S. D., Pumford, N. R., Khairallah, E. A., Boekelheide, K., Pohl, L. R., Amouzadeh, H. R., and Hinson, J. A., Selective protein covalent binding and target organ toxicity. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol., 143, 1–12 (1997).
Dantas, A. P., Salomao, K., Barbosa, H. S., and De Castro, S. L., The effect of Bulgarian propolis against Trypanosoma cruzi and during its interaction with host cells. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro., 101, 207–211 (2006).
Davis, M., Ideo, G., Harrison, N. G., and Williams, R., Early inhibition of hepatic bilirubin conjugation after paracetamol (acetaminophen) administration in the rat. Digestion, 13, 42–48 (1975).
de Campos, R. O., Paulino, N., da Silva, C. H., Scremin, A., and Calixto J. B., Anti-hyperalgesic effect of an ethanolic extract of propolis in mice and rats. Pharm. Pharmacol., 50, 1187–1193 (1998).
Donnelly, P. J., Walker, R. M., and Racz, W. J., Inhibition of mitochondrial respiration in vivo is an early event in acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. Arch. Toxicol., 68, 110–118 (1994).
El-Ghazaly, M. A. and Khayyal, M. T., The use of aqueous propolis extract against radiation-induced damage. Drugs Exp. Clin. Res., 21, 229–236 (1995).
Gumbrecht, J. R. and Franklin, M. R., The alteration of hepatic cytochrome P-450 subpopulations of phenobarbital-induced and uninduced rat by regioselective hepatotoxins. Drug Meta. Dispos., 11, 312–318 (1983).
Halk, P. B., Oster, B. L., and Summerson, W. H., The Practical Physiological Chemistry 14th ed. McGraw Hill Book Co. New York, pp. 1123 (1954).
Haro, A., Lopez-Aliaga, I., Lisbona, F., Barrionuevo, M., Alferez, M. J., and Campos, M. S., Beneficial effect of pollen and/or propolis on the metabolism of iron, calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium in rats with nutritional ferropenic anemia. J. Agric. Food Chem., 48, 5715–5722 (2000).
Hart, S. G., Cartun, R. W., Wyand, D. S., Khairallah, E. A., and Cohen, S. D., Immunohistochemical localization of acetaminophen in target tissues of the CD-1 mouse: Correspondence of covalent binding with toxicity. Fund. Appl. Toxicol., 24, 260–274 (1995).
Itinose, A. M., Sakuno, M. L., and Bracht, A., Metabolic effects of acetaminophen. Studies in the isolated perfused rat liver. Cell Biochem. Funct., 7, 263–273 (1989).
Jaeschke, H., Knight, T. R., and Bajt, M. L., The role of oxidant stress and reactive nitrogen species in acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Toxicol. Lett., 144, 279–288 (2003).
Kato, R., and Gillette, J. R., Effect of starvation on NADPH dependent enzymes in liver microsomes of male and female rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 150, 279–284 (1965).
Krol, W., Scheller, S., Shani, J., Pietsz, G., and Czuba, Z., Synergistic effect of ethanolic extract of propolis and antibiotics on the growth of Staphylococcus aureus. Arzneimittelforschung, 43, 607–609 (1993).
Lee, S. M., Cho, T. S., Kim, D. J., and Cha, Y. N., Protective effect of ethanol against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Role of NADH:quinone reductase. Biochem. Pharmacol., 58, 1547–1555 (1999).
Lewis, D. F. V., Essential requirements for substrate binding affinity and selectivity toward human CYP2 family enzymes. Arch. Biochem. Biophy., 409, 32–44 (2003).
Lowry, O. H., Rosenbrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., and Randall, R. J., Protein measurement with Folin’s phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem., 193, 265–275 (1951).
Moreno, M. I., Isla, M. I., Sampietro, A. R., and Vattuone, M. A., Comparison of the free radical-scavenging activity of propolis from several regions of Argentina. J. Ethnopharmacol., 71, 109–114 (2000).
Muriel, P., Garciapina, T., Perez-Alvarez, V., and Murelle, M., Silymarin protect against paracetamol induced lipid peroxidation and liver damage. J. Appl. Toxicol., 12, 439–442 (1992).
Murugesh, K. S., Yeligar, V. C., Maiti, B. C., and Maity, T. K., Hepatoprotective and antioxidative role of Berberis tinctoria Lesch leaves on paracetamol induced hepatic damage in rats. Iranian J. Pharmacol. Ther., 4, 64–69 (2005).
Nirala, S. K., Bhadauria, M., Mathur, R., and Mathur, A., Influence of α-tocopherol, propolis and piperine on therapeutic potential of tiferron against beryllium induced toxic manifestations. J. Appl. Toxicol., 28, 44–54 (2008).
Orsolic, N. and Basic, I., Immunomodulation by water-soluble derivative of propolis: a factor of antitumor reactivity. J. Ethnopharmacol., 84, 265–273 (2003).
Potter, W. Z., Thorgeirsson, S. S., Jollow, D. J., and Mitchell J. R., Acetaminophen-induced hepatic necrosis, V. Correlation of hepatic necrosis, covalent binding and glutathione depletion in hamsters. Pharmacology, 12, 129–143 (1974).
Raso, G, Meli, R., Di Carlo, G., Pacilio, M., and Di Carlo, R., Inhibition of inducile nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 expression by flavonoids in macrophage J774A. 1. Life Sci., 68, 921–931 (2001).
Reitman, S. and Frankel, S., A colorimetric method for determination of serum glutamic oxaloacetic and glutamic pyruvic transaminases. Am. J. Clin. Pathol., 28, 56–63 (1957).
Russoa, A., Cardileb, V., Sanchezc, F., Troncosoc, N., Vanellaa, A., and Garbarinod, J. A., Chilean propolis: antioxidant activity and antiproliferative action in human tumor cell lines. Life Sci., 76, 545–558 (2004).
Schenkman, J. B. and Cinti, D. L., Preparation of microsomes with calcium. Methods Enzymol., 52, 83–89 (1978).
Seifter, S., Dayton, S., Novic, B., and Muintwyler, E., The estimation of glycogen with anthrone reagent. Arch. Biochem., 25, 191–200 (1950).
Sener, G., Sehirli, O., Cetinel, S., Yegen, B. G., Gedik, N., and Ayanoglu-Dulger, G., Protective effects of MESNA (2-mercaptoethane sulfonate) against acetaminophen-induced hepatorenal oxidative damage in mice. J. Appl. Toxicol., 25, 20–29 (2005).
Seth, P. K. and Tangri, K. K., Biochemical effects of newer salicylic acid congeners. J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 18, 831–833 (1966).
Shankar, K., Vaidya, V. S., Apte, U. M., Manautou, J. E., Ronis, M. J. J., Bucci, T. J., and Mehendale, H. M., Type 1 diabetic mice are protected from acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Toxicol. Sci., 73, 220–234 (2003).
Sharma, S. K. and Krishna Murti, C. R., Production of lipid peroxides by brain. J. Neurochem., 15, 147–149 (1968).
Shimazawa, M., Chikamatsu, S., Morimoto, N., Mishima, S., Nagai, H., and Hara, H., Neuroprotection by Brazilian Green Propolis against In vitro and In vivo Ischemic Neuronal Damage. Evid. Compl. Alt. Med., 2, 201–207 (2005).
Shukla, S., Bhadauria, M., and Jadon, A., Effect of propolis extract on acute carbon tetrachloride induced hepatotoxicity. Indian J. Exp. Biol., 42, 993–997 (2004).
Shukla, S., Bhadauria, M., and Jadon, A., Evaluation of hepatoprotective potential of propolis extract in carbon tetrachloride induced liver injury in rats. Indian J. Biochem. Biophys., 42, 321–325 (2005).
Snedecor, G. W. and Cochran, W. G., Statistical Method, 8th Edition. Iowa State University Press, Ames. Iowa (1994).
Stepanovic, S., Antic, N., Dakic, I., and Svabic-Vlahovic, M., In vitro antimicrobial activity of propolis and synergism between propolis and antimicrobial drugs. Microbiol. Res., 158, 353–357 (2003).
Swarup, H., Arora, S., and Pathak, S. C., Laboratory techniques in modern biology. Kalyani Publishers, New Delhi, pp. 187–189 (1992).
Thomas, S. H. L., Paracetomol (acetaminophen) poisoning. Pharmacol. Ther., 60, 91–120 (1993).
Tirmenstein, M. A. and Nelson, S. D., Subcellular binding and effects on calcium homeostasis produced by acetaminophen and a non-hepatotoxic regioisomer, 3-hydroxyacetoanilide in mouse liver. J. Biol. Chem., 264, 9814–9819 (1989).
Wroblewski F. and La Due J. S., Colorimetric method for LDH. In: Wootton I.D.P. (Ed.), Microanalysis in Medical Biochemistry 4th edn. J and A Churchill Ltd., 104 Gloucester Place, pp. 115–118 (1955).
Yanpallewar, S. U., Sen, S., Tapas, S., Kumar, M., Raju, S. S., and Acharya, S. B., Effect of Azadirachta indica on paracetamol-induced hepatic damage in albino rats. Phytomed., 10, 391–396 (2003).
Zaher, H., Buters, J. T., Ward, J. M., Bruno, M. K., Lucas, A. M., Stern, S. T., Cohen, S. D., and Gonzalez, F. J., Protection against acetaminophen toxicity in CYP1A2 and CYP2E1 double-null mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol., 152, 193–199 (1998).
Zlatkis, A., Zak, B., and Boyle, A. J., A new method for the direct determination of serum cholesterol. J. Lab. Clin. Med., 41, 486–492 (1953).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nirala, S.K., Bhadauria, M. Propolis reverses acetaminophen induced acute hepatorenal alterations: A biochemical and histopathological approach. Arch. Pharm. Res. 31, 451–461 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-001-1178-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-001-1178-5