Abstract
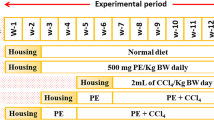
Propolis is a natural product produced by bees that was discovered through the study of traditional cures and knowledge of indigenous people throughout the world. It is rich in vitamins A, B, C, and E, and in amino acids, copper, iron, manganese, and zinc. The investigators studied the duration-dependent hepatoprotective effects of propolis extract (200 mg/kg, orally) against carbon tetrachloride (CCI4; 1.5 ml/kg, intraperitoneally)-induced liver damage in rats. Administration of CCI4 caused a sharp elevation in the activity of serum transaminases and serum alkaline phosphatase. A significant depletion in hepatically reduced glutathione was observed with significantly enhanced hepatic lipid peroxidation. After CCI4 administration, glycogen contents and activities of alkaline phosphatase, adenosine tri phosphatase, and succinic dehydrogenase were significantly decreased, whereas total protein contents and activity of acid phosphatase were increased in the liver and kidney. Propolis extract reversed alterations in all parameters when administered within 6, 12, and 24 h of toxicant exposure. Propolis therapy produced duration-dependent protection, with maximal protection achieved at 24 h after CCI4 exposure. It is believed that propolis in its natural form has general pharmacologic value and marked hepatoprotective potential because of its composition of minerals, flavonoids, and phenolic compounds.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bankova V. Chemical diversity of propolis and the problem of standardization.J Ethnopharmacol. 2005;100:114–117.
Park SH, Min TS. Caffeic acid phenethyl ester ameliorates changes in IGFs secretion and gene expression in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.Life Sci. 2006;78:1741–1747.
Padmavathi R, Senthilnathan P, Chodon D, Sakthisekaran D. Therapeutic effect of paclitaxel and propolis on lipid peroxidation and antioxidant system in 7,12-dimethyl benz(a)anthraceneinduced breast cancer in female Sprague Dawley rats.Life Sci. 2006;78:2820–2825.
Kujumgiev A, Tsretkova I, Serkedjieva Yu, Bankova V, Christov R, Popov S. Antibacterial, antifungal and antiviral activities of propolis of different geographic origin.J Ethnopharmacol. 1999;64:235–240.
Hu F, Hepburn HR, Li Y, Chen M, Radloff SE, Daya S. Effects of ethanol and water extracts of propolis (bee glue) on acute inflammatory animal models.J Ethnopharmacol. 2005;100:276–283.
Morello S, Vellecco V, Alfieri A, Mascolo N, Cicala C. Vasorelaxant effect of the flavonoid galangin on isolated rat thoracic aorta.Life Sci. 2006;78:825–830.
Shimizu K, Ashida H, Matsuura Y, Kanazawa K. Antioxidative bioavailability of artepillin C in Brazilian propolis.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2004;424:181–188.
Orsolic N, Knezevic AH, Sver L, Terzic S, Basic I. Immunomodulatory and antimetastatic action of propolis and related polyphenolic compounds.J Ethnopharmacol. 2004;94:307–315.
Banskota AH, Tezuka Y, Kodata SH. Recent progress in pharmacological research of propolis.Phytother Res. 2001;15:561–571.
Pascual C, Gonzalez R, Torriceila RG. Scavenging action of propolis extract against oxygen radicals.J Ethnopharmacol. 1994;41:9–13.
Moreno MI, Isla MI, Sampietro AR, Vattuone MA. Comparison of the free radical scavenging activity of propolis from several regions of Argentina.J Ethnopharmacol. 2000;71:109–114.
Shukla S, Bhadauria M, Jadon A. Effect of propolis extract on acute carbon tetrachloride induced hepatotoxicity.Indian J Exp Biol. 2004;42:993–997.
Reitman S, Frankel S. A colorimetric method for the determination of serum glutamic oxaloacetic and glutamic pyruvic transaminases.Am J Clin Pathol. 1957;28:56–63.
Halk PB, Oster BL, Summerson WH.Practical Physiological Chemistry. 14th ed. New York: McGraw Hill; 1954:1123.
Sharma SK, Krishna Murti CR. Production of lipid peroxides by brain.J Neurochem. 1968;15: 147–149.
Brehe JE, Burch HB. Enzymatic assay for glutathione.Anal Biochem. 1976;74:189–197.
Scifter S, Dayton S, Novic B, Muintwyler E. The estimation of glycogen with anthrone reagent.Arch Biochem. 1950;25:191–200.
Lowry OH, Rosenbrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent.J Biol Chem. 1951;193:265–275.
Seth PK, Tangari KK. Biochemical effects of some newer salicylic acid congeners.J Pharm Pharmacol. 1966;18:831–833.
Slatter EC, Bonner WD. The effect of fluoride on the succinic oxidase system.J Biochem. 1952;82:185–191.
Snedecor GW, Cochran WG.Statistical Methods. 8th ed. Ames, Iowa: Iowa State University Press; 1994:217–236.
Kadhska MB, Gladen BC, Baird DD, et al. Biomarkers of oxidative stress study: are plasma antioxidants markers of CCI4 poisoning?Free Radie Biol Med. 2000;28:838–845.
Rajesh MG, Latha MS. Preliminary evaluation of the antihepatotoxic activity of Kamilari, a polyherbal formulation.J Ethnopharmacol. 2004;91:99–104.
Suja SR, Latha PG, Pushpangandan P, Rajasekharan S. Evaluation of hepatoprotective effects ofHelminthostachys zeylanica (L.) Hook against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver damage in Wistar rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2004;92:61–66.
Rastogi S, Rana SVS. Influence of parathyroidectomy on liver glycogen in rats treated with carbon tetrachloride.Indian J Exp Biol. 1990;28:794–795.
Abraham P, Wilfred G. Lysosomal enzymes in the pathogenesis of carbon tetrachloride induced injury to the kidney and testis in the rat.Indian J Pharmacol. 2000;32:250–251.
Shukla S, Jadon A, Bhadauria M. Comparative effect ofTerminalia belerica fruit extract and its active principle against carbon tetrachloride induced toxicity in rats.Indian J Pharm Sci. 2005;67:681–686.
Shukla S, Bhadauria M, Sharma A, Jadon A. Hepatoprotective effect of proprietary herbal formulation (PHF) on experimental liver damage in rats.Toxicol Int. 2005;12:75–81.
Lee TY, Mai LM, Wang GJ, Chiu JH, Lin YL, Lin HC. Protective mechanism ofSalvia miltiorrhiza on carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in rats.J Pharmacol Sci. 2003;91:202–210.
Pinchuk I, Lichtenberg D. The mechanism of action of antioxidants against lipoprotein peroxidation: evaluation based on kinetic experiments.Prog Lipid Res. 2002;41:279–314.
Jeon TI, Hwang SG, Park NG, et al. Antioxidative effect of chitosan on chronic carbon tetrachloride induced hepatic injury in rats.Toxicology. 2003;187:67–73.
Lin CC, Yen MH, Lo TS, Lin JM. Evaluation of hepatoprotective and antioxidant activity ofBoehmeria nivea var. nivea and B.nivea var. tenacissima.J Ethnopharmacol. 1998;60:9–17.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhadauria, M., Nirala, S.K. & Shukla, S. Duration-dependent hepatoprotective effects of propolis extract against carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver damage in rats. Adv Therapy 24, 1136–1145 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02877719
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02877719