Abstract
Acute mesenteric ischaemia is a life-threatening vascular emergency that requires early diagnosis and intervention to adequately restore mesenteric blood flow and to prevent bowel necrosis and patient death. Its overall mortality is 60–80% and the reported incidence is increasing. This case report emphasises that a patient with early detection and radiological management of acute mesenteric ischaemia being symptomatic for COVID-19 can avoid major bowel surgery and negate any morbidity or mortality associated with the same.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
COVID-19 has been a tyrant for the year 2020 and continues to be so in 2021 also, even though vaccines have started been administered worldwide. COVID-19 and acute mesenteric ischaemia (AMI) seem to be a very deadly combination knowing the destructive nature of both alone. However, early detection and treatment of both can be quite comfortable for both doctor and patient as we have shown in this case report. Newer evidence states that COVID-19 pneumonia induces a hypercoagulable state leading to vascular and microvascular thrombotic events. Common life-threatening conditions associated with COVID-19 are mesenteric ischaemia and pulmonary embolism [1]. Acute mesenteric ischaemia is a potentially fatal vascular emergency with overall mortality of 60% to 80% [2]. However till date, only few cases of SMA thrombosis in COVID-19 positive patients are reported and most have succumbed to COVID-19 or mesenteric ischaemia [3,4,5]. Physicians treating COVID-19 usually treat respiratory symptoms and may completely overlook any other uncommon pathology.
We report the first symptomatic COVID-19 patient presenting with bowel ischaemia and mesenteric arterial thrombosis treated early with catheter directed thrombolysis and thrombus aspiration without bowel gangrene or need for laparotomy.
Case Report
A 37-year-old COVID-19 positive gentleman presented in the late hours with severe abdominal pain not resolving with medication and associated intermittent episodes of vomiting. He had irregular spikes of 102F fever since 72 h but was hemodynamically stable. Clinical examination showed a soft abdomen with mild guarding over epigastric and paraumbilical region. He was started on symptomatic treatment and blood investigations were called for. Serum lactate was borderline elevated with serum procalcitonin being 0.56. Other relevant tests were also within normal limits (PT: 13 s, INR: 1.20, aPTT: 32.6 s) while D-dimer was elevated to 3.1 mg/L suggestive of thrombosis. However, pain did not subside and continued to aggravate even with high doses of NSAIDs and opioid analgesics.
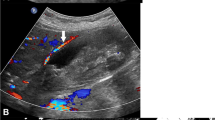
Contrast enhanced CT with angiography of abdomen showed thrombus at the origin of superior mesenteric artery extending into the jejunal arcades with impending gangrene of bowel (Fig. 1a). He was urgently taken up for catheter directed thrombolysis overnight (Fig. 1b). Inj. Actilyse (recombinant human tPA), 8 mg given bolus followed by 1 mg/h, was given via 4F 10-cm Cragg-McNamara thrombolysis infusion catheter into the thrombosed SMA. Reshoot angiogram with thrombus aspiration using 7F clot aspiration catheter done on post-operative day 1 showed complete resolution of thrombosis with opening up of jejunal arcades and the main SMA trunk (Fig. 2a and b). All the hardware was removed and puncture sites secured. Patient was transferred post-operatively to COVID isolation ward and observed as per hospital protocol. He passed stools the very next day with no abdominal symptoms. He was started orally from post-operative day 3 and was completely discharged from hospital after 5 days stay in the COVID-19 ward. Prothrombotic workup done was unremarkable.
Discussion
In the course of COVID-19 disease, hypoxia, inflammatory mediators and many other factors secondary to ACE2 receptor expression may predispose to arterial and venous thrombosis [6]. The exact mechanism of coagulopathy in COVID-19 is still being elucidated. Till now deciphered pathway is that both virus and damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) from injured host tissue can activate monocytes. Activated monocytes release inflammatory cytokines and chemokines that stimulate neutrophils, lymphocytes, platelets and vascular endothelial cells. Monocytes and other cells express tissue factor and phosphatidylserine on their surfaces and initiate coagulation. Healthy endothelial cells maintain their anti-thrombogenicity by expressing glycocalyx and its binding protein antithrombin. Damaged endothelial cells change their properties to procoagulant following disruption of the glycocalyx and loss of anticoagulant proteins. As a result microthrombi and inflammatory mediators formed are postulated to cause mesenteric ischaemia as COVID-19. Patients with severe COVID-19 complicated by AMI may present with abdominal pain, nausea/vomiting, diarrhoea, abdominal distention or worsening systemic status (sepsis). Case reports worldwide have shown high morbidity and mortality when COVID-19 and mesenteric arterial thrombosis occur together.
In mesenteric ischaemia, the time lag between onset of symptom and treatment is crucial for good outcome. The optimal time for intervention is initial 12 h from symptom onset, when it is possible to perform vascular surgery effectively without requiring intestinal resection. However, patients with COVID-19 often present late or treatment of respiratory symptoms is given precedence over abdominal symptoms [2]. Bowel symptoms tend to be more urgent to manage. Once organ failure sets in, the scenario ends up more frequently as a vicious cycle.
Till now around six cases of SMA thrombosis in COVID-19 positive patients have been reported in the world (3, 2 and 1 patient in Strasbourg, Paris and Italy, respectively). Of these, one patient who was managed conservatively did not survive. In the 4 operated patients, only two (28 years female, 52 years male) survived while one (56 years male) was still on ventilatory support [7].
Our patient primarily came with severe abdominal pain not responding to medications and high fever which made us more suspicious for COVID-19. Early CT angiogram of the abdomen gave us the diagnosis of acute superior mesenteric artery thrombosis with jejunal thrash and impending gangrene of bowel. Early diagnosis and efficient thrombolysis resulted in better bowel salvage with complete resolution of symptoms on post-operative day 1 with patient starting oral intake from post-operative day 3. Early management of arterial thrombosis compromising blood flow even with COVID-19 can help in reducing morbidity of COVID-19 and thus reduce overall mortality rates.
Conclusion
Being one of the most challenging clinical problems with many causes, it often results in delayed diagnosis and treatment. The outcome depending on the rapidity of diagnosis and treatment, all clinicians should have a strong suspicion and an aggressive approach towards this problem. The outcomes can be bettered, if patients treated with endovascular approach to avoid the morbidity and mortality associated with open surgeries.
References
Qanadli SD, Gudmundsson L, Rotzinger DC (2020) Catheter-directed thrombolysis in COVID-19 pneumonia with acute PE: Thinking beyond the guidelines. Thromb Res 192:9–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.thromres.2020.05.007
Heys SD, Brittenden J, Crofts TJ (1993) Acute mesenteric ischaemia: the continuing difficulty in early diagnosis. Postgrad Med J 69:48–51
Beccara L, Pacioni C, Ponton S, Francavilla S, Cuzzoli A (2020) Arterial mesenteric thrombosis as a complication of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Eur J Case Rep Intern Med 7(5):001690. https://doi.org/10.12890/2020_001690
de Barry O, Mekki A, Diffre C, Seror M, Hajjam ME, Carlier RY (2020) Arterial and venous abdominal thrombosis in a 79-year-old woman with COVID-19 pneumonia. Radiol Case Rep 15:1054–1057. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radcr.2020.04.055
Ignat M, Philouze G, Aussenac-Belle L, Faucher V, Collange O, Mutter D, Pessaux P (2020) Small bowel ischemia and SARS-CoV-2 infection: an underdiagnosed distinct clinical entity. Surg J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surg.2020.04.035
Klok FA, Kruip MJHA, van der Meer NJM, Arbous MS, Gommers DAMPJ, Kant KM, Kaptein FHJ, van Paassen J, Stals MAM, Huisman MV, Endeman H (2020) Incidence of thrombotic complications in critically ill ICU patients with COVID-19. Thromb Res 191:145–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.013
Karna ST, Panda R, Maurya AP, Saigal S (2020) Superior mesenteric artery thrombosis in COVID-19 pneumonia: an underestimated diagnosis-first case report in Asia. Indian J Surg 2020:1–3. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12262-020-02638-5
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balani, P., Bhuiyan, A.S., Dalal, V.N. et al. Early Detection and Successful Management of Acute Mesenteric Ischaemia in Symptomatic COVID-19 Patient. Indian J Surg 84, 209–211 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12262-021-02839-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12262-021-02839-6