Abstract
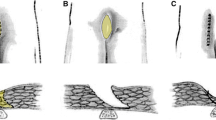
The aim of this study is to evaluate the effectiveness and feasibility of Limberg and Karydakis flap in complicated and recurrent cases of pilonidal sinus. This study was performed on 54 patients with complicated or recurrent (PSD) who referred to Minya University Hospital from January 2018 to January 2019. Patients were randomly divided into two groups, group A who were subjected to the Limberg flap and group B who were subjected to the Karydakis flap technique. Regarding postoperative complications, the occurrence of wound breakdown in the Karydakis group was 40.7% versus 11.1% in the Limberg group. No recurrence occurred in the Limberg group but recurrence observed in six cases in the Karydakis group. In the Karydakis group, eight patients had infection in comparison to one case in the Limberg group. All these differences were statistically significant. The overall patient satisfaction in the Limberg group was significantly higher than that in the Karydakis group. It is concluded that Limberg flap rotation is clearly preferred in management of recurrent and complicated PNS for safety reasons given its low recurrence and postoperative complication rates.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Petersen S, Koch R, Stelzner S, Wendlandt TP, Ludwig K (2002) Primary closure techniques in chronic pilonidal sinus: a survey of the result of different surgical approaches. Dis Colon Rectum 45(11):1458–1462
Bertelsen CA (2011) Cleft-lift operation for pilonidal sinuses under tumescent local anesthesia: a prospective cohort study of peri- and postoperative pain. Dis Colon Rectum 54(7):895e900
Muzi MG, Milito G, Cadeddu F, Nigro C, Andreoli F, Amabile D, Farinon AM (2010) Randomized comparison of Limberg flap versus modified primary closure for the treatment of pilonidal disease. Am J Surg 200(1):9–14
Krand O, Yalt T, Berber I, Kara VM, Tellioglu G (2009) Management of pilonidal sinus disease with oblique excision and bilateral gluteus maximus fascia advancing flap: result of 278 patients. Dis Colon Rectum 52:1172–1177
Can MF, Sevinc MM, Hancerliogullari O, Yilmaz M, Yagci G (2010) Multicenter prospective randomized trial comparing modified Limberg flap transposition and Karydakis flap reconstruction in patients with sacrococcygeal pilonidal disease. Am J Surg 200(3):318–327
Bessa SS (2013) Comparison of short-term results between the modified Karydakis flap and the modified Limberg flap in the management of pilonidal sinus disease: a randomized controlled study. Dis Colon Rectum 56(4):491–498
Humphries AE, Duncan JE (2010) Evaluation and management of pilonidal disease. Surg Clin North Am 90(1):113–124
Søndenaa K, Nesvik I, Andersen E, Natås O, Søreide JA (1995) Bacteriology and complications of chronic pilonidal sinus treated with excision and primary suture. Int J Color Dis 10:161–166
Lieto E, Castellano P, Pinto M, Zamboli A, Pignatelli C, Galizia G (2010) Dufourmentel rhomboid flap in the radical treatment of primary and recurrent sacrococcygeal pilonidal disease. Dis Colon Rectum 53(7):1061–1068
Mentes O, Bagci M, Bilgin T, Ozgul O, Ozdemir M (2008) Limberg flap procedure for pilonidal sinus disease: results of 353 patients. Langenbeck's Arch Surg 393:185–189
Lee PJ, Raniga S, Biyani DK, Watson AJ, Faragher IG, Frizelle FA (2008) Sacrococcygeal pilonidal disease. Color Dis 10(7):639–650
Ersoy E, Devay AO, Aktimur R, Doganay B, Ozdoğan M, Gundoğdu RH (2009) Comparison of the short-term results after Limberg and Karydakis procedures for pilonidal disease: randomized prospective analysis of 100 patients. Color Dis 11(7):705–710
Alvandipour M, Zamani MS, Ghorbani M, Charati JY, Karami MY (2019) Comparison of Limberg flap and Karydakis flap surgery for the treatment of patients with pilonidal sinus disease: a single-blinded parallel randomized study. Ann Coloproctol; 1–6
Kohla SM, Alsesy AA, Abd El-Aziz TF, Mohammed MA, Abo Zaid MA (2016) Comparative study between the Karydakis technique and the Limberg flap in pilonidal sinus. Menoufia Med J 29:539–544
Bostanoglu S, Sakcak I, Avsar FM, Cosgun E, Hamamci EO (2010) Comparison of Karydakis technique with Limberg flap procedure in pilonidal sinus disease: advantages of Karydakis technique. Pak J Med Sci 26(4):773–777
Karaca T, Yoldaş O, Bilgin BÇ, Ozer S, Yoldaş S et al (2012) Comparison of short-term results of modified Karydakis flap and modified Limberg flap for pilonidal sinus surgery. Int J Surg 10(10):601–606
Arslan K, Said Kokcam S, Koksal H, Turan E, Atay A, Dogru O. Which flap method should be preferred for the treatment of pilonidal sinus? A prospective randomized study. Tech
McCallum IJ, King PM, Bruce J (2008) Healing by primary closure versus open healing after surgery for pilonidal sinus: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 336(7649):868–871. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.39517.808160.BE
Petersen S, Koch R, Stelzner S, Wendlandt TP, Ludwig K (2002) Primary closure techniques in chronic pilonidal sinus: a survey of the - results of different surgical approaches. Dis Colon Rectum 45(11):1458–1467. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10350-004-6451-2
Ashok, Nikhilesh (2018) Comparison of Karydakis flap and Limberg flap in pilonidal sinus. Int J Surg Surg Tech 2(2):1–4
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to offer their sincere thanks to all patients and their relevant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The protocol of the study was discussed and approved regarding ethics of research in the general surgical department. The study had been approved by the ethical committee for human studies in our institution. Full written, informed consent was signed from all participants.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Manuscript has been read and approved by all the authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elhiny, A.A.H., Saad, D.A. & Farahat, M.S. Effectiveness and Feasibility of Limberg and Karydakis Flap in Recurrent and Complicated Pilonidal Sinus Disease. Indian J Surg 83, 55–60 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12262-020-02236-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12262-020-02236-5