Abstract
Purpose
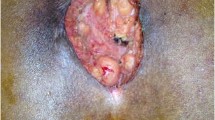
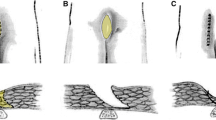
Pilonidal sinus disease is common especially in young adult males. Many surgical and nonsurgical methods have been described. Some surgical techniques for the treatment still have high recurrence rate. The aim of this study was to evaluate advantages and long term results of Limberg flap surgical technique.
Methods
From November 2001 to December 2004, 353 patients [335 male, 18 female; average age = 24.65 ± 4.2 (range, 15–53) years] with primary or recurrent pilonidal sinus disease were operated on under spinal anesthesia by rhomboid excision and Limberg flap. Follow-up examinations were made at the end of the 4 weeks and 3, 6, 12, 18, and 24 months after surgery.
Results
The mean duration of symptoms was 23.28 ± 16.09 (range, 2–140) months. The mean duration of hospital stay was 4.51 ± 2.85 (range, 2–19) days. Thirty nine patients (11%) had recurrent disease. Total wound dehiscence and flap necrosis did not occur in any patient. Recurrences were observed in 11 patients (3.1%) at the end of the follow up period.
Conclusion
Quick healing time, short hospital stay, early return to daily life, low complication and recurrence rate are the important advantages of the Limberg flap procedure. We think using closed suction drain in Limberg flap operation is not necessary. In the light of this study results, Limberg flap surgical technique may be an ideal operation for pilonidal sinus disease.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Spivak H, Brooks VL, Nussbaum M, Friedman I (1996) Treatment of chronic pilonidal disease. Dis Colon Rectum 39:1136–1139
Hodgson WJB, Greenstein RJ (1981) A comparative study between Z-plasty and incision and drainage or excision with marsupialization for pilonidal sinuses. Surg Gynecol Obstet 153:842–844
Armstrong JH, Barcia PJ (1994) Pilonidal sinus disease: the conservative approach. Arch Surg 129:914–919
Goligher JC (1975) Surgery of anus, rectum and colon. 3rd edn. Bailliere Tindall, London, pp 206–208
Patey DH, Scraff RW (1948) Pilonidal sinus in a barber’s hand with observations on postnatal pilonidal sinus. Lancet 2:484–486
Karydakis GE (1992) Easy and successful treatment of pilonidal sinus after explanation of its causative process. ANZ J Surg 62:385–389
Buie LA, Curtiss RK (1952) Pilonidal disease. Surg Clin North Am 32:1247–1259
Hull TL, Wu J (2002) Pilonidal disease. Surg Clin North Am 82:1169–1185
Schneider IHF, Thaler K, Kockerling TF (1994) Treatment of pilonidal sinuses by phenol injections. Int J Colorectal Dis 9:200–202
Gage AA, Dutta P (1977) Cryosurgery for pilonidal disease. Am J Surg 133:249–254
Solla JA, Rotherbenger DA (1990) Choronic pilonidal disease. An assessment of 150 cases. Dis Colon Rectum 33:758–761
da Silva JH (2000) Pilonidal cyst: cause and treatment. Dis Colon Rectum 43:1146–1156
Allen-Mersh TG (1990) Pilonidal sinus finding the right track for treatment. Br J Surg 77:123–132
Dufourmental C, Mouly R, Baruch J, Banzet P (1996) Sacrococcygeal cysts and fistulas. Pathogenic and therapeutic discussion. Ann Chir Plast 11:181–186
Guyuron B, Dinner MI, Dowden RV (1983) Excision and grafting in the treatment of recurrent pilonidal sinus disease. Surg Gynecol Obstet 156:201–204
Al-Jaberi TM (2001) Excision and simple primary closure of chronic pilonidal sinus. Eur J Surg 167:133–135
McLaren CA (1985) Partial closure and other techniques in pilonidal sinus surgery: an assessment of 157 cases. Br J Surg 71:561–562
Topgül K, Ozdemir E, Kilic K, Gökbayir H, Ferahköşe Z (2003) Log-term results of Limberg procedure for treatment of pilonidal sinus: a report of 200 cases. Dis Colon Rectum 46:1545–1548
Erdem E, Sungurtekin U, Neşşar M (1998) Are postoperative drains necessary with the Limberg flap for treatment of pilonidal sinus? Dis Colon Rectum 41:1427–1431
Eryilmaz R, Sahin M, Alimoglu O, Dasıran F (2003) Surgical treatment of sacrococcygeal pilonidal sinus with the Limberg transposition flap. Surgery 134:745–749
Daphan C, Tekelioglu MH, Sayılgan C (2004) Limberg flap repair for pilonidal sinus disease. Dis Colon Rectum 47:233–237
Khatari VP, Espinosa MH, Amin AK (1994) Management of pilonidal sinus by simple V and Y fasciocutaneus flap. Dis Colon Rectum 37:1232–1235
Roth RF, Moorman WL (1977) Treatment of pilonidal sinus and cysts by conservative excision and W-plasty closure. Plast Reconstr Surg 60:412–415
Petersen S, Koch R, Stelzner S, Wendland T-P, Ludwig K (2002) Primary closure techniques in chronic pilonidal sinus: A survey of the results of different surgical approaches. Dis Colon Rectum 45:1458–1467
Franckowiak JJ, Jackmann RJ (1962) The etiology of pilonidal sinus. Dis Colon Rectum 5:28–36
Sondenaa K, Andersen E, Nesvik I, Soreide JA (1995) Patient characteristics and symptoms in chronic pilonidal sinus disease. Int J Colorectal Dis 10:39–42
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mentes, O., Bagci, M., Bilgin, T. et al. Limberg flap procedure for pilonidal sinus disease: results of 353 patients. Langenbecks Arch Surg 393, 185–189 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-007-0227-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-007-0227-9