Abstract
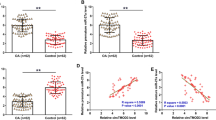
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the main cause of pain and disability in the elderly. It is reported that circular RNA BRMS1L (BRMS1 like transcriptional repressor) (circBRMS1L) is upregulated in the synovial fluid of OA patients. Nevertheless, the biological function of circBRMS1L in OA has not been validated. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced chondrocytes (C28/I2) were used as OA cell models in vitro. Expression patterns of circBRMS1L, microRNA (miR)-142-5p, and Toll-like Receptor 4 (TLR4) mRNA were verified by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Loss-of-function experiments were performed to explore the influence of circBRMS1L on LPS-induced extracellular matrix (ECM) degradation, apoptosis, and inflammation in C28/I2 cells. Protein levels were detected by western blotting. The regulatory mechanism of circBRMS1L in OA was explored by bioinformatics analysis, dual-luciferase reporter, RNA immunoprecipitation, and/or RNA pull-down assays. CircBRMS1L was prominently upregulated in OA cartilage tissues and LPS-stimulated C28/I2 cells. Inhibition of circBRMS1L reduced LPS-induced ECM degradation, apoptosis, inflammation, and oxidative stress in C28/I2 cells. MiR-142-5p was downregulated while TLR4 was upregulated in OA cartilage tissues and LPS-stimulated C28/I2 cells. CircBRMS1L adsorbed miR-142-5p to regulate TLR4 expression. MiR-142-5p inhibitor reversed circBRMS1L silencing-mediated effects on LPS-induced ECM degradation, apoptosis, inflammation, and oxidative stress in C28/I2 cells. TLR4 elevation overturned the inhibitory influence of miR-142-5p mimic on LPS-induced ECM degradation, apoptosis, inflammation, and oxidative stress in C28/I2 cells. Notably, circBRMS1L activated the nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) pathway by the miR-142-5p/TLR4 axis. LPS-induced ECM degradation, apoptosis, inflammation, and oxidative stress in chondrocytes were at least partially regulated by the circBRMS1L/miR-142-5p/TLR4/NF-κB pathway, highlighting a new mechanism responsible for OA advancement.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jeffries, M. A. (2019) Osteoarthritis year in review 2018: genetics and epigenetics. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 27: 371–377.
Kraus, V. B., F. J. Blanco, M. Englund, M. A. Karsdal, and L. S. Lohmander (2015) Call for standardized definitions of osteoarthritis and risk stratification for clinical trials and clinical use. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 23: 1233–1241.
Bruyère, O., G. Honvo, N. Veronese, N. K. Arden, J. Branco, E. M. Curtis, N. M. Al-Daghri, G. Herrero-Beaumont, J. Martel-Pelletier, J.-P. Pelletier, F. Rannou, R. Rizzoli, R. Roth, D. Uebelhart, C. Cooper, and J.-Y. Reginster (2019) An updated algorithm recommendation for the management of knee osteoarthritis from the European Society for Clinical and Economic Aspects of Osteoporosis, Osteoarthritis and Musculoskeletal Diseases (ESCEO). Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 49: 337–350.
Kapoor, M., J. Martel-Pelletier, D. Lajeunesse, J.-P. Pelletier, and H. Fahmi (2011) Role of proinflammatory cytokines in the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 7: 33–42.
Goldring, M. B. and M. Otero (2011) Inflammation in osteoarthritis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 23: 471–478.
Ansari, M. Y., N. Ahmad, and T. M. Haqqi (2020) Oxidative stress and inflammation in osteoarthritis pathogenesis: role of polyphenols. Biomed. Pharmacother. 129: 110452.
Hwang, H. S. and H. A. Kim (2015) Chondrocyte apoptosis in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 16: 26035–26054.
Charlier, E., B. Relic, C. Deroyer, O. Malaise, S. Neuville, J. Collée, M. G. Malaise, and D. De Seny (2016) Insights on molecular mechanisms of chondrocytes death in osteoarthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 17: 2146.
Wang, F. S., C. W. Kuo, J. Y. Ko, Y. S. Chen, S. Y. Wang, H. J. Ke, P. C. Kuo, C. H. Lee, J. C. Wu, W. B. Lu, M. H. Tai, H. Jahr, and W. S. Lian (2020) Irisin mitigates oxidative stress, chondrocyte dysfunction and osteoarthritis development through regulating mitochondrial integrity and autophagy. Antioxidants (Basel) 9: 810.
Chen, L.-L. and L. Yang (2015) Regulation of circRNA biogenesis. RNA Biol. 12: 381–388.
Suzuki, H. and T. Tsukahara (2014) A view of pre-mRNA splicing from RNase R resistant RNAs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 15: 9331–9342.
Liu, Q., X. Zhang, X. Hu, L. Yuan, J. Cheng, Y. Jiang, and Y. Ao (2017) Emerging roles of circRNA related to the mechanical stress in human cartilage degradation of osteoarthritis. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 7: 223–230.
Li, H.-Z., Z. Lin, X.-H. Xu, N. Lin, and H.-D. Lu (2018) The potential roles of circRNAs in osteoarthritis: a coming journey to find a treasure. Biosci. Rep. 38: BSR20180542.
Zhang, Z., T. Yang, and J. Xiao (2018) Circular RNAs: promising biomarkers for human diseases. EBioMedicine 34: 267–274.
Shen, S., Y. Wu, J. Chen, Z. Xie, K. Huang, G. Wang, Y. Yang, W. Ni, Z. Chen, P. Shi, Y. Ma, and S. Fan (2019) CircSERPINE2 protects against osteoarthritis by targeting miR-1271 and ETS-related gene. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 78: 826–836.
Wu, Y., Y. Zhang, Y. Zhang, and J.-J. Wang (2017) CircRNA hsa_circ_0005105 upregulates NAMPT expression and promotes chondrocyte extracellular matrix degradation by sponging miR-26a. Cell Biol. Int. 41: 1283–1289.
Yu, F., C. Xie, J. Sun, H. Feng, and X. Huang (2018) Circular RNA expression profiles in synovial fluid: a promising new class of diagnostic biomarkers for osteoarthritis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 11: 1338–1346.
Tay, Y., J. Rinn, and P. P. Pandolfi (2014) The multilayered complexity of ceRNA crosstalk and competition. Nature 505: 344–352.
Li, S., Z. Jin, and X. Lu (2017) MicroRNA-192 suppresses cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in human rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes by downregulating caveolin 1. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 432: 123–130.
Xiao, P., X. Zhu, J. Sun, Y. Zhang, W. Qiu, J. Li, and X. Wu (2021) LncRNA NEAT1 regulates chondrocyte proliferation and apoptosis via targeting miR-543/PLA2G4A axis. Hum. Cell 34: 60–75.
Fan, X., J. Yuan, J. Xie, Z. Pan, X. Yao, X. Sun, P. Zhang, and L. Zhang (2018) Long non-protein coding RNA DANCR functions as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate osteoarthritis progression via miR-577/SphK2 axis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 500: 658–664.
Wang, T., Z. Hao, C. Liu, L. Yuan, L. Li, M. Yin, Q. Li, Z. Qi, and Z. Wang (2020) LEF1 mediates osteoarthritis progression through circRNF121/miR-665/MYD88 axis via NF-κB signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 11: 598. (Erratum published 2020, Cell Death Dis. 11: 689)
Cao, J., Z. Liu, L. Zhang, and J. Li (2019) miR-940 regulates the inflammatory response of chondrocytes by targeting MyD88 in osteoarthritis. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 461: 183–193.
Xiang, Y., Y. Li, L. Yang, Y. He, D. Jia, and X. Hu (2020) miR-142-5p as a CXCR4-targeted microRNA attenuates SDF-1-induced chondrocyte apoptosis and cartilage degradation via inactivating MAPK signaling pathway. Biochem. Res. Int. 2020: 4508108.
Roy, A., M. Srivastava, U. Saqib, D. Liu, S. M. Faisal, S. Sugathan, S. Bishnoi, and M. S. Baig (2016) Potential therapeutic targets for inflammation in toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-mediated signaling pathways. Int. Immunopharmacol. 40: 79–89.
Choi, M.-C., J. Jo, J. Park, H. K. Kang, and Y. Park (2019) NF-κB signaling pathways in osteoarthritic cartilage destruction. Cells 8: 734.
Fernández-Torres, J., Y. Zamudio-Cuevas, A. López-Reyes, D. Garrido-Rodríguez, K. Martínez-Flores, C. A. Lozada, J. F. Muñóz-Valle, E. Oregon-Romero, and G. A. Martínez-Nava (2018) Gene-gene interactions of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in knee osteoarthritis. Mol. Biol. Rep. 45: 1089–1098.
Singh, P., K. B. Marcu, M. B. Goldring, and M. Otero (2019) Phenotypic instability of chondrocytes in osteoarthritis: on a path to hypertrophy. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1442: 17–34.
Frazer, A., R. A. Bunning, M. Thavarajah, J. M. Seid, and R. G. Russell (1994) Studies on type II collagen and aggrecan production in human articular chondrocytes in vitro and effects of transforming growth factor-beta and interleukin-1beta. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2: 235–245.
Ding, Y., L. Wang, Q. Zhao, Z. Wu, and L. Kong (2019) MicroRNA-93 inhibits chondrocyte apoptosis and inflammation in osteoarthritis by targeting the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 43: 779–790.
Luo, X., J. Wang, X. Wei, S. Wang, and A. Wang (2020) Knockdown of lncRNA MFI2-AS1 inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced osteoarthritis progression by miR-130a-3p/TCF4. Life Sci. 240: 117019.
Salmena, L., L. Poliseno, Y. Tay, L. Kats, and P. P. Pandolfi (2011) A ceRNA hypothesis: the Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA language? Cell 146: 353–358.
Liu, S., Z. Xiao, F. Ai, F. Liu, X. Chen, K. Cao, W. Ren, X. Zhang, P. Shu, and D. Zhang (2017) miR-142-5p promotes development of colorectal cancer through targeting SDHB and facilitating generation of aerobic glycolysis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 92: 1119–1127. (Erratum published 2018, Biomed. Pharmacother. 99: 1033–1036)
Bai, X., Y. Zhou, P. Chen, M. Yang, and J. Xu (2018) MicroRNA-142-5p induces cancer stem cell-like properties of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma via inhibiting PTEN. J. Cell. Biochem. 119: 2179–2188.
Li, X., W. Chen, Y. Jin, R. Xue, J. Su, Z. Mu, J. Li, and S. Jiang (2019) miR-142-5p enhances cisplatin-induced apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells by targeting multiple anti-apoptotic genes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 161: 98–112.
Yan, J., B. Yang, S. Lin, R. Xing, and Y. Lu (2019) Downregulation of miR-142-5p promotes tumor metastasis through directly regulating CYR61 expression in gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer 22: 302–313.
Ji, Y., Q. Y. Fang, S. N. Wang, Z. W. Zhang, Z. J. Hou, J. N. Li, and S. Q. Fu (2020) Lnc-RNA BLACAT1 regulates differentiation of bone marrow stromal stem cells by targeting miR-142-5p in osteoarthritis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 24: 2893–2901.
Sasaki, C. Y., T. J. Barberi, P. Ghosh, and D. L. Longo (2005) Phosphorylation of RelA/p65 on serine 536 defines an I{kappa}B{alpha}-independent NF-{kappa}B pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 280: 34538–34547.
Viatour, P., M. P. Merville, V. Bours, and A. Chariot (2005) Phosphorylation of NF-kappaB and IkappaB proteins: implications in cancer and inflammation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 30: 43–52.
Qiu, W.-J., M.-Z. Xu, X.-D. Zhu, and Y.-H. Ji (2019) MicroRNA-27a alleviates IL-1β-induced inflammatory response and articular cartilage degradation via TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway in articular chondrocytes. Int. Immunopharmacol. 76: 105839.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. The research was reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of Xingtai People’s Hospital.
All subjects signed informed consents and then underwent surgical operations at the Xingtai People’s Hospital.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, R., Li, L., Wang, J. et al. CircBRMS1L Participates in Lipopolysaccharide-induced Chondrocyte Injury via the TLR4/NF-κB Pathway through Serving as a miR-142-5p Decoy. Biotechnol Bioproc E 28, 112–124 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-021-0224-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-021-0224-9