Abstract
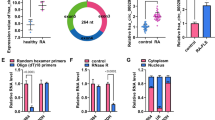
Fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs) play an important role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). This study was conducted to explore the role of microRNA (miR)-192 in the regulation of the biology of RA-FLSs. The expression of miR-192 in RA and healthy synovial tissues was measured. The effects of overexpression of miR-192 on RA-FLS proliferation and apoptosis were investigated. Luciferase reporter assay and Western blot analysis were performed to identify direct target genes of miR-192. RA synovial tissues had significantly lower levels of miR-192 than healthy controls (P = 0.004). Moreover, miR-192 levels were 2.9-fold lower in RA-FLSs relative to normal human FLSs (P < 0.05). Ectopic expression of miR-192 significantly inhibited the proliferation and caused a cell cycle arrest at the G0/G1 phase in RA-FLSs. Moreover, miR-192 overexpression triggered apoptosis, which was accompanied by an increase in caspase-3 activity and Bax/Bcl-2 ratio. Caveolin 1 (CAV1) was identified to be a direct target of miR-192. Overexpression of miR-192 led to a reduction of endogenous CAV1 in RA-FLSs. Silencing of CAV1 significantly decreased cell proliferation and promoted apoptosis in RA-FLSs. Rescue experiments with a miR-192-resistant variant of CAV1 showed that enforced expression of CAV1 restored cell proliferation and attenuated apoptosis in miR-192-overexpressing RA-FLSs. In conclusion, miR-192 is downregulated in RA synovial tissues and restoration of its expression elicits growth-suppressive effects on RA-FLSs by targeting CAV1. The miR-192/CAV1 pathway may represent a novel target for prevention and treatment of RA.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pethő Z, Tanner MR, Tajhya RB, Huq R, Laragione T, Panyi G, Gulko PS, Beeton C (2016) Different expression of β subunits of the KCa1.1 channel by invasive and non-invasive human fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Arthritis Res Ther 18:103
Rockel JS, Kapoor M (2016) Autophagy: controlling cell fate in rheumatic diseases. Nat Rev Rheumatol 12:517–531
Bartok B, Hammaker D, Firestein GS (2014) Phosphoinositide 3-kinase δ regulates migration and invasion of synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol 192:2063–2070
Bottini N, Firestein GS (2013) Duality of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in RA: passive responders and imprinted aggressors. Nat Rev Rheumatol 9:24–33
Onyido EK, Sweeney E, Nateri AS (2016) Wnt-signalling pathways and microRNAs network in carcinogenesis: experimental and bioinformatics approaches. Mol Cancer 15:56
Churov AV, Oleinik EK, Knip M (2015) MicroRNAs in rheumatoid arthritis: altered expression and diagnostic potential. Autoimmun Rev 14:1029–1037
Mu N, Gu J, Huang T, Zhang C, Shu Z, Li M, Hao Q, Li W, Zhang W, Zhao J, Zhang Y, Huang L, Wang S, Jin X, Xue X, Zhang W, Zhang Y (2016) A novel NF-κB/YY1/microRNA-10a regulatory circuit in fibroblast-like synoviocytes regulates inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Sci Rep 6:20059
Yang S, Yang Y (2015) Downregulation of microRNA-221 decreases migration and invasion in fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Med Rep 12:2395–2401
Wu F, Zikusoka M, Trindade A, Dassopoulos T, Harris ML, Bayless TM, Brant SR, Chakravarti S, Kwon JH (2008) MicroRNAs are differentially expressed in ulcerative colitis and alter expression of macrophage inflammatory peptide-2 alpha. Gastroenterology 135:1624–1635
Rao R, Nagarkatti P, Nagarkatti M (2015) Role of miRNA in the regulation of inflammatory genes in staphylococcal enterotoxin B-induced acute inflammatory lung injury and mortality. Toxicol Sci 144:284–297
Wu J, Wang R, Ye Z, Sun X, Chen Z, Xia F, Sun Q, Liu L (2015) Protective effects of methane-rich saline on diabetic retinopathy via anti-inflammation in a streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat model. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 466:155–161
Jin H, Qiao F, Wang Y, Xu Y, Shang Y (2015) Curcumin inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis of human non-small cell lung cancer cells through the upregulation of miR-192-5p and suppression of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Oncol Rep 34:2782–2789
Sun J, Fan Z, Lu S, Yang J, Hao T, Huo Q (2016) MiR-192 suppresses the tumorigenicity of prostate cancer cells by targeting and inhibiting nin one binding protein. Int J Mol Med 37:485–492
Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, Funovits J, Felson DT, Bingham CO 3rd, Birnbaum NS, Burmester GR, Bykerk VP, Cohen MD, Combe B, Costenbader KH, Dougados M, Emery P, Ferraccioli G, Hazes JM, Hobbs K, Huizinga TW, Kavanaugh A, Kay J, Kvien TK, Laing T, Mease P, Ménard HA, Moreland LW, Naden RL, Pincus T, Smolen JS, Stanislawska-Biernat E, Symmons D, Tak PP, Upchurch KS, Vencovsky J, Wolfe F, Hawker G (2010) 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum 62:2569–2581
Botla SK, Savant S, Jandaghi P, Bauer AS, Mücke O, Moskalev EA, Neoptolemos JP, Costello E, Greenhalf W, Scarpa A, Gaida MM, Büchler MW, Strobel O, Hackert T, Giese NA, Augustin HG, Hoheisel JD (2016) Early epigenetic downregulation of microRNA-192 expression promotes pancreatic cancer progression. Cancer Res 76:4149–4159
Luan TY, Zhu TN, Cui YJ, Zhang G, Song XJ, Gao DM, Zhang YM, Zhao QL, Liu S, Su TY, Zhao RJ (2015) Expression of caveolin-1 is correlated with lung adenocarcinoma proliferation, migration, and invasion. Med Oncol 32:207
Chatterjee M, Ben-Josef E, Thomas DG, Morgan MA, Zalupski MM, Khan G, Andrew Robinson C, Griffith KA, Chen CS, Ludwig T, Bekaii-Saab T, Chakravarti A, Williams TM (2015) Caveolin-1 is associated with tumor progression and confers a multi-modality resistance phenotype in pancreatic cancer. Sci Rep 5:10867
Liu WR, Jin L, Tian MX, Jiang XF, Yang LX, Ding ZB, Shen YH, Peng YF, Gao DM, Zhou J, Qiu SJ, Dai Z, Fan J, Shi YH (2016) Caveolin-1 promotes tumor growth and metastasis via autophagy inhibition in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol 40:169–178
Jin Y, Lu J, Wen J, Shen Y, Wen X (2015) Regulation of growth of human bladder cancer by miR-192. Tumour Biol 36:3791–3797
Geng L, Chaudhuri A, Talmon G, Wisecarver JL, Are C, Brattain M, Wang J (2014) MicroRNA-192 suppresses liver metastasis of colon cancer. Oncogene 33:5332–5340
Yang SY, Choi SA, Lee JY, Park AK, Wang KC, Phi JH, Koh EJ, Park WY, Park SH, Hwang do W, Jung HW, Kim SK (2015) miR-192 suppresses leptomeningeal dissemination of medulloblastoma by modulating cell proliferation and anchoring through the regulation of DHFR, integrins, and CD47. Oncotarget 6:43712–43730
Feng S, Cong S, Zhang X, Bao X, Wang W, Li H, Wang Z, Wang G, Xu J, Du B, Qu D, Xiong W, Yin M, Ren X, Wang F, He J, Zhang B (2011) MicroRNA-192 targeting retinoblastoma 1 inhibits cell proliferation and induces cell apoptosis in lung cancer cells. Nucleic Acids Res 39:6669–6678
Zhu D, Xie H, Li H, Cai P, Zhu H, Xu C, Chen P, Sharan A, Xia Y, Tang W (2015) Nidogen-1 is a common target of microRNAs MiR-192/215 in the pathogenesis of Hirschsprung’s disease. J Neurochem 134:39–46
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Jin, Z. & Lu, X. MicroRNA-192 suppresses cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in human rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes by downregulating caveolin 1. Mol Cell Biochem 432, 123–130 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-3003-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-3003-3