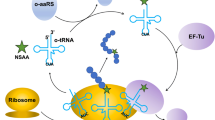
Abstract
Nature uses 20 canonical amino acids as the standard building blocks of proteins; however, the incorporation of unnatural amino acids (Uaas) can endow polypeptide sequences with new structural and functional features. Although aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases (aaRSs) can accept an array of Uaas in place of their natural counterparts, Uaas generally are charged to tRNAs with substantially lower efficiencies. This particularly makes it difficult to incorporate multiple Uaas into a protein sequence. In this study, we discuss the use of a cell-free protein synthesis system as a versatile platform for the efficient incorporation of multiple Uaas into proteins. Taking advantage of the open nature of cell-free protein synthesis that allows flexible manipulation of its ingredients, we explored the application of Uaas in 10 mM range of concentrations to kinetically overcome the low affinity of aaRSs towards unnatural amino acids. Supplementation of recombinant aaRSs was also investigated to further increase the Uaa-tRNA pools. As a result, under the modified reaction conditions, as many as five different Uaas could be incorporated into a single protein without compromising the yield of protein synthesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Refrerences
Liu, C. C. and P. G. Schultz (2010) Adding new chemistries to the genetic code. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 79: 413–444.
Bose, M., D. Groff, J. Xie, E. Brustad, and P. G. Schultz (2006) The incorporation of a photoisomerizable amino acid into proteins in E. coli. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128: 388–389.
Schultz, K. C., L. Supekova, Y. Ryu, J. Xie, R. Perera, and P. G. Schultz (2006) A genetically encoded infrared probe. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128: 13984–13985.
Tang, Y., G. Ghirlanda, W. A. Petka, T. Nakajima, W. F. DeGrado, and D. A. Tirrell (2001) Fluorinated coiled-coil proteins prepared in vivo display enhanced thermal and chemical stability. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 40: 1494–1496.
Meng, H. and K. Kumar (2007) Antimicrobial activity and protease stability of peptides containing fluorinated amino acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129: 15615–15622.
Wang, F., W. Niu, J. Guo, and P. G. Schultz (2012) Unnatural amino acid mutagenesis of fluorescent proteins. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51: 10132–10135.
Hartman, M. C., K. Josephson, and J. W. Szostak (2006) Enzymatic aminoacylation of tRNA with unnatural amino acids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 103: 4356–4361.
Hartman, M. C., K. Josephson, C. W. Lin, and J. W. Szostak (2007) An expanded set of amino acid analogs for the ribosomal translation of unnatural peptides. PLoS ONE. 2: e9–2.
Lepthien, S., L. Merkel, and N. Budisa (2010) In vivo double and triple labeling of proteins using synthetic amino acids. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 49: 5446–5450.
Link, A. J. and D. A. Tirrell (2005) Reassignment of sense codons in vivo. Methods. 36: 291–298.
Kiick, K. L., E. Saxon, D. A. Tirrell, and C. R. Bertozzi (2002) Incorporation of azides into recombinant proteins for chemoselective modification by the Staudinger ligation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 99: 19–24.
Bennett, B. D., E. H. Kimball, M. Gao, R. Osterhout, S. J. Van Dien, and J. D. Rabinowitz (2009) Absolute metabolite concentrations and implied enzyme active site occupancy in Escherichia coli. Nat. Biotechnol. 5: 593–599.
Minks, C., S. Alefelder, L. Moroder, R. Huber, and N. Budisa (2000) Towards new protein engineering: In vivo building and folding of protein shuttles for drug delivery and targeting by the selective pressure incorporation (SPI) method. Tetrahedron. 56: 9431–9442.
Ahn, J. H., K. H. Lee, J. W. Shim, E. Y. Lee, and D. M. Kim (2013) Streamlined cell-free protein synthesis from sequence information. Biotechnol. Bioproc. Eng. 18: 1101–1108.
Mathew, S., G. Shin, M. Shon, and H. Yun (2013) High throughput methods for ω-tramsaminases. Biotechnol. Bioproc. Eng. 18: 1–7.
Josephson, K., M. C. Hartman, and J. W. Szostak (2005) Ribosomal synthesis of unnatural peptides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127: 11727–11735.
Ozawa, K., M. J. Headlam, D. Mouradov, S. J. Watt, J. L. Beck, K. J. Rodgers, R. T. Dean, T. Huber, G. Otting, and N. E. Dixon (2005) Translational incorporation of L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine into proteins. FEBS J. 272: 3162–3171.
Stigers, D. J., Z. I. Watts, J. E. Hennessy, H. K. Kim, R. Martini, M. C. Taylor, K. Ozawa, J. W. Keillor, N. E. Dixon, and C. J. Easton (2011) Incorporation of chlorinated analogues of aliphatic amino acids during cell-free protein synthesis. Chem. Commun. 47: 1839–1841.
Kim, T. W., J. W. Keum, I. S. Oh, C. Y. Choi., C. G. Park, and D. M. Kim (2006) Simple procedures for the construction of a robust and cost-effective cell-free protein synthesis system. J. Biotechnol. 126: 554–561.
Kim, T. W., H. C. Kim, I. S. Oh, and D. M. Kim (2008) A highly efficient and economical cell-free protein synthesis system using the S12 extract of Escherichia coli. Biotechnol. Bioproc. Eng. 13: 464–469.
Pedelacq, J. D., S. Cabantous, T. Tran, T. C. Terwilliger, and G. S. Waldo (2006) Engineering and characterization of a superfolder green fluorescent protein. Nat. Biotechnol. 24: 79–88.
Keum, J. W., J. H. Ahn, C. Y. Choi, K. H. Lee, Y. C. Kwon, and D. M. Kim (2006) The presence of a common downstream box enables the simultaneous expression of multiple proteins in an E. coli extract. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 350: 562–567.
Kim, D. M. and C. Y. Choi (1996) A semicontinuous prokaryotic coupled transcription/translation system using a dialysis membrane. Biotechnol. Prog. 12: 645–649.
Ahn, J. H., M. Y. Hwang, I. S. Oh, K. M. Park, G. H. Hahn, C. Y. Choi, and D. M. Kim (2006) Preparation method for Escherichia coli S30 extracts completely dependent upon tRNA addition to catalyze cell-free protein synthesis. Biotechnol. Bioproc. Eng. 11: 420–424.
Schagger, H. (2006) Tricine-SDS-PAGE. Nat. Protoc. 1: 16–22.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oh, SJ., Lee, KH., Kim, HC. et al. Translational incorporation of multiple unnatural amino acids in a cell-free protein synthesis system. Biotechnol Bioproc E 19, 426–432 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-013-0849-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-013-0849-4