Abstract
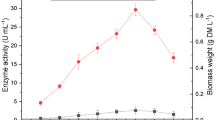
The production of ligninolytic enzymes by the fungus Schizophyllum sp. F17 using a cost-effective medium comprised of agro-industrial residues in solid-state fermentation (SSF) was optimized. The maximum activities of the enzymes manganese peroxidase (MnP), laccase (Lac), and lignin peroxidases (LiP) were 1,200, 586, and 109 U/L, respectively, on day 5 of SSF. In vitro decolorization of three structurally different azo dyes by the extracellular enzymes was monitored to determine its decolorization capability. The results indicated that crude MnP, but not LiP and Lac, played a crucial role in the decolorization of azo dyes. After optimization of the dye decolorization system with crude MnP, the decolorization rates of Orange IV and Orange G, at an initial dye concentration of 50 mg/L, were enhanced to 76 and 57%, respectively, after 20 min of reaction at pH 4 and 35°C. However, only 8% decolorization of Congo red was observed. This enzymatic reaction system revealed a rapid decolorization of azo dyes with a low MnP activity of 24 U/L. Thus, this study could be the basis for the production and application of MnP on a larger scale using a low-cost substrate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Torres, E., I. Bustos-Jaimes, and S. L. Borgne (2003) Potential use of oxidative enzymes for the detoxification of organic pollutants. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 46: 1–15.
Robinson, T., G. McMullan, R. Marchant, and P. Nigam (2001) Remediation of dyes in textile effluent: A critical review on current treatment technologies with a proposed alternative. Bioresour. Technol. 77: 247–255.
Saratale, R. G., G. D. Saratale, J. S. Chang, and S. P. Govindwar (2011) Bacterial decolorization and degradation of azo dyes: A review. Taiwan. J.Inst. Chem. Eng. 42: 138–157.
Vandevivere, P. C., R. Bianchi, and W. Verstraete (1998) Treatment and reuse of wastewater from the textile wet-processing industry: Review of emerging technologies. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 72: 289–302.
Saratale, R. G., G. D. Saratale, D. C. Kalyani, J. S. Chang, and S. P. Govindwar (2009) Enhanced decolorization and biodegradation of textile azo dye Scarlet R by using developed microbial consortium-GR. Bioresour. Technol. 100: 2493–2500.
Zollinger, D. Ph., E. Bulten, A. Christenhusz, M. Bos, and W. E. van der Linden (1987) Computerized conductometric determination of stability constants of complexes of crown ethers with alkali metal salts and with neutral molecules in polar solvents. Anal. Chem. Acta 198: 207–222.
Chang, J.S., C. Chou, Y. C. Lin, P. J. Lin, J. Y. Ho, and T. L. Hu (2001) Kinetic characteristics of bacterial azo-dye decolorization by Pseudomonas luteola. Water Res. 35: 2841–2850.
Saratale, R. G., G. D. Saratale, J. S. Chang, and S. P. Govindwar (2009) Decolorization and biodegradation of textile dye Navy blue HER by Trichosporon beigelii NCIM-3326. J. Hazard. Mater. 166: 1421–1428.
Zhao, X. H. and I. R. Hardin (2007) HPLC and spectrophotometric analysis of biodegradation of azo dyes by Pleurotus ostreatus. Dyes Pigments. 73: 322–325.
Chang, J. S. and T. S. Kuo (2000) Kinetics of Bacterial Decolorization of Azo Dye with Escherichia coli NO3. Bioresour. Technol. 75: 107–111.
Zhang, J., M. Y. Feng, Y. C. Jiang, M. C, Hu. S. Li, and Q. G. Zhai (2012) Efficient decolorization/degradation of aqueous azo dyes using buffered H2O2 oxidation catalyzed by a dosage below ppm level of chloroperoxidase. Chem. Eng. J. 191: 236–242.
Zollinger, H. (1991) Colour Chemistry: Synthesis, Properties and Applications of Organic Dyes and Pigments. 5th ed., pp. 187. VCH Publishers, Weinheim, Germany.
Zeng, X. K., Y. J. Cai, X. R. Liao, X. L. Zeng, W. X. Li, and D. B. Zhang (2011) Decolorization of synthetic dyes by crude laccase from a newly isolated Trametes trogii strain cultivated on solid agro-industrial residue. J. Hazard. Mater. 187: 517–525.
Rai, H. S., M. S. Bhattacharya, J. Singh, T. K. Bansal, P. Vats, and U. C. Banerjee (2005) Removal of dyes from the effluent of textile and dyestuff manufacturing industry: A review of emerging techniques with reference to biological treatment. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 35: 219–238.
Verma, P. and D. Madamwar (2003) Decolorization of Synthetic Dyes by a Newly Isolated Strain of Serratia maerascens. World. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 19: 615–618.
Pointing, S. B. (2001) Feasibility of bioremediation by white-rot fungi. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 57: 20–33.
Wesenberg, D., I. Kyriakides, and S. N. Agathos (2003) Whiterot fungi and their enzymes for the treatment of industrial dye effluents. Biotechnol. Adv. 22: 161–187.
Radha, K. V., I. Regupathi, A. Arunagiri, and T. Murugesan (2005) Decolorization studies of synthetic dyes using Phanerochaete chrysosporium and their kinetics. Proc. Biochem. 40: 3337–3345.
Singh, S. and K. Pakshirajan (2010) Enzyme activities and decolourization of single and mixed azo dyes by the white-rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 64: 146–150.
Heinfling, A., M. Bergbauer, and U. Szewzyk (1997) Biodegradation of azo and phthalocyanine dyes by Trametes versicolour and Bjerkandera adusta. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 48: 261–266.
Kaal, E. E. J., J. A. Field, and T. W. Joyce (1995) Increasing ligninolytic enzyme activities in several white-rot Basidiomycetes by nitrogen-sufficient media. Bioresour. Technol. 2: 133–139.
Leontievsky, A. A., N. M. Myasoedova, and L. A. Golovleva (1994) Production of ligninolytic enzymes of the white rot fungus Panus tigrinus. J. Biotechnol. 3: 299–307.
Couto, S. R. and M. Á. Sanromán (2006) Application of solidstate fermentation to food industry-A review. J. Food. Eng. 76: 291–302.
Yu, G. C., X. H. Wen, R. Li, and Y. Qian (2006) In vitro degradation of a reactive azo dye by crude ligninolytic enzymes from nonimmersed liquid culture of Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Proc. Biochem. 41: 1987–1993.
Xu, F.J., H. Z. Chen, and Z. Z. Li (2001) Solid-state production of lignin peroxidase (LiP) and manganese peroxidase (MnP) by Phanerochaete chrysosporium using syeam-exploded straw as substrate. Bioresour. Technol. 80: 149–151.
Li, X. D. and R. Jia (2008) Decolorization and biosorption for Congo red by system rice hull-Schizophyllum sp. F17 under solid-state condition in a continuous flow packed-bed bioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 99: 6885–6892.
Jia, R., B. K. Tang, and X. B. Zhang (2004) Effect of veratryl alcohol and tween-80 ligninase on production and its roles in decolorization of azo dyes by white-rot basidiomycete PM2. Chin.. J. Biotechnol. 20: 302–305.
Xiao, Y. Z., J. Wang, Y. P. Wang, C. L. Pu, and Y. Y. Shi (2002) Studies on production, purification and partial characteristics of the extracellular laccase from Armilliria mellea. Chin. J. Biotechnol. 18: 457–462.
Naveena, B. J., M. Altaf, K. Bhadriah, and G. Reddy (2005) Selection of medium components by Plackett-Burman design for production of L(+) lactic acid by Lactobacillus amylophilus GV6 in SSF using wheat bran. Bioresour. Technol. 96: 485–490.
Zhou, J. Y., X. J. Yu, C. Ding, Z. P. Wang, Q. Q. Zhou, H. Pao, and W. M. Cai (2011) Optimization of phenol degradation by Candida tropicalis Z-04 using Plackett-Burman design and response surface methodology. J. Environ. Sci. 23: 22–30.
Singh, A., S. Tuteja, N. Singh, and N. R. Bishnoi (2011) Enhanced saccharification of rice straw and hull by microwavealkali pretreatment and lignocellulolytic enzyme production. Bioresour. Technol. 102: 1773–1782.
Levin, L., F. Forchiassin, and A. Viale (2005) Ligninolytic enzyme production and dye decolorization by Trametes trogii: Application of the Plackett-Burman experimental design to evaluate nutritional requirements. Proc. Biochem. 40: 1381–1387.
Cheng, X,B., R, Jia, P. S. Li, S. Q. Tu, Q. Zhu, W. Zh. Tang, and X. D. Li (2007) Purification of a new manganese peroxidase of the white-rot fungus Schizophyllum sp. F17, and decolorization of azo dyes by the enzyme. Enz. Microb. Tech. 41: 258–264.
Yang, J. S., H. L. Yuan, H. X. Wang, and W. X. Chen (2005) Purification and characterization of lignin peroxidases from Penicillium decumbens P6. World J. Microb. Biot. 21: 435–440.
Fakoussa, R. M. and M. Hofrichter (1999) Biotechnology and microbiology of coal degradation. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 52: 25–40.
Pricelius, S., C. Held, S. Sollner, S. Deller, M. Murkovic, R. Ullrich, M. Hofrichter, A. Cavaco-Paulo, P. Macheroux, and G. M. Guebitz (2007) Enzymatic reduction and oxidation of fibrebound azo-dyes. Enz. Microb. Tech. 40: 1732–1738.
Roberge, C., D. Amos, D. Pollard, and P. Devine (2009) Preparation and application of cross-linked aggregates of chloroperoxidase with enhanced hydrogen peroxide tolerance. J. Mol. Catal. B: Enz. 56: 41–45.
Park, J. B. and D. S. Clark (2006) Deactivation mechanisms of chloroperoxidase during biotransformations. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 93: 1190–1195.
Pazarlioglu, N. K., R. O. Urek, and F. Ergun (2005) Biodecolourization of Direct Blue 15 by immobilized Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Proc. Biochem. 40: 1923–1929.
Parshetti, G. K., S. D. Kalme, S. S. Gomare, and S. P. Govindwar (2007) Biodegradation of Reactive blue-25 by Aspergillus ochraceus NCIM-1146. Bioresour. Technol. 98: 3638–3642.
Kaushik, P. and A. Malik (2009) Fungal dye decolourization: Recent advances and future potential. Environ. Int. 35: 127–141.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, J., Jia, R., Zheng, L. et al. Rapid decolorization of azo dyes by crude manganese peroxidase from Schizophyllum sp. F17 in solid-state fermentation. Biotechnol Bioproc E 18, 868–877 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-013-0357-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-013-0357-6