Abstract
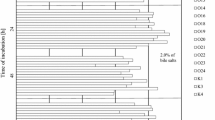
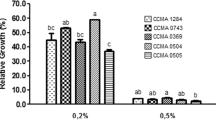
In this study, twenty Lactobacillus plantarum strains which were isolated from the fecal samples of humans were investigated in vitro for their characteristics as potential new probiotic strains. The L. plantarum strains were examined for resistance to gastric acidity in simulated gastric juice at pH 2.0, 2.5, 3.0, and 3.5. The growth of test cultures with different pH was monitored after 0, 10, 30, 60, 90, and 120 min of incubation using a spectrophotometer at 550 nm. At the same time, samples were serially diluted in sterile PBS, and counts of viable bacteria were determined by plate counts using MRS agar for each pH and time parameter. The strains were also examined for resistance to 0.4% phenol, production of H2O2, adhesion to Caco-2 cell line and antimicrobial activity. It was determined that the artificial gastric juice, even at pH 2.0, did not significantly change the viability of the cultures. Except L. plantarum AA1-2, all strains were detected at 8 ∼ 9 log10 CFU/g. It was found that all L. plantarum strains showed good resistance to 0.4% phenol, and only one strain (AC18-82) produced H2O2. Good adhesion of L. plantarum strains to Caco-2 cells was observed in this experiment. These selected strains also showed antimicrobial activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
FAO/WHO (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations and World Health Organization) (2001) Expert Consultation Report. Evaluation of health and nutritional properties of powder milk and live lactic acid bacteria. Rome, Italy.
Tuomola, E., R. Crittenden, M. Playne, E. Isolauri, and S. Salminen (2001) Quality assurance criteria for probiotic bacteria. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 73: 393–398.
Ouwehand, A. C., S. Salminen, and E. Isolauri (2002) Probiotics: An overview of beneficial effects. Anton. Leeuw. Int. J. G. 82: 279–289.
Gilliland, S. E. and D. K. Walker (1990) Factors to consider when selecting a culture of Lactobacillus acidophilus as a dietary adjunct to produce a hypocholesterolemic effect in humans. J. Dairy. Sci. 73: 905–911.
Kos, B., J. Šušković, J. Beganović, K. Gjuračić, J. Frece, C. Iannaccone, and F. Canganella (2008) Characterization of the three selected probiotic strains for the application in food industry. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 24: 699–707.
Salminen, O., S. Lahtinen, and L. Ahtee (1996) Expressionof Fosprotein in various rat brain are as following acute nicotine and diazepam. Pharmacol. Biochem. Be. 54: 241–248.
Bianchi, M. A., D. Del Rio, N. Pellegrini, G. Sansebastiano, and E. Neviani (2004) A fluorescence-based method for the detection of adhesive properties of lactic acid bacteria to Caco-2 cells. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 39: 301–305.
Chauviere, G., M. H. Coconnier, S. Kerneis, J. Fourniat, and A. L. Servin (1992) Adhesion of Lactobacillus acidophilus strain LB to human enterocyte-like Caco-2 cells. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 138: 1689–1696.
Wang, B., H. Wei, J. Yuan, Q. Li, Y. Li, N. Li, and J. Li (2008) Identification of a surface protein from Lactobacillus reuteri JCM1081 that adheres to porcine gastric mucin and human enterocyte-like HT-29 Cells. Curr. Microbiol. 57: 33–38.
Moussavi, M. and M. C. Adams (2009) An in vitro study on bacterial growth interactions and intestinal epithelial cell adhesion characteristics of probiotic combinations. Curr. Microbiol. 60: 327–335.
Duary, R. K., Y. S. Rajput, V. K. Batish, and S. Grover (2011) Assessing the adhesion of putative indigenous probiotic lactobacilli to human colonic epithelial cells. Indian J. Med. Res. 134: 664–671.
De Vries, M. C., E. E. Vaughan, M. Kleerebezem, and W. M. De Vos (2006) Lactobacillus plantarum-survival, functional and potential probiotic properties in the human intestinal tract. Int. Dairy J. 16: 1018–1028.
Tallon, B., P. Bressollier, and M. C. Urdaci (2003) Isolation and characterization of two exopolysaccharides produced by Lactobacillus plantarum EP56. Res. Microbiol. 154: 705–712.
Bujalance, C., E. Moreno, M. Jimenez-Valera, and A. Ruiz-Bravo (2007) A probiotic strain of Lactobacillus plantarum stimulates lymphocyte responses in immunologically intact and immuno compromised mice. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 113: 28–34.
Fuentes, S., M. Egert, M. Jimenez-Valera, M. Monteoliva-Sanchez, A. Ruiz-Bravo, and H. Smidt (2008) A strain of Lactobacillus plantarum affects segmented filamentous bacteria in the Intestine of immuno suppressed mice. Fems Microbiol. Ecol. 63: 65–72.
Cammarota, M., M. De Rosa, A. Stellavato, M. Lamberti, I. Marzaioli, and M. Giuliano (2009) In vitro evaluation of Lactobacillus plantarum DSMZ 12028 as a probiotic: Emphasis on innate immunity. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 135: 90–98.
Başyiğit Kılıç, G. and A. G. Karahan (2010) Identification of lactic acid bacteria isolated from the fecal samples of healthy humans and patients with dyspepsia and determination of their pH, bile and antibiotic tolerance properties. J. Mol. Microb. Biotech. 18: 220–229.
Corcoran, B. M., C. Stanton, G. F. Fitzgerald, and R. P. Ross (2005) Survival of probiotic lactobacilli in acidic environments is enhanced in the presence of metabolizable sugars. Appl. Environ. Microb. 71: 3060–3067.
Marshall, V. M. (1979) A note on screening hydrogen peroxideproducing lactic acid bacteria using a non-toxic chromogen. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 47: 327–328.
Hechard, Y., M. Dherbomez, Y. Cenatiempo, and F. Lettllier (1990) Antagonism of lactic acid bacteria from goats’ milk against pathogenic strains assessed by the ‘sandwich method’. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 11: 185–188.
Zago, M., M. E. Fornasari, D. Carminati, P. Burns, V. Suàrez, G. Vinderola, J. Reinheimer, and G. Giraffa (2011) Characterization and probiotic potential of Lactobacillus plantarum strains isolated from cheeses. Food Microbiol. 28: 1033–1040.
Chou, L. and B. Weimer (1999) Isolation and characterization of acid and bile tolerant isolates from strains of Lactobacillus acidophilus. J. Dairy Sci. 82: 23–31.
Corzo, G. and S. E. Gilliland (1999) Bile salt hydrolase activity of three strains of Lactobacillus acidophilus. J. Dairy Sci. 82: 472–480.
Jacobsen, C. N., V. Rosenfeldt-Nielsen, A. E. Hayford, P. L. Møller, K. F. Michaelsen, A. Pærregaard, B. Sandström, M. Tvede, and M. Jakobsen (1999) Screening of probiotic activities of forty-seven strains of Lactobacillus spp. by in vitro techniques and evaluation of the colonization ability of five selected strains in humans. Appl. Environ. Microb. 65: 4949–4956.
Cebeci, A. and C. Gürakan (2003) Properties of potential probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum strains. Food Microbiol. 20: 511–518.
Pisano, M. B., F. Patrignani, S. Cosentino, M. E. Guerzoni, C. M. A. P. Franz, and W. H. Holzapfel (2011) Diversity and functional properties of Lactobacillus plantarum-group strains isolated from Italian cheese products. Dairy Sci. Technol. 91: 65–76.
Xanthopoulos, V., E. Litopoulou-Tzanetaki, and N. Tzanetakis (2000) Characterisation of Lactobacillus isolates from infant faeces as dietary adjuncts. Food Microbiol. 17: 205–215.
Aswathy, R. G., B. Ismail, R. P. John, and K. M. Nampoothiri (2008) Evaluation of the probiotic characteristics of newly isolated lactic acid bacteria. Appl. Biochem. Biotech. 151: 244–255.
Vizoso Pinto, M. G., C. M. A. P. Franz, U. Schillinger, and W. H. Holzapfel (2006) Lactobacillus spp. with in vitro probiotic properties from human faeces and traditional fermented products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 109: 205–214.
Klebanoff, S. J. and R. W. Coombs (1991) Viricidal effect of Lactobacillus acidophilus on human immunodeficiency virus type 1: Possible role in heterosexual transmission. J. Exp. Med. 174: 289–292.
Aymerich, T., M. T. Artigas, J. M. Monfort, and M. Hugas (2000) Effect of sausage ingredients and additives on the production of enterocins A and B by Enterococcus faecium CTC492. Optimization of in vitro production and anti-listerial effect in dry fermented sausages. J. Appl. Microbiol. 88: 686–694.
Wei, H., G. Wolf, and W. P. Hammes (2006) Indigenous microorganisms from iceberg lettuce with adherence and antagonistic potential for use as protective culture. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. 7: 294–301.
Siripatrawan, U. and B. R. Harte (2007) Solid phase microextraction/gas chromatography/massspectrometry integrated with chemometrics for detection of Salmonella typhimurium contamination in a packaged fresh vegetable. Anal. Chim. Acta 581: 63–70.
Amin, M., H. Goodarzi, Z. Orang, S. Farsi, and M. Jorfi (2011) Isolation and identification of Lactobacillus species from the vagina and their antimicrobial properties. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 5: 3300–3304.
Ridwan, B. U., C. J. M. Koning, M. G. H. Besselink, H. M. Timmerman, E. C. Brouwer, J. Verhoef, H. G. Gooszen, and L. M. A. Akkermans (2008) Antimicrobial activity of a multispecies probiotic (Ecologic 641) against pathogens isolated from infected pancreatic necrosis. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 46: 61–67.
Hamama, A., A. El Marrakchi, and F. El Othmani (1992) Occurrence of Yersinia enterocolitica in milk and dairy products in Morocco. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 16: 69–77.
Binderova, E. and D. Rysanek (1999) Microbial contaminants of milk processed by high-temperature short-time pasteurization. Vet. Med. Czech. 44: 301–307.
Navrotilava, P., J. Schlegelova, A. Sustackova, E. Napravnikova, J. Lukasova, and E. Klimova (2004) Prevalence of Listeria monocytogenes in milk, meat and food stuff of animal origin and the phenotype of antibiotic resistance of isolated strains. Vet. Med. Czech. 49: 243–252.
Kumaresan, G. and R. A. Villi (2008) Incidence of Pseudomonas species in pasteurized milk. Tamilnadu J. Vet. Animal Sci. 4: 56–59.
Matijasic, B. B., M. Narat, and M. Zoric (2003) Adhesion of two Lactobacillus gasseri probiotic strains on Caco-2 cells. Food Technol. Biotech. 41: 83–88.
Candela, M., G. Seibold, B. Vitali, S. Lachenmaier, B. J. Eikmanns, and P. Brigidi (2005) Real-time PCR quantification of bacterial adhesion to Caco-2 cells: Competition between bifidobacteria and enteropathogens. Res. Microbiol. 156: 887–895.
Nawaz, M., J. Wang, A. Zhou, C. Ma, X. Wu, and J. Xu (2011) Screening and characterization of new potentially probiotic lactobacilli from breast-fed healthy babies in Pakistan. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 5: 1428–1436.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kılıç, G.B., Kuleaşan, H., Sömer, V.F. et al. Determining potential probiotic properties of human originated Lactobacillus plantarum strains. Biotechnol Bioproc E 18, 479–485 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-012-0785-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-012-0785-8