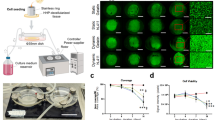
Abstract
Endothelial cell coverage of blood-contacting devices is crucial to their eventual success in the clinic. Two established human cell lines derived from HUVEC (human umbilical vascular endothelial cells), CRL 2922 and CRL 2873, have been widely utilized to study and model endothelial cell biology. However, it is not clear if these two cell lines would be useful for modeling primary endothelial cell interaction with newly-formulated biomaterials in tissue engineering applications. Hence, this study was conducted to compare the adhesion and proliferation characteristics of HUVEC grown on seven different substrata, tissue culture polystyrene (TCPS), gelatin, chitosan, poly-L-lysine, hyaluronan, poly-L-lactic acid (PLLA), and polylactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA). The short-term adhesive behavior (2 h) of HUVEC on the various substrata was not closely-replicated by either CRL 2873 or CRL 2922. This was likely because the 2 h timeframe is too short for identification of differences in the interaction among the three cell types grown on various substrata. There was much faster proliferation of CRL 2922 on all seven substrata when compared to HUVEC and CRL 2873. Moreover, the proliferation rates of CRL 2922 on the various substrata showed little variation. In contrast, HUVEC and CRL 2873 displayed similar trends in proliferation rates, with gelatin and TCPS yielding the highest rates, and PLLA and PLGA yielding the lowest rates. Hence, CRL 2873 is better suited for modeling primary endothelial cell interaction with newly-formulated biomaterials than CRL 2922. The advantage of using CRL 2873 over HUVEC for biomaterial screening is that it is immortalized and displays much less inter-batch variability than primary culture.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Merx, M. W., A. Zernecke, E. A. Liehn, A. Schuh, E. Skobel, B. Butzbach, P. Hanrath, and C. Weber (2005) Transplantation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells improves left ventricular function in a rat model of myocardial infarction. Basic Res. Cardiol. 100: 208–216.
Inamori, M., H. Mizumoto, and T. Kajiwara (2009) An approach for formation of vascularized liver tissue by endothelial Cell-covered hepatocyte spheroid integration. Tissue Eng. Part A. 15: 2029–2037.
Consigny, P. M. (2000) Endothelial cell seeding on prosthetic surfaces. J. Long Term Eff. Med. Implants. 10: 79–95.
Venkatraman, S., F. Boey, and L. L. Lao (2008) Implanted cardiovascular polymers: Natural, synthetic and bio-inspired. Prog. Poly. Sci. 33: 853–874.
Gao, C., X. Hu, Y. Hong, J. Guan, and J. Shen (2003) Photografting of poly(hydroxylethyl acrylate) onto porous polyurethane scaffolds to improve their endothelial cell compatibility. J. Biomater Sci. Polym. Ed. 14: 937–950.
Risbud, M. V., E. Karamuk, R. Moser, and J. Mayer (2002) Hydrogel-coated textile scaffolds as three-dimensional growth support for human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs): Possibilities as coculture system in liver tissue engineering. Cell Transplant. 11: 369–377.
Chu, C. F., A. Lu, M. Liszkowski, and R. Sipehia (1999) Enhanced growth of animal and human endothelial cells on biodegradable polymers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1472: 479–485.
Campillo-Fernández, A. J., R. E. Unger, K. Peters, S. Halstenberg, M. Santos, M. Salmerón Sánchez, J. M. Meseguer Dueñas, M. Monleón Pradas, J. L. Gómez Ribelles, and C. J. Kirkpatrick (2009) Analysis of the biological response of endothelial and fibroblast cells cultured on synthetic scaffolds with various hydrophilic/hydrophobic ratios: Influence of fibronectin adsorption and conformation. Tissue Eng. Part A. 15: 1331–1341.
Gifford, S. M., M. A. Grummer, S. A. Pierre, J. L. Austin, J. Zheng, and I. M. Bird (2004) Functional characterization of HUVEC-CS: Ca2+ signaling, ERK 1/2 activation, mitogenesis and vasodilator production. J. Endocrinol. 182: 485–499.
Ahn, K., S. Pan, K. Beningo, and D. Hupe (1995) A permanent human cell line (EA.hy926) preserves the characteristics of endothelin converting enzyme from primary human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Life Sci. 56: 2331–2341.
Ishiyama, M., Y. Miyazono, K. Sasamoto, Y. Ohkura, and K. Ueno (1997) A highly water-soluble disulfonated tetrazolium salt as a chromogenic indicator for NADH as well as cell viability. Talanta 44: 1299–1305.
American Type Culture Collection Catalog. http://www.atcc.org/ATCCAdvancedCatalogSearch/ProductDetails/tabid/452/Default.aspx?ATCCNum=CRL-1730&Template=cellBiology.
Takahashi, K., Y. Sawasaki, J. Hata, K. Mukai, and T. Goto (1990) Spontaneous transformation and immortalization of human endothelial cells. In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. 26: 265–274.
Fontijn, R., C. Hop, H. J. Brinkman, R. Slater, A. Westerveld, J. A. van Mourik, and H. Pannekoek (1995) Maintenance of vascular endothelial cell-specific properties after immortalization with an amphotrophic replication-deficient retrovirus containing human papilloma virus 16 E6/E7 DNA. Exp. Cell Res. 216: 199–207.
Kiessling, F., J. Kartenbeck, and C. Haller (1999) Cell-cell contacts in the human cell line ECV304 exhibit both endothelial and epithelial characteristics. Cell Tissue Res. 297: 131–140.
Brown, J., S. J. Reading, S. Jones, C. J. Fitchett, J. Howl, A. Martin, C. L. Longland, F. Michelangeli, Y. E. Dubrova, and C. A. Brown (2000) Critical evaluation of ECV304 as a human endothelial cell model defined by genetic analysis and functional responses: A comparison with the human bladder cancer derived epithelial cell line T24/83. Lab Invest. 80: 37–45.
Suda, K., B. Rothen-Rutishauser, M. Günthert, and H. Wunderli-Allenspach (2001) Phenotypic characterization of human umbilical vein endothelial (ECV304) and urinary carcinoma (T24) cells: Endothelial versus epithelial features. In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. Anim. 37: 505–514.
Lidington, E. A., D. L. Moyes, A. M. McCormack, and M. L. Rose (1999) A comparison of primary endothelial cells and endothelial cell lines for studies of immune interactions. Transpl. Immunol. 7: 239–246.
MacLeod, R. A., W. G. Dirks, Y. Matsuo, M. Kaufmann, H. Milch, and H. G. Drexler (1999) Widespread intraspecies cross-contamination of human tumor cell lines arising at source. Int. J. Cancer 83: 555–563.
Tanabe, H., Y. Takada, D. Minegishi, M. Durematsu, T. Mansui, and H. Mizusawa (1999) Cell line individualization by STR multiplex system in the cell bank found cross-contamination between ECV304 and EJ-1/T24. Tiss. Cul. Res. Commu. 18: 329–338.
Unger, R. E., V. Krump-Konvalinkova, K. Peters, and C. J. Kirkpatrick (2002) In vitro expression of the endothelial phenotype: Comparative study of primary isolated cells and cell lines, including the novel cell line HPMEC-ST1.6R. Microvasc. Res. 64: 384–397.
Imbert, E., A. A. Poot, C. G. Figdor, and J. Feijen (1998) Different growth behaviour of human umbilical vein endothelial cells and an endothelial cell line seeded on various polymer surfaces. Biomat. 19: 2285–2290.
Puklin-Faucher, E. and M. P. Sheetz (2009) The mechanical integrin cycle. J. Cell Sci. 122: 179–186.
Arnaout, M. A., S. L. Goodman, and J. P. Xiong (2007) Structure and mechanics of integrin-based cell adhesion. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 19: 495–507.
Zutter, M. M. (2007) Integrin-mediated adhesion: Tipping the balance between chemosensitivity and chemoresistance. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 608: 87–100.
Morgan, M. R., M. J. Humphries, and M. D. Bass (2007) Synergistic control of cell adhesion by integrins and syndecans. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 8: 957–969.
Campbell, I. D. (2008) Studies of focal adhesion assembly. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 36: 263–266.
Jockusch, B. M., P. Bubeck, K. Giehl, M. Kroemker, J. Moschner, M. Rothkegel, M. Rüdiger, K. Schlüter, G. Stanke, and J. Winkler (1995) The molecular architecture of focal adhesions. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 11: 379–416.
Eliceiri, B. P. and D. A. Cheresh (2000) Role of alpha v integrins during angiogenesis. Cancer J. 6: 245–249.
Byzova, T. V., R. Rabbani, S. E. D’souza, and E. F. Plow (1998) Role of integrin alpha(v)beta3 in vascular biology. Thromb. Haemost. 80: 726–734.
Shattil, S. J. (1995) Function and regulation of the beta 3 integrins in hemostasis and vascular biology. Thromb. Haemost. 74: 149–155.
Denis, C. V. (2002) Molecular and cellular biology of von Willebrand factor. Int. J. Hematol. 75: 3–8.
Woodfin, A., M. B. Voisin, and S. Nourshargh (2007) PECAM-1: A multi-functional molecule in inflammation and vascular biology. Arterioscler Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 27: 2514–2523.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heng, B.C., Xia, Y., Shang, X. et al. Comparison of the adhesion and proliferation characteristics of HUVEC and two endothelial cell lines (CRL 2922 and CRL 2873) on various substrata. Biotechnol Bioproc E 16, 127–135 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-010-0141-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-010-0141-9