Abstract
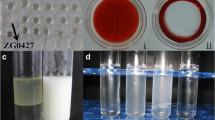
In this study, a biosurfactant-producing bacterial strain was isolated from oil-contaminated soil on the basis of its ability to degrade crude oil and tributyrin (C4:0). LSC04 was identified as Bacillus amyloliquefaciens LSC04 via 16S rRNA gene analysis and partial gyrA gene sequence analysis. The biosurfactants were purified and structural analysis results showed that B. amyloliquefaciens LSC04 generated a lipopeptide biosurfactant. Two main ions of 1,086.9 and 1,491.2 were measured via matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. The m/z 1,491.2 was shown to correspond to the lipopeptide fengycin B, but the m/z 1,086.9 ion did not correspond to any known lipopeptide. As constituents of the peptides and the lipophilic portion of the m/z 1,491.2; 10 amino acids (Ile-Tyr-Gln-Pro-Val-Glu-Ser-Tyr-Orn-Glu); and β-hydroxy-C17 fatty acid were identified via ESI-MS/MS. Structurally, the lipopeptide of a molecular mass of 1,491.2 differed from fengycin B and fengycin A by a substitution of serine for the threonine residue in position 4, and the amino acid residue in position 6 was equal to that of fengycin A. The major compound, which had a molecular mass of 1,491.2 Da was designated “Fengycin S”.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kretschner, A., H. Bock, and F. Wagnee (1982) Chemical and physical characterization of interfacial-active lipids from Rhodococcus erythropolis grown on n-alkane. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 44: 864–870.
Cho, W. S., E. H. Lee, E. H. Shim, J. S. Kim, H. W. Ryu, and K. S. Cho (2005) Bacterial communities of biofilms sampled from seepage groundwater contaminated with petroleum oil. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 15: 952–964.
Baek, K. H., H. S. Kim, S. H. Moon, I. S. Lee, H. M. Oh, and B. D. Yoon (2004) Effects of soil types on the biodegradation of crude oil by Nocardia sp. H17-1. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 15: 901–905.
Banat, I. M (1995) Characterization of biosurfactants and their use in pollution removal-state of the art. Acta Biotechnol. 15: 251–267.
Desai, J. D. and I. M. Banat (1997) Microbial production of surfactants and their commercial potential. Micrbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 61: 47–64.
Zajic, J. E., H. Guignard, and D. F. Gerson (1977) Properties and biodegradation of a bioemulsifier from Corynebacterium hydrocarboclatus. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 19: 1303–1302.
Rosenberg, E. and E. Z. Ron (1999) High- and low-molecular-mass microbial surfactants. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 52: 154–162.
Kuiper, I., E. L. Lagendijk, R. Pickford, J. P. Derrick, G. E. Lamers, J. E. T. Oates, B. J. Lugtenberg, and G. V. Bloemberg (2004) Characterization of two Pseudomonas putida lipopeptide biosurfactants, putisolvin I and II, which inhibit biofilm formation and break down existing biofilms. Mol. Microbiol. 51: 97–113.
Roongsawang, N., J. Thaniyavarn, S. Thaniyavarn, T. Kameyama, M. Haruki, T. Imanaka, M. Moriawa, and S. Kanaya (2002) Isolation and characterization of a halotolerant Bacillus subtilis BBK-1 which produces three kinds of lipopeptides: bacillomycin L, plipastatin, and surfactin. Extremophiles 6: 499–506.
Steller, S. and J. Vater (2000) Purification of the fengycin synthetase multienzyme system from Bacillus subtilis b213. J. Chromatogr. B: Biomed. Sci. Appl. 737: 267–275.
Hou, X., S. M. Boyetchko, M. Brkic, D. Olson, A. R. S. Ross, and D. D. Hegedus (2006) Characterization of the anti-fungal activity of a Bacillus spp. associated with sclerotia from Sclerotinia scelerotiorum. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 72: 644–653.
Ongena, M., P. Jacques, Y. Toure, J. Destain, A. Jabrane, and P. Thonart (2005) Involvement of fengycin-type lipopeptides in the multifaceted biocontrol potential of Bacillus subtilis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 69: 29–38.
Steller, S., D. Vollenbroich, F. Leenders, T. Stein, B. Conrad, J. Hofemeister, P. Jacques, and J. Vater (1999) Structural and functional organization of the fengycin synthetase multienzyme system from Bacillus subtilis b213 and A1/3. Chem. Biol. 6: 31–41.
Vater, J., B. Kablitz, C. Wilde, P. Franke, N. Mehta, and S. S. Cameotra (2002) Matrix-assisted laser desertion ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry of lipopeptide biosurfactants in whole cells and culture filtrates of Bacillus subtilis C-1 isolated from petroleum sludge. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 68: 6210–6219.
Wang, J., J. Liu, X. Wang, J. Yao, and Z. Yu (2004) Application of electrospray ionization mass spectrometry in rapid typing of fengycin homologues produced by Bacillus subtilis. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 39: 98–102.
Cutting, S. M. and H. P. B. Vander (1990) Genetic analysis. pp. 27–74. In: C. R. Harwood and S. M. Cutting (eds). Molecular Biological Methods for Bacillus. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., NJ, USA.
Magaritis, A., K. Kennedy, J. E. Zajic, and D. F. Gerson (1979) Biosurfactant production by Nocardia erythropolis. Dev. Ind. Microbiol. 20: 623–630.
Calvo, C., C. F. Martinez, A. Mota, V. Bejar, and E. Quesada (1998) Effect of cations, pH and sulfate content on the viscosity and emusifying activity on the Halomonas eurithalina. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 20: 205–209.
Cirigliano, M. C. and G. M. Carman (1985) Purification and characterization of liposan, a bioemusifier from Candida lipolytica. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 50: 846–850.
Eppard, M. W., E. Krrumbein, C. Kock, E. Rhiel, J. T. Sraley, and E. Stackebrandt (1996) Morphological, physiological, and molecular characterization of actinomycetes isolated from dry soil, rocks, and monuments surfaces. Arch. Microbiol. 166: 12–22.
Gray, J. P. and R. P. Herwig (1996) Phylogenetic analysis of the bacterial of the bacterial communities in marine sediments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 62: 4049–4059.
Kuske, C. R., S. M. Bams, and J. D. Busch (1997) Diverse uncultivated bacterial groups from soils of the arid southwestern United States that are present in many geographic regions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 63: 3614–3621.
Siefert, J. L., S. M. Larios, L. K. Nakamura, R. A. Slepecky, J. H. Paul, E. R. Moore, G. E. Fox, and P. J. Jurtshuk (2000) Phylogeny of marine Bacillus isolates from the Gulf of Mexico. Curr. Microbiol. 41: 84–88.
Wise, W. G., J. V. McArthur, and L. J. Skimkets (1997) Bacterial diversity of a Carolima bay as determined by 16S rRNA gene analysis: confirmation of novel taxa. Appl. Environ. Micrbiol. 63: 1505–1514.
Reva, O. N., C. Dixelius, J. Meijer, and F. G. Priest (2004) Taxonomic characterization and plant colonizing abilities of some bacteria related to Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and Bacillus subtilis. FEMS Ecol. Microbiol. 48: 249–259.
Chun, J. and K. S. Bae (2000) Phylogenetic analysis of Bacillus subtilis and related taxa based on partial gyrA gene sequence. Antonie van Leewenhoek 78: 123–127.
Lee, S. C., Y. J. Jung, J. S. Yoo, Y. S. Cho, I. H. Cha, and Y. L. Choi (2002) Characteristic of biosurfactants produced by Bacillus sp. LSC11. Kor. J. Life Sci. 12: 745–751.
Kim, S. H., E. J. Lim, S. O. Lee, J. D. Lee, and T. H. Lee (2000) Purification and characterization of biosurfactants from Nocardia sp. L-417. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 31: 249–253.
Suk, W. S., H. J. Son, G. Lee, and S. J. Lee (1999) Purification and characterization of biosurfactants produced by Pseudomonas sp. SW 1. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 9: 56–61.
Yakimov, M. M., K. N. Timmis, V. Wray, and H. L. Fredrickson (1995) Characterisation of a new lipopeptide surfactant produced by thermotolerant and halotolerant subsurface Bacillus licheniformis BAS50. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 61: 1706–1713.
Batista, S. B., A. H. Mounteer, F. R. Amorim, and M. R. Totola (2005) Isolation and characterization of biosurfactant/bioemusifier producing bacteria from petroleum contaminated sites. Bioresour. Technol. 97: 868–875.
Kim, S. H., S. C. Lee, I. H. Park, J. S. Yoo, W. H. Joo, C. W. Hwang, and Y. L. Choi (2005) Isolation and characterization of biosurfactant from Bacillus atrophaeus DYL-130. Kor. J. Life Sci. 15: 679–684.
Lee, S. C., J. S. Yoo, S. H. Kim, S. Y. Chung, C. W. Hwang, W. H. Joo, and Y. L. Choi (2006) Production and characterization of lipopeptide biosurfactant from Bacillus subtilis A8-8. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 16: 716–723.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sang-Cheol, L., Kim, SH., Park, IH. et al. Isolation, purification, and characterization of novel fengycin S from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens LSC04 degrading-crude oil. Biotechnol Bioproc E 15, 246–253 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-009-0037-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-009-0037-8