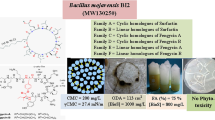
Abstract
Aiming the production of lipopeptides biosurfactants (BioS), we isolated a new strain identified as Bacillus subtilis ZNI5 from a hydrocarbon contaminated soil. Lipopeptides purification by anionic exchange chromatography and identification by Reverse Phase High Performance Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (RP-HPLC–MS) permitted the selection of different homologues divided into four families. The first family corresponds to Surfactin isoforms with molecular weights of 1007, 1021 and 1035 Da; the second family correspond to Iturin isoforms with molecular weights of 1028, 1042 and 1056 Da; the third family correspond to a single isoform called Licheniformin with molecular weight of 1410 and the fourth family correspond to newly identified isoforms named Inesfactin with molecular weights of 973 and 987 Da. Regarding the functional properties of the ZNI5 BioS, it was characterized as a powerful surface-active agent that decreases the Surface Tension of water from 72 mN/m to about 32 mN/m with a CMC value of 350 mg/L more efficient than chemical surfactants (Triton X100; CTAB and SDS). Moreover, it has the capacity to disperse oil to about 80 mm at a concentration of 800 mg/L showing close efficiencies to the listed chemical surfactants. In addition, the physic–chemical characterization of the surface activities of ZNI5 BioS showed great thermal, pH and salts activity and stability enabling its use in the bioremediation fields and for diverse industrial applications.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data sets supporting the conclusions of this article are included in the article.
Abbreviations
- ZNI5 BioS:
-
Biosurfactant produced by Bacillus subtilis ZNI5
References
Femina Carolin C, Senthil Kumar P, Tsopbou Ngueagni P (2021) A review on new aspects of lipopeptide biosurfactant: types, production, properties and its application in the bioremediation process. J Hazard Mater 407:124827
Mnif I, Ghribi D (2015) Microbial derived surface active compounds: properties and screening concept. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 31:1001–1020
Mnif I, Ghribi D (2015) High molecular weight bioemulsifiers, main properties and potential environmental and biomedical applications. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 31:691–706
Mnif I, Ghribi D (2015) Review lipopeptides biosurfactants: mean classes and new insights for industrial, biomedical, and environmental applications. J Pept Sci 104:129–147
Mnif I, Ghribi D (2015) Lipopeptide surfactants: production, recovery and pore forming capacity. Peptides 71:100–112
Mnif I, Sahnoun R, Ellouze-Chaabouni S, Ghribi D (2013) Evaluation of B. subtilis SPB1 biosurfactants’ potency for diesel-contaminated soil washing: optimization of oil desorption using Taguchi design. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:851–861
Mnif I, Ellouze-Chaabouni S, Ghribi D (2013) Economic production of Bacillus subtilis SPB1 biosurfactant using local agro-industrial wastes and its application in enhancing solubility of diesel. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 88:779–787
Mnif I, Ellouze-Chaabouni S, Ayedi Y, Ghribi D (2014) Treatment of diesel-and kerosene-contaminated water by B. subtilis SPB1 biosurfactant-producing strain. Water Environ Res 86:707–716
Mnif I, Mnif S, Sahnoun R, Maktouf S, Ayedi Y, Ellouze-Chaabouni S, Ghribi D (2015) Biodegradation of diesel oil by a novel microbial consortium: comparison between co-inoculation with biosurfactant-producing strain and exogenously added biosurfactants. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:14852–14861
Mnif I, Sahnoun R, Ellouz-Chaabouni S, Ghribi D (2017) Application of bacterial biosurfactants for enhanced removal and biodegradation of diesel oil in soil using a newly isolated consortium. Process Saf Environ Prot 109:72–81
do Amaral Marques NSA, Lima e Silva TA, da Silva Andrade RF, Branco Júnior JF, Okada K, Campos Takaki GM (2017) Lipopeptide biosurfactant produced by Mucor Circinelloides UCP/WFCC 0001 applied in the removal of crude oil and engine oil from soil. Acta Sci 41(1):e38986
Mnif I, Fendri R, Ghribi D (2015) Malachite green bioremoval by a newly isolated strain Citrobacter sedlakii RI11; enhancement of the treatment by biosurfactant addition. J Water Sci Technol 72:1283–1293
Mnif I, Fendri R, Ghribi D (2015) Biosorption of congo red from aqueous solution by Bacillus weihenstephanensis RI12; effect of SPB1 biosurfactant addition on biodecolorization potency. Water Sci Technol 72:865–874
Mnif I, Maktouf S, Fendri R, Kriaa M, Ellouze S, Ghribi D (2016) Improvement of methyl orange dye biotreatment by a novel isolated strain, Aeromonas veronii GRI, by SPB1 biosurfactant addition. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:1742–1754
Bouassida M, Fourati N, Ghazala I, Ellouze-Chaabouni S, Ghribi D (2018) Potential application of Bacillus subtilis SPB1 biosurfactants in laundry detergent formulations: compatibility study with detergent ingredients and washing performance. Eng Life Sci 18:70–77
Mohanty SS, Koul Y, Varjani S, Pandey A, Ngo HH, Chang J-S, Wong JWC, Bui X-T (2021) A critical review on various feedstocks as sustainable substrates for biosurfactants production: a way towards cleaner production. Microb Cell Fact. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-021-01613-3
Karlapudi AP, Venkateswarulu TC, Tammineedi J, Kanumuri L, Ravuru BK, Dirisala V, Kodali VP (2018) Role of biosurfactants in bioremediation of oil pollution-a review. Petroleum 4(3):241–249
Song D, Liang S, Zhang Q, Wang J, Yan L (2013) Development of high efficient and low toxic oil spill dispersants based on sorbitol derivants nonionic surfactants and glycolipid biosurfactants. J Environ Prot 4:16
Nikolova C, Gutierrez T (2021) Biosurfactants and their applications in the oil and gas industry: current state of knowledge and future perspectives. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2021.626639
Guodong Q, Yupeng Z, Xuhe R, Jie C (2015) Research on development and effectiveness evaluation technology of new environment-friendly oil spill dispersant. Aquatic Procedia 3:245–253
Pi G, Mao L, Bao M, Li Y, Gong H, Zhang J (2015) Preparation of oil-in-seawater emulsions based on environmentally benign nanoparticles and biosurfactant for oil spill remediation. ACS Sustain Chem 3:2686–2693
Mnif I, Ellouz-Chaabouni S, Ghribi D (2017) Glycolipid biosurfactants, main classes, functional properties and related potential applications in environmental biotechnology. J Polym Environ 26:2192–2206
Da Silva RS, Almeida D, Brasileiro P, Rufino R, Luna J, Sarubbo L (2017) Biosurfactant formulation of Pseudomonas cepacia and application in the removal of oil from coral reef. Chem Eng Trans 57:649–654
Sakthipriya N, Kumar G, Agrawal A, Doble M, Sangwai JS (2021) Impact of biosurfactants, surfactin, and rhamnolipid produced from Bacillus subtilis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, on the enhanced recovery of crude oil and its comparison with commercial surfactants. Energy Fuels 35(12):9883–9893
Kleindienst S, Seidel M, Ziervogel K, Grim S, Loftis K, Harrison S, Malkin SY, Perkins MJ, Field J, Sogin ML (2015) Chemical dispersants can suppress the activity of natural oil-degrading microorganisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112:14900–14905
Popovech M (2017): Analysis of hazards of dispersant constituents and review of toxicological studies, International Oil Spill Conference Proceedings. International Oil Spill Conference, pp. 311–330
Freitas BG, Brito JM, Brasileiro PP, Rufino RD, Luna JM, Santos VA, Sarubbo LA (2016) Formulation of a commercial biosurfactant for application as a dispersant of petroleum and by-products spilled in oceans. Front Microbiol 7:1646
Rongsayamanont W, Soonglerdsongpha S, Khondee N, Pinyakong O, Tongcumpou C, Sabatini DA, Luepromchai E (2017) Formulation of crude oil spill dispersants based on the HLD concept and using a lipopeptide biosurfactant. J Hazard Mater 334:168–177
Mnif I, Bouallegue A, Bouassida M, Ghribi D (2021) Surface properties and heavy metals chelation of lipopeptides biosurfactants produced from date flour by Bacillus subtilis ZNI5: optimized production for application in bioremediation. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-021-02635-2
Ghribi D, Abdelkefi-Mesrati L, Mnif I, Kammoun R, Ayadi I, Saadaoui I, Maktouf S, Chaabouni-Ellouze S (2012) Investigation of antimicrobial activity and statistical optimization of Bacillus subtilis SPB1 biosurfactant production in solid-state fermentation. J Biomed Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/373682
Landy M, Warren G, RosenmanM S, Colio L (1948) Bacillomycin: an antibiotic from Bacillus subtilis active against pathogenic fungi. Proc Soc Exp Biol 67:539–541
Bechard J, Eastwell K, Sholberg P, Mazza G, Skura B (1998) Isolation and partial chemical characterization of an antimicrobial peptide produced by a strain of Bacillus subtilis. J Agric Food Chem 46:5355–5361
Rodrigues L, Teixeira J, Oliveira R (2006) Low-cost fermentative medium for biosurfactant production by probiotic bacteria. Biochem Eng J 32:135–142
Ben Ayed H, Jridi M, Maalej H, Nasri M, Hmidet N (2014) Characterization and stability of biosurfactant produced by Bacillus mojavensis A21 and its application in enhancing solubility of hydrocarbon. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 89:1007–1014
Chen Z, Wu Q, Wang L, Chen S, Lin L, Wang H, Xu Y (2020) Identification and quantification of surfactin, a nonvolatile lipopeptide in Moutai liquor. Int J Food Prop 23:189–198
Hentati D, Chebbi A, Hadrich F, Frikha I, Rabanal F, Sayadi S, Manresa A, Chamkha M (2019) Production, characterization and biotechnological potential of lipopeptide biosurfactants from a novel marine Bacillus stratosphericus strain FLU5. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 167:441–449
Jemil N, Hmidet N, Manresa A, Rabanal F, Nasri M (2019) Isolation and characterization of kurstakin and surfactin isoforms produced by Enterobacter cloacae C3 strain. J Mass Spectrom 54:7–18
Kecskeméti A, Bartal A, Bóka B, Kredics L, Manczinger L, Shine K, Alharby NS, Khaled JM, Varga M, Vágvölgyi C (2018) High-frequency occurrence of surfactin monomethyl isoforms in the ferment broth of a Bacillus subtilis strain revealed by ion trap mass spectrometry. Molecules 23:2224
Mnif I, Grau-Campistany A, Coronel-León J, Hammami I, Triki MA, Manresa A, Ghribi D (2016) Purification and identification of Bacillus subtilis SPB1 lipopeptide biosurfactant exhibiting antifungal activity against Rhizoctonia bataticola and Rhizoctonia solani. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:6690–6699
Yang H, Li X, Li X, Yu H, Shen Z (2015) Identification of lipopeptide isoforms by MALDI-TOF-MS/MS based on the simultaneous purification of iturin, fengycin, and surfactin by RP-HPLC. Anal Bioanal Chem 407:2529–2542
Gong A-D, Li H-P, Yuan Q-S, Song X-S, Yao W, He W-J, Zhang J-B, Liao Y-C (2015) Antagonistic mechanism of iturin A and plipastatin A from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens S76–3 from wheat spikes against Fusarium graminearum. PLoS ONE 10:e0116871
Wang Y, Zhang C, Liang J, Wu L, Gao W, Jiang J (2020) Iturin a extracted from Bacillus subtilis WL-2 Affects Phytophthora infestans via cell structure disruption, oxidative stress, and energy supply dysfunction. Front Microbiol 11:2205
Zhao Q, Mei X, Xu Y (2016) Isolation and identification of antifungal compounds produced by Bacillus Y-IVI for suppressing Fusarium wilt of muskmelon. Plant Prot Sci 52:167–175
Zhou S, Liu G, Zheng R, Sun C, Wu S (2020) Structural and functional insights into iturin W, a novel lipopeptide produced by the deep-sea bacterium Bacillus sp. strain wsm-1. Appl Environ Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01597-20
Biria D, Maghsoudi E, Roostaazad R, Dadafarin H, Lotfi AS, Amoozegar M (2010) Purification and characterization of a novel biosurfactant produced by Bacillus licheniformis MS3. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 26:871–878
Mnif I, Bouallegue A, Mekki S, Ghribi D (2021) Valorization of date juice by the production of lipopeptide biosurfactants by a Bacillus mojavensis BI2 strain: bioprocess optimization by response surface methodology and study of surface activities. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-021-02606-7
Pacwa-Płociniczak M, Płaza GA, Piotrowska-Seget Z, Cameotra SS (2011) Environmental applications of biosurfactants: recent advances. Int J Mol Sci 12:633–654
Cao X-H, Liao Z-Y, Wang C-L, Yang W-Y, Lu M-F (2009) Evaluation of a lipopeptide biosurfactant from Bacillus natto TK-1 as a potential source of anti-adhesive, antimicrobial and antitumor activities. Braz J Microbiol 40:373–379
Durval IJB, Resende AHM, Figueiredo MA, Luna JM, Rufino RD, Sarubbo LA (2019) Studies on biosurfactants produced using Bacillus cereus isolated from seawater with biotechnological potential for marine oil-spill bioremediation. J Surfactants Deterg 22:349–363
Diniz Rufino R, Moura de Luna J, de Campos Takaki GM, Asfora Sarubbo L (2014) Characterization and properties of the biosurfactant produced by Candida lipolytica UCP 0988. Electron J Biotechnol 17:6–6
Ghazala I, Bouassida M, Krichen F, Manuel Benito J, Ellouz-Chaabouni S, Haddar A (2017) Anionic lipopeptides from Bacillus mojavensis I4 as effective antihypertensive agents: production, characterization, and identification. Eng Life Sci 17:1244–1253
Ghazala I, Bouallegue A, Haddar A, Ellouz-Chaabouni S (2019) Characterization and production optimization of biosurfactants by Bacillus mojavensis I4 with biotechnological potential for microbial enhanced oil recovery. Biodegradation 30:235–245
Jemil N, Ayed HB, Hmidet N, Nasri M (2016) Characterization and properties of biosurfactants produced by a newly isolated strain Bacillus methylotrophicus DCS1 and their applications in enhancing solubility of hydrocarbon. World J Microbiol 32:175
Martins PC, Bastos CG, Granjeiro PA, Martins VG (2018) New lipopeptide produced by Corynebacterium aquaticum from a low-cost substrate. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 41:1177–1183
Purwasena IA, Astuti DI, Syukron M, Amaniyah M, Sugai Y (2019) Stability test of biosurfactant produced by Bacillus licheniformis DS1 using experimental design and its application for MEOR. J Pet Sci Eng 183:106383
Pathak KV, Keharia H (2014) Application of extracellular lipopeptide biosurfactant produced by endophytic Bacillus subtilis K1 isolated from aerial roots of banyan (Ficus benghalensis) in microbially enhanced oil recovery (MEOR). Biotechnology 4:41–48
Phulpoto IA, Yu Z, Bowen H, Ndayisenga F, Jinmei L, Liang H, Qazi MA (2020) Production and characterization of surfactin-like biosurfactant produced by novel strain Bacillus nealsonii S2MT and it’s potential for oil contaminated soil remediation. Microb Cell Fact. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-020-01402-4
Zhu Z, Zhang B, Cai Q, Ling J, Lee K, Chen B (2020) Fish waste based lipopeptide production and the potential application as a bio-dispersant for oil spill control. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 8:734
Ravindran A, Sajayan A, Priyadharshini GB, Selvin J, Kiran GS (2020) Revealing the efficacy of thermostable biosurfactant in heavy metal bioremediation and surface treatment in vegetables. Front Microbiol 11:222
Lechuga M, Fernández-Serrano M, Jurado E, Núñez-Olea J, Ríos F (2016) Acute toxicity of anionic and non-ionic surfactants to aquatic organisms. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 125:1–8
Lémery E, Briançon S, Chevalier Y, Bordes C, Oddos T, Gohier A, Bolzinger M-A (2015) Skin toxicity of surfactants: structure/toxicity relationships. Colloids Surf A 469:166–179
Rebello S, Asok AK, Mundayoor S, Jisha M (2014) Surfactants: toxicity, remediation and green surfactants. Environ Chem Lett 12:275–287
Pornsunthorntawee O, Wongpanit P, Chavadej S, Abe M, Rujiravanit R (2008) Structural and physicochemical characterization of crude biosurfactant produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa SP4 isolated from petroleum-contaminated soil. Biores Technol 99:1589–1595
De Almeida DG, Da Silva S, RdCF LJM, Rufino RD, Santos VA, Banat IM, Sarubbo LA (2016) Biosurfactants: promising molecules for petroleum biotechnology advances. Front Microbiol 7:1718
Feng J-Q, Gang H-Z, Li D-S, Liu J-F, Yang S-Z, Mu B-Z (2019) Characterization of biosurfactant lipopeptide and its performance evaluation for oil-spill remediation. RSC Adv 9:9629–9632
Liu J-F, Mbadinga SM, Yang S-Z, Gu J-D, Mu B-Z (2015) Chemical structure, property and potential applications of biosurfactants produced by Bacillus subtilis in petroleum recovery and spill mitigation. Int J Mol Sci 16:4814–4837
Silva RDCF, Almeida DG, Rufino RD, Luna JM, Santos VA, Sarubbo LA (2014) Applications of biosurfactants in the petroleum industry and the remediation of oil spills. Int J Mol Sci 15:12523–12542
Chandran P, Das N (2010) Biosurfactant production and diesel oil degradation by yeast species Trichosporon asahii isolated from petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soil. Int J Eng Sci Technol 2:6942–6953
Qiao N, Shao Z (2010) Isolation and characterization of a new product by surfactant hydrocarbon-degrading bacterium Alcanivorax dieselolei B-5. J Appl Microbiol 108:1207–1216
Negin C, Ali S, Xie Q (2017) Most common surfactants employed in chemical enhanced oil recovery. Petroleum 3:197–211
Hewelke E, Szatyłowicz J, Hewelke P, Gnatowski T, Aghalarov R (2018) The impact of diesel oil pollution on the hydrophobicity and CO2 efflux of forest soils. Water Air Soil Pollut. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-3720-6
Gospodarek J, Rusin M, Barczyk G, Nadgórska-Socha A (2021) The effect of petroleum-derived substances and their bioremediation on soil enzymatic activity and soil invertebrates. Agronomy 11:80
Ahmed F, Fakhruddin ANMA (2018) Review on environmental contamination of petroleum hydrocarbons and its biodegradation. Int J Environ Sci Nat Res 11(3):63–69
Takashi A, Jin GY, Mizumoto S, Shahedur RM, Okuno K, Shoda M (2009) Solid state fermentation of lipopeptide antibiotic iturin A by using a novel solid state fermentation reactor system. J Environ Sci 21:S162–S165
Ghojavand H, Vahabzadeh F, Mehranian M, Radmehr M, Shahraki KA, Zolfagharian F, Emadi M, Roayaei E (2008) Isolation of thermotolerant, halotolerant, facultative biosurfactant-producing bacteria. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 80:1073–1085
Thimon L, Peypoux F, Michel G (1992) Interactions of surfactin, a biosurfactant from Bacillus subtilis, with inorganic cations. Biotech Lett 14:713–718
Huszcza E, Burczyk B (2003) Biosurfactant production by Bacillus coagulans. J Surfact Deterg 6:61–64
Chen Y, Liu SA, Mou H, Ma Y, Li M, Hu X (2017) Characterization of lipopeptide biosurfactants produced by Bacillus licheniformis MB01 from marine sediments. Front Microbiol 8:871
Karbalaei-Heidari HR, Taghavi L, Hasanizadeh P (2019) Functional evaluation and physicochemical characterization of a lipopeptide biosurfactant produced by the Stenotrophomonas sp. IE-93. Ir J Sci Technol Transact A 43:1447–1455
Kiran GS, Priyadharsini S, Sajayan A, Priyadharsini GB, Poulose N, Selvin J (2017) Production of lipopeptide biosurfactant by a marine Nesterenkonia sp. and its application in food industry. Front Microbiol 8:1138
Zouari O, Lecouturier D, Rochex A, Chataigne G, Dhulster P, Jacques P, Ghribi D (2019) Bio-emulsifying and biodegradation activities of syringafactin producing Pseudomonas spp. strains isolated from oil contaminated soils. Biodegradation 30:259–272
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported by grants from the Tunisian Ministry of Higher Education, Scientific Research and Technology. It is a part of a research project on biosurfactant production, characterization and application.
Funding
Funding for this research work was granted by the Ministry of Higher Education and Research of Tunisia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors directly participated in the planning, execution, or analysis of this study. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
All authors read the final manuscript and approved its submission to Journal of Polymers and the Environment.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mnif, I., Rajhi, H., Bouallegue, A. et al. Characterization of Lipopeptides Biosurfactants Produced by a Newly Isolated Strain Bacillus subtilis ZNI5: Potential Environmental Application. J Polym Environ 30, 2378–2391 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-021-02361-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-021-02361-6