Abstract
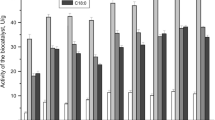
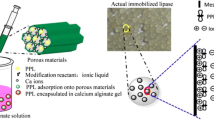
The immobilization of phospholipase D produced by Streptomyces sp. YU100 was evaluated to see it would be practical for industrial applications. To accomplish this, the purified enzyme, which contained 53 unit/mg of protein, was subjected to immobilization on various matrices. When immobilization supports including calcium alginate gel, polyacrylamide gel, and macroporous resin were evaluated, the highest enzyme retention ratio (> 42%) was observed on a Dowex MSA-2 macro-porous resin. This may have occurred as a result of the ability of the hydrophobic domain of phospholipase D to interact with the polystyrene backbone of the resin, as well as the ability of the dimethylethanolamine group of the MSA-2 resin to retain the enzyme by forming hydrogen bonds with the acidic residues of the enzyme. Upon the operation of a reactor packed with enzyme that had been immobilized on a Dowex MSA-2 resin, greater than 80% of the initial enzyme activity was retained for 16 days. During the reaction, phosphatidylcholine became bound to the immobilized resin and interfered with the enzyme reaction, therefore, the resin was washed with ethyl ether every 2 h. A process for recovering excessive l-serine from phospholipids using the Dowex MR-3 resin was designed, and the separated l -serine was employed again after replacing the amount that was used.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Crook, T. H., J. Tinklenberg, J. Yesavage, W. Petrie, M. G. Nunzi, and D. C. Massari (1991) Effects of phos-phatidylserine in age-associated memory impairment. Neurology 41: 644–649.
Monteleone, P., M. Maj, L. Beinat, M. Natale, and D. Kemali (1992) Blunting by chronic phosphatidylserine administration of the stress-induced activation of the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis in healthy men. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 42: 385–388.
Sakai, M., H. Yamatoya, and S. Kudo (1996) Pharmacological effects of phosphatidylserine enzymatically synthesized from soybean lecithin on brain functions in rodents. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 42: 47–54.
Suzuki, S., H. Yamatoya, M. Sakai, A. Kataoka, M. Furushiro, and S. Kudo (2001) Oral administration of soybean lecithin transphosphatidylated phosphatidylserine improves memory impairment in aged rats. J. Nutr. 131: 2951–2956.
Okawa, Y. and T. Yamaguchi (1975) Studies on phospholipases from Streptomyces. II. Purification and properties of Streptomyces hachijoensis phospholipase D. J. Biochem. 78: 363–372.
Shimbo, K., H. Yano, and Y. Miyamoto (1990) Purification and properties of phospholipase D from Streptomyces lydicus. Agric. Biol. Chem. 54: 1189–1193.
Shimbo, K., Y. Iwasaki, T. Yamane, and K. Ina (1993) Purification and properties of phospholipase D from Streptomyces antibioticus. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 57: 1946–1948.
Imamura, S. and Y. Horiuti (1979) Purification of Streptomyces chromofuscus phospholipase D by hydrophobic affinity chromatography on palmitoyl cellulose. J. Biochem. 85: 79–95.
Jeong, S. J., S. H. Lee, and T. B. Uhm (2004) Nucleotide sequence of an extracellular phospholipase D gene from Streptomyces somaliensis and transphosphatidylation activity of its enzyme. Kor. J. Microbiol. 32: 78–83.
Ogino, C., Y. Negi, T. Matsumiya, K. Nakaoka, A. Kondo, S. Kuroda, S. Tokuyama, U. Kikkawa, T. Yamane, and H. Fukuda (1999) Purification, characterization, and sequence determination of phospholipase D secreted by Streptoverticillium cinnamoneum. J. Biochem. 125: 263–269.
Lim, S. K., J. W. Choi, E. T. Lee, Y. H. Khang, S. D. Kim, and D. H. Nam (2002) Isolation of Streptomyces sp. YU100 producing extracellular phospholipase D. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 12: 71–76.
Lim, S. K., J. W. Choi, M. H. Chung, E. T. Lee, Y. H. Khang, S. D. Kim, and D. H. Nam (2002) Production and characterization of extracellular phospholipase D from Streptomyces sp. YU100. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 12: 189–195.
Moon, M.-W., J.-K. Lee, T.-K. Oh, C.-S. Shin, and H.-K. Kim (2006) Gene cloning of Streptomyces phospholipase D P821 suitable for synthesis of phosphatidylserine. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 16: 408–413.
Shinonaga, M.-A., Y. Kawamura, K. Shimbo, and T. Yamane (1996) Continuous production of phospholipase D by Streptomyces lydicus D-121 immobilized with cross-linked chitosan beads. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 81: 310–314.
Takami, M. and Y. Suzuki (1995) Transphosphatidylation reaction of phosphatidylcholine to 4-methoxyphenol in water-immiscible organic solvents with immobilized phospholipase D. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 79: 313–316.
Fukuda, H., Y. Turugida, T. Nakajima, E. Nomura, and A. Kondo (1996) Phospholipase D production using immobilized cells of Streptoverticillium cinnamoneum. Biotechnol. Lett. 18: 951–956.
Dittrich, N. and R. Ulbrich-Hofmann (2001) Transphosphatidylation by immobilized phospholipase D in aqueous media. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 34: 189–194.
Lee, D. H., J. M. Kim, H. Y. Shin, S. W. Kang, and S. W. Kim (2006) Biodiesel production using a mixture of immobilized Rhizopus oryzae and Candida rugosa lipases. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 11: 522–525.
Imamura, S. and Y. Horiuti (1978) Enzymatic determination of phospholipase D activity with choline oxidase. J. Biochem. 83: 677–680.
Iwasaki, Y., N. Mishima, K. Mizumoto, H. Nakano, and T. Yamane (1995) Extracellular production of phospholipase D of Streptomyces antibioticus using recombinant Escherichia coli. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 79: 417–421.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yon, J.O., Lee, J.S., Kim, B.G. et al. Immobilization of Streptomyces phospholipase D on a Dowex macroporous resin. Biotechnol Bioproc E 13, 102–107 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-007-0188-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-007-0188-4