Abstract
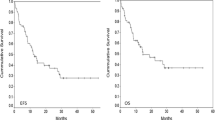
We present the results of a retrospective study of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) treatment in Serbia in the period 2000–2012. Treatment was performed in four centers, two of which were located in Belgrade, one in Nis, and one in Novi Sad. Children affected by non-acute promyelocytic leukemia (non-APL) subtypes received treatment regimens derived from protocols of Berlin Frankfurt Munster AML study group, whereas children with APL were treated according to the AIEOP/GIMEMA ATRA plus Idarubicin “AIDA” protocol. Total number of patients was 106, out of whom 48 were girls (45.3 %) and 58 boys (54.7 %); median age at diagnosis was 9.0 years (range 1 month–17.9 years). In total, 82.1 % of patients achieved complete remission after induction treatment. Twelve patients (11.3 %) died during induction, before achieving complete remission; there were nine deaths during remission (10.5 %) and 20 patients relapsed (23.2 %). Median time of follow-up was 54 months. Two patients (1.9 %) were lost to follow-up. Event-free survival was 50.3 % and overall survival was 58.9 %.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaspers GJ, Zwaan CM. Pediatric acute myeloid leukemia: towards high-quality cure of all patients. Haematologica. 2007;92(11):1519–32.
Krstovski N, Janic D, Dokmanovic L. Childhood acute myeloid leukaemia. J Pediatr Sci. 2010;2(3):e23.
Krstovski N, Tosic N, Janic D, et al. Incidence of FLT3 and nucleophosmin gene mutations in childhood acute myeloid leukemia: Serbian experience and the review of the literature. Med Oncol. 2010;27(3):640–5.
Kuzmanovic M, Rasovic N, Bunjevacki G, Scekic-Guc M, Bunjevacki V. Minimally differentiated acute myeloid leukemia (AML-M0) in children: a single center experience. Med Pediatr Oncol. 2000;34(5):364–5.
Creutzig U, Zimmermann M, Ritter J, et al. Treatment strategies and long-term results in paediatric patients treated in four consecutive AML-BFM trials. Leukemia. 2005;19(12):2030–42.
Testi AM, Biondi A, Lo Coco F, et al. GIMEMA-AIEOPAIDA protocol for the treatment of newly diagnosed acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) in children. Blood. 2005;106(2):447–53.
Ravindranath Y, Chang M, Steuber CP, et al. Pediatric Oncology Group (POG) studies of acute myeloid leukemia (AML): a review of four consecutive childhood AML trials conducted between 1981 and 2000. Leukemia. 2005;19(12):2101–16.
Creutzig U, Ritter J, Zimmermann M, et al. Improved treatment results in high-risk pediatric acute myeloid leukemia patients after intensification with high-dose cytarabine and mitoxantrone: results of Study Acute Myeloid Leukemia-Berlin-Frankfurt-Munster 93. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19(10):2705–13.
Xu XJ, Tang YM, Song H, Yang SL, Shi SW, Wei J. Long-term outcome of childhood acute myeloid leukemia in a developing country: experience from a children’s hospital in China. Leuk Lymphoma. 2010;51(12):2262–9.
Zhai XW, Cheng FW, Lee V, et al. Improved survival outcome of childhood acute myeloid leukemia with intensified chemotherapy in Chinese children. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2011;28(4):269–78.
Perel Y, Auvrignon A, Leblanc T, et al. Treatment of childhood acute myeloblastic leukemia: dose intensification improves outcome and maintenance therapy is of no benefit—multicenter studies of the French LAME (Leucemie Aigue Myeloblastique Enfant) Cooperative Group. Leukemia. 2005;19(12):2082–9.
Smith FO, Alonzo TA, Gerbing RB, Woods WG, Arceci RJ. Long-term results of children with acute myeloid leukemia: a report of three consecutive Phase III trials by the Children’s Cancer Group: CCG 251, CCG 213 and CCG 2891. Leukemia. 2005;19(12):2054–62.
Gibson BE, Wheatley K, Hann IM, et al. Treatment strategy and long-term results in paediatric patients treated in consecutive UK AML trials. Leukemia. 2005;19(12):2130–8.
Rubnitz JE, Gibson B, Smith FO. Acute myeloid leukemia. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2008;55(1):21–51, ix.
Gallegos-Castorena S, Medina-Sanson A, Gonzalez-Ramella O, Sanchez-Zubieta F, Martinez-Avalos A. Improved treatment results in Mexican children with acute myeloid leukemia using a Medical Research Council (MRC)-acute myeloid leukemia 10 modified protocol. Leuk Lymphoma. 2009;50(7):1132–7.
Dokmanovic L, Krstovski N, Vukanic D, et al. Pediatric non-Hodgkin lymphoma: a retrospective 14-year experience with Berlin-Frankfurt-Munster (BFM) protocols from a tertiary care hospital in Serbia. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2012;29(2):109–18.
Micic D, Slavkovic B, Rasovic Gvozdenovic N, et al. History of treatment and long-term outcome in children with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in Serbia. Mag Euro Med Oncol. 2011;4:174–7.
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nada, K., Milos, K., Dragana, V. et al. Treatment results of childhood acute myeloid leukemia in Serbia. memo 6, 63–68 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12254-012-0051-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12254-012-0051-y