Abstract
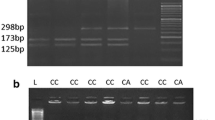
This pilot case-control study was conducted to test the hypothesis that the TATC (rs71682890) and CAA (rs34917480) insertion/deletion polymorphisms of RTN4 3’-UTR are associated with the susceptibility to uterine leiomyoma (UL). The study recruited 286 premenopausal women with UL and 450 unrelated postmenopausal women not presenting the disease as control subjects. The polymorphisms of rs71682890 and rs34917480 were genotyped with the method of polymerase chain reaction polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PCR - PAGE). No statistically significant association was observed between the TATC insertion/deletion polymorphism and UL risk. However, increased UL risk was identified to be significantly associated with CAA insertion/deletion polymorphism in the recessive and codominant model. The present study provided evidence for the first time that CAA polymorphism in RTN4 3’-UTR, but not TATC polymorphism may be involved in susceptibility to UL.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Duhan N (2011) Current and emerging treatments for uterine myoma - an update. Int J Womens Health 3:231–241
Hart RKY, Yeong CT, Seed P, Taylor A, Braude P (2001) A prospective controlled study of the effect of intramural uterine fibroids on the outcome of assisted conception. Hum Reprod 16:2411–2417
Ptacek TSC, Walker CL, Sell SM (2007) Physical mapping of distinct 7q22 deletions in uterine leiomyoma and analysis of a recently annotated 7q22 candidate gene. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 174:116–120
Morgan Ortiz FPRB, Elorriaga García E, Báez Barraza J, Quevedo Castro E, Peraza Garay Fde J (2011) Uterine leiomyomas during pregnancy and its impact on obstetric outcome. Ginecol Obstet Mex 79(8):467–473
Lee EJ, Kong G, Lee SH, Rho SB, Park CS, Kim BG, Bae DS, Kavanagh JJ, Lee JH (2005) Profiling of differentially expressed genes in human uterine leiomyomas. Int J Gynecol Cancer 15(1):146–154. doi:10.1111/j.1048-891x.2005.15016.x
Flynn MJM, Datta S, Myers E (2006) Health care resource use for uterine fibroid tumors in the United States. Am J Obstet Gynecol 195(4):955–964
Luoto RKJ, Rutanen EM, Taipale P, Perola M, Koskenvuo M (2000) Heritability and risk factors of uterine fibroids–the Finnish Twin Cohort study. Maturitas 37(1):15–26
Chen Y, Tang X, Cao X, Chen H, Zhang X (2006) Human Nogo-C overexpression induces HEK293 cell apoptosis via a mechanism that involves JNK-c-Jun pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 348(3):923–928. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.07.166
Shimakage MIN, Ohshima K, Kawahara K, Oka T, Yasui K, Matsumoto K, Inoue H, Watari A, Higashiyama S, Yutsudo M (2006) Down-regulation of ASY/Nogo transcription associated with progression of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Int J Cancer 119(7):1648–1653
Jung TYJS, Lee KH, Cao VT, Jin SG, Moon KS, Kim IY, Kang SS, Kim HS, Lee MC (2011) Nogo-A expression in oligodendroglial tumors. Neuropathology 31(1):11–19
Yicun Chen XT, Zhang X, Zhuang L (2009) New mutations of Nogo-C in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Biol Rep 36:377–380
Novak G, Tallerico T (2006) Nogo A, B and C expression in schizophrenia, depression and bipolar frontal cortex, and correlation of Nogo expression with CAA/TATC polymorphism in 3’-UTR. Brain Res 1120(1):161–171. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2006.08.071
Novak G, Kim D, Seeman P, Tallerico T (2002) Schizophrenia and Nogo: elevated mRNA in cortex, and high prevalence of a homozygous CAA insert. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 107(2):183–189
Zhou B, Rao L, Li Y, Gao L, Li C, Chen Y, Xue H, Liang W, Lv M, Song Y, Peng Y, Zhang L (2009) The association between dilated cardiomyopathy and RTN4 3’UTR insertion/deletion polymorphisms. Clin Chim Acta 400(1–2):21–24. doi:10.1016/j.cca.2008.09.028
Chen Y, Zhou B, Li H, Peng Y, Wang Y, Rao L (2011) Analysis of RTN4 3’UTR insertion/deletion polymorphisms in ventricular septal defect in a Chinese Han population. DNA Cell Biol 30(5):323–327. doi:10.1089/dna.2010.1116
Shi S, Zhou B, Wang Y, Chen Y, Zhang K, Wang K, Quan Y, Song Y, Rao L, Zhang L (2012) Genetic variation in RTN4 3’-UTR and susceptibility to cervical squamous cell carcinoma. DNA Cell Biol 31(6):1088–1094. doi:10.1089/dna.2011.1548
Sole X, Guino E, Valls J, Iniesta R, Moreno V (2006) SNPStats: a web tool for the analysis of association studies. Bioinformatics 22:1928–1929
Wei TGA, Qian HR, Su C, Helvering LM, Kulkarini NH, Shou J, N'Cho M, Bryant HU, Onyia JE (2007) DNA microarray data integration by ortholog gene analysis reveals potential molecular mechanisms of estrogen-dependent growth of human uterine fibroids. BMC Womens Health 7:5
Hiroshi Ishikawa SR, Demura M, Rademaker AW, Kasai T, Inoue M, Usui H, Shozu M, Bulun SE (2009) High aromatase expression in uterine leiomyoma tissues of African-American women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94:1752–1756
Ishwad CSFR, Hanley K, Davare J, Meloni AM, Sandberg AA, Surti U (1997) Two discrete regions of deletion at 7q in uterine leiomyomas. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 19:156–160
Xing YPPW, Morton CC (1997) The del(7q) subgroup in uterine leiomyomata: genetic and biologic characteristics. Further evidence for the secondary nature of cytogenetic abnormalities in the pathobiology of uterine leiomyomata. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 98(69–74):69
Meloni AMSU, Sandberg AA (1991) Deletion of chromosome 13 in leiomyomas of the uterus. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 53:199–203
Jennelle C, Hodge KTC, Huyck KL, Somasundaram P, Panhuysen CIM, Stewart EA, Morton CC (2009) Uterine leiomyomata and decreased height: a common HMGA2 predisposition allele. Hum Genet 125(3):257–263
Bowden WSJ, Kovanci E, Rajkovic A (2009) Detection of novel copy number variants in uterine leiomyomas using high-resolution SNP arrays. Mol Hum Reprod 15(9):563–568
Yaqin Chen SZ, Xiang R (2010) RTN3 and RTN4: candidate modulators in vascular cell apoptosis and atherosclerosis. J Cell Biochem 111:797–800
Oertle T, Huber C, van der Putten H, Schwab ME (2003) Genomic structure and functional characterisation of the promoters of human and mouse nogo/rtn4. J Mol Biol 325(2):299–323
Yang J, Yu L, Bi AD, Zhao SY (2000) Assignment of the human reticulon 4 gene (RTN4) to chromosome 2p14–2p13 by radiation hybrid mapping. Cytogenet Cell Genet 88(1–2):101–102
GrandPre T, Nakamura F, Vartanian T, Strittmatter SM (2000) Identification of the Nogo inhibitor of axon regeneration as a Reticulon protein. Nature 403(6768):439–444. doi:10.1038/35000226
Chen YC, Lu DD, Cao XR, Zhang XR (2005) RTN4-C gene expression in hepatocellular carcinoma and its influence on SMMC7721 cell growth and apoptosis. Yi Chuan Xue Bao 32(9):891–897
Zheng H, Xue S, Lian F, Wang YY (2011) A novel promising therapy for vein graft restenosis: overexpressed Nogo-B induces vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis by activation of the JNK/p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Med Hypotheses 77(2):278–281. doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2011.04.035
Watari A, Yutsudo M (2003) Multi-functional gene ASY/Nogo/RTN-X/RTN4: apoptosis, tumor suppression, and inhibition of neuronal regeneration. Apoptosis 8(1):5–9
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30871044, No. 81172440 and No. 30901596), the Applied Basic Research Programs of Science and Technology Commission Foundation of Sichuan Province (No. 2010SZ0122 and No. 2009SZ0163), and by Program for Chang-jiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University.
Disclosure Statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Kui Zhang and Peng Bai have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, K., Bai, P., Shi, S. et al. Association of Genetic Variations in RTN4 3’-UTR with Risk of Uterine Leiomyomas. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 19, 475–479 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-013-9604-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-013-9604-6