Abstract
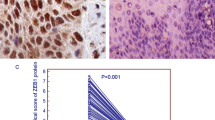
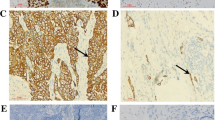
The objective is to explore the expression of high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) and its relationship with lymph node metastasis and the prognosis of patients as well as possible mechanism. The expression of HMGB1, vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGF-C) and lymphatic vessel endothelial hyaluronan receptor 1 (LYVE1) in ESCC tissues, which were obtained from 72 patients who underwent radical esophagectomy, was detected through immunohistochemistry, firstly. The correlations between HMGB1 and VEGF-C, and micro-lymphatic vessel density (MLD), and lymph node metastasis, and the prognosis of patients, were analyzed by statistic analysis. The plasmid of small interference RNA (siRNA) targeting HMGB1, giving siHMGB1, was transfected into exponentially growing KYSE150 human esophageal squamous cancer cells and the expression of HMGB1 mRNA and protein was observed by Real-time PCR and Western Blot and the expression of VEGF-C was examined by ELISA. HMGB1 expressed highly in the nuclei and cytoplasm of carcinoma cells as well as the extracellular space in ESCC and was associated with lymph node metastasis, MLD, the expression of VEGF-C, TNM stage and the prognosis of patients (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01). In vitro, siHMGB1 inhibited the expression of HMGB1 mRNA and protein and the secretion of VEGF-C in KYSE150 cells. In ESCC, HMGB1 expresses highly and affects the prognosis of patients through regulating the expression of VEGF-C to promote lymphangiogenesis and lymph node metastasis, and HMGB1 might serve as the marker of progression and potential target for anti-lymphangiogenesis therapy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Duff SE, Li C, Jeziorska M, Kumar S, Saunders MP, Sherlock D, O’Dwyer ST, Jayson GC (2003) Vascular endothelial growth factors C and D and lymphangiogenesis in gastrointestinal tract malignancy. Br J Cancer 89:426–30
Aurello P, Rossi Del Monte S, D’Angelo F, Cicchini C, Ciardi A, Bellagamba R, Ravaioli M, Ramacciato G (2009) Vascular endothelial growth factor C and microvessel density in gastric carcinoma: correlation with clinicopathological factors. Our experience and review of the literature. Oncol Res 17:405–11
Shimoda H, Takahashi Y, Kajiwara T, Kato S (2003) Demonstration of the rat lymphatic vessels using immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization for 5′- nucleotidase. Biomed Res 24:51–7
Liu P, Chen W, Zhu H, Liu B, Song S, Shen W, Wang F, Tucker S, Zhong B, Wang D (2009) Expression of VEGF-C correlates with a poor prognosis based on analysis of prognostic factors in 73 patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinomas. Jpn J Clin Oncol 39:644–50
Czura CJ, Wang H, Tracey KJ (2001) Dual roles for HMGB1: DNA binding and cytokine. J Endotoxin Res 7:315–21
Yao X, Zhao G, Yang H, Hong X, Bie L, Liu G (2010) Overexpression of high-mobility group box 1 correlates with tumor progression and poor prognosis in human colorectal carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 136:677–84
Palumbo R, Sampaolesi M, De Marchis F, Tonlorenzi R, Colombetti S, Mondino A, Cossu G, Bianchi ME (2004) Extracellular HMGB1, a signal of tissue damage, induces mesoangioblast migration and proliferation. J Cell Biol 164:441–49
Gnanasekar M, Thirugnanam S, Ramaswamy K (2009) Short hairpin RNA (shRNA) constructs targeting high mobility group box-1 (HMGB1) expression leads to inhibition of prostate cancer cell survival and apoptosis. Int J Oncol 34:425–431
Tang D, Kang R, Zeh HJ 3rd, Lotze MT (2010) High-mobility group box 1 and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 1799:131–40
Kusume A, Sasahira T, Luo Y, Isobe M, Nakagawa N, Tatsumoto N, Fujii K, Ohmori H, Kuniyasu H (2009) Suppression of dendritic cells by HMGB1 is associated with lymph node metastasis of human colon cancer. Pathobiology 76:155–62
Moriwaka Y, Luo Y, Ohmori H, Fujii K, Tatsumoto N, Sasahira T, Kuniyasu H (2010) HMGB1 attenuates anti-metastatic defense of the lymph nodes in colorectal cancer. Pathobiology 77:17–23
Kang HJ, Lee H, Choi HJ, Youn JH, Shin JS, Ahn YH, Yoo JS, Paik YK, Kim H (2009) Non-histone nuclear factor HMGB1 is phosphorylated and secreted in colon cancers. Lab Invest 89:948–59
Schlueter C, Weber H, Meyer B, Rogalla P, Röser K, Hauke S, Bullerdiek J (2005) Angiogenetic signaling through hypoxia HMGB1: an angiogenetic switch molecule. Am J Path 166:1259–63
Weidner N, Semple JP, Welch WR, Folkman J (1991) Tumor angiogenesis and metastasis –correlation in invasive breast carcinoma. N Engl J Med 324:1–8
Chen C, Sun J, Liu G, Chen J (2009) Effect of small interference RNA targeting HIF-1α mediated by rAAV combined L-ascorbate on pancreatic tumors in athymic mice. Pathol Oncol Res 15:109–14
Tuomela J, Valta M, Seppänen J, Tarkkonen K, Väänänen HK, Härkönen P (2009) Overexpression of vascular endothelial growth factor C increases growth and alters the metastatic pattern of orthotopic PC-3 prostate tumors. BMC Cancer 9:362
Zeh HJ 3rd, Lotze MT (2005) Addicted to death: invasive cancer and the immune response to unscheduled cell death. J Immunother 28:1–9
Ito N, DeMarco RA, Mailliard RB, Han J, Rabinowich H, Kalinski P, Stolz DB, Zeh HJ 3rd, Lotze MT (2007) Cytolytic cells induce HMGB1 release from melanoma cell lines. J Leukoc Biol 81:75–83
Acknowledgments
We thank Guo Yuhong and Luo Ye for their technologic support. This work was supported by National Nature Science Foundation of China (Grant 81071981) and Tianjin Municipal Bureau of Public Health Science Foundation (Grant 09KZ82 &2010KZ68).
Funding
National Nature Science Foundation of China (Grant 81071981) and Tianjin Municipal Bureau of Public Health Science Foundation (Grant 09KZ82 & 2010KZ68)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chuangui, C., Peng, T. & Zhentao, Y. The Expression of High Mobility Group Box 1 is Associated with Lymph Node Metastasis and Poor Prognosis in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 18, 1021–1027 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-012-9539-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-012-9539-3