Abstract
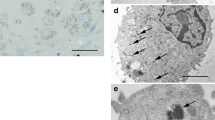
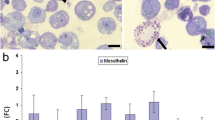
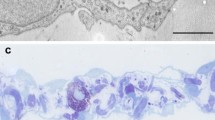
Intraperitoneal injection of Freund’s adjuvant induces acute peritonitis. By the time of the Freund’s adjuvant treatment the flat, simple squamous epithelial cells became rounded, cuboidal shaped, many of them have lost their connection with the neighbouring cells and detached from the basement membrane. The macrophage markers’ (ED1, OX43 and CD68) expression also increased in the mesothelial cells and more mesothelin and anti-ED1 double-labelled cells were found freely present close to the surface. The cytokeratin expression of the mesothelial cells has gradually decreased. At the 5th day of the inflammation practically there was no cytokeratin labelling present in the mesothelial cells and the mesothelin expression has significantly decreased. Parallel to this mesothelial cells started to express vimentin, a characteristic mesenchymal intermediate filament protein indicating that they gradually lost their epithelial character and gained mesenchymal phenotype. These results strongly suggest that under the effect of Freund’s adjuvant treatment (inflammation) mesothelial cells can undergo epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and differentiate into phagocytotic (macrophage-like) cells. Studying the caveolae/caveolin-1 on the plasma membrane of mesothelial cells we found that the Freund’s adjuvant treatment has changed the cellular distribution of caveolin-1: as the inflammation progressed strong caveolin-1 labelling was found inside of the cytoplasm (in perinuclear localization) indicating that inflammation induced the caveolae internalization. These results indicate that caveolae/caveolin-1 might play important regulatory role in signal transduction leading to trasdifferentiation.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EMT:
-
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
References
Savagner P (2001) Leaving the neighbourhood: Molecular mechanisms involved during epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Bioesssay 23:912–923
Camenisch TD, Molin DG, Person A, Runyan RB, Gittenberger-de Groot AC, McDonald JA, Klewer SE (2002) Temporal and distinct TGFß ligand requirements during mouse and avian endocardial cushon morphogenesis. Dev Biol 248:170–181
Piek E, Moustakas A, Kurisaki A, Heldin CH, ten Dijke P (1999) TGF-(beta) type I receptor/Alk-5 and Smad proteins mediate epithelial to mesenchymal transdifferentiation in NMuMG breast epithelial cells. J Cell Sci 112(Suppl):4557–4568
Moustakas A, Pardali K, Gaal A, Heldin CH (2002) Mechanisms of TGF-beta signalling in regulation of cell growth and differentiation. Immunol Lett 82:85–91
Kredict RT (1999) The peritoneal membrane in chronic peritoneal dialysis patients. Kidney Int 55:341–356
Boyer B, Valles AM, Edme N (2000) Induction and regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Biochem Pharmacol 60:1091–1099
Yang J, Liu Y (2001) Dissection of key events in tubular epithelial to myofibroblast transition and its implication in renal interstitial fibrosis. Am J Pathol 159:1465–1475
Tomasek JJ, Gabbiani G, Hinz B, Chaponnier C, Brown RA (2002) Myofibroblasts and mechanoregulation of connective tissue remodelling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3:349–363
Katz S, Balogh P, Kiss AL (2011) Mesothelial cells can detach from the mesentery and differentiate into macrophage-like cells. APMIS 119:782–793
Dijkstra CD, Döpp EA, Joling P, Kraal G (1985) The heterogeneity of mononuclear phagocytes in lymphoid organs: distinct macrophages subpopulation in the rat recognized by monoclonal antibodies ED1, ED2 and ED3. Immunology 54:589–599
Wiese C, Rollentschek A, Kania G, Blyszczuk P, Tarasova KV, Wersto RP, Boheler KR, Wobus AM (2004) Nestin expression—a property of multi-lineage progenitor cells? Cell Mol Life Sci 61:2510–2522
Yanez-Mó M, Lara-Pezzi E, Selgas R, Ramirez-Huesca M et al (2003) Peritoneal dialysis and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of mesothelial cells. New England J Medicine 348:403–413
von Ruhland CJ, Campbell L, Gumbleton M, Jasani B, Newman G (2004) Immunolocalization of caveolin-1 in rat and human mesothelium. JHistochem and Cytochem 52:1415–1425
Bishop AL, Hall A (2000) Rho GTPases and their effector proteins. Biochem J 348:241–255
Braga VM, Machesky LM, Hall A, Hotchin NA (1997) The small GTPases Rho and Rac are required for establishment of cadherin-dependent cell-cell contacts. J Cell Biol 137:1421–1431
Hordjik PL, Klooster JP, van der Kammen RA, Michiels F, Oomen LC, Collard JG (1997) Inhibition of invasion of epithelial cells by Tiam-1-Rac signalling. Science 278:1464–1466
Bakin AV, Rinehart C, Tomlinson AK, Arteaga CL (2002) p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase is required for TGFß-mediated fibroblastic transdifferentiation and cell migration. J Cell Science 115:3193–3206
Bakin AV, Tomlinson AK, Bhowmick NA, Moses HL, Arteaga CL (2000) Phosphatidyl inositol 3-kinase function is required for TGFbeta-mediated epithelial to mesenchymal transition and cell migration. J Biol Chem 275:36803–36810
Patel HH, Murray F, Insel PA (2008) Caveolae as organizers of pharmacologically relevant signa transduction molecules. Ann Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 48:359–391
Pelkmans L, Helenius A (2002) Endocytosis via caveolae. Traffic 3:311–320
Krajewska WM, Maslowska I (2004) Caveolins: structure and function in signal transduction. Cell Mol Biol Lett 9:195–220
Razani B, Zhang ZL, Bitzer M, von Gersdorff G, Böttinger EP, Lisanti MP (2001) Caveolin-1 regulates transforming growth factor (TGF)-ß-SMAD signalling through an interaction with the TGF-ß type I receptor. J Biol Chem 276:6727–6738
Zwaagstra JC, El-Alfy M, O’Connor-McCourt MD (2001) Transforming growth factor (TGF)-ß 1 internalization: modulation by ligand interaction with TGF-ß receptors types I and II and a mechanism that is distinct from clathrin-mediated endocytosis. J Biol Chem 276:27237–27245
Acknowledgements
The authors are very much grateful to Prof. Dr. C.D. Dijkstra (Amsterdam, The Netherlands) to provide ED1 antibody as a generous gift. We are grateful to Margit Kutasi and Katalin Lőcsey-Szemere for their valuable technical work. We are gratefully acknowledging Dr. Elisabeth Fromm for the language correction. This work was supported by TÁMOP. 4.2.1.B-09/1/KMR-2010-0001 grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katz, S., Balogh, P., Nagy, N. et al. Epithelial-To-Mesenchymal Transition Induced by Freund’s Adjuvant Treatment in Rat Mesothelial Cells: A Morphological and Immunocytochemical Study. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 18, 641–649 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-011-9489-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-011-9489-1