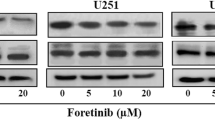
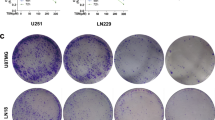
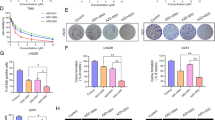
Abstract
Accumulating evidences suggest that glutamate plays a key role in the proliferation and invasion of malignant glioblastoma (GBM) tumors. It has been shown that GBM cells release and exploit glutamate for proliferation and invasion through AMPA glutamate receptors. Additionally, amplification of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene occurs in 40–50% of GBM. Since, PI3K/Akt is considered one of the main intracellular pathways involved in EGFR activation, AKT functions could trigger EGFR signaling. Thus, we investigated whether EGFR-phospho-Akt pathway is involved on the glutamate inducing U-87MG human GBM cell line proliferation. For these purpose, we treated the U-87MG cell line with 5 to 200 mM of glutamate and assessed the number of viable cells by trypan blue dye exclusion test. An increase in cell number (50%) was found at 5 mM glutamate, while the addition of DNQX (500 µM), an antagonist of AMPA receptor, inhibited the effect of glutamate on the U87-MG cells proliferation. Also, at 5 mM glutamate we observed an increase on the EGFR and phospho-Akt contents evaluated by immunohistochemistry. Moreover, U-87MG cells treated with glutamate exhibited an increase about 2 times in the EGFR mRNA expression. While, in the presence of the anti-EGFR gefitinib (50 μM) or the PI3K inhibitor wortmannin (5 μM), the U-87MG proliferation was restored to control levels. Together, our data suggest that glutamate signaling mediated by AMPA receptor induces U-87MG human GBM cell line proliferation via EGFR-phospho-Akt pathway.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CNS:
-
central nervous system
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s modified essential medium
- DNQX:
-
6,7-Dinitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione
- EGFR:
-
epidermal growth factor receptor
- FCS:
-
fetal calf serum
- GBM:
-
malignant glioblastoma
- PI3K:
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
- PIP2:
-
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-biphosphate
- PIP3:
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-triphosphate
References
Gupta T, Sarin R (2002) Poor-prognosis high-grade gliomas: evolving an evidence-based standard of care. Lancet Oncol 3:557–564
Nieder C, Astner ST, Mehta MP et al (2008) Improvement, clinical course, and quality of life after palliative radiotherapy for recurrent glioblastoma. Am J Clin Oncol 31:300–305
Hadziahmetovic M, Lo SS, Clarke JW et al (2008) Palliative treatment of poor prognosis patients with malignant gliomas. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 8:125–132
Behin A, Hoang-Xuan K, Carpentier AF et al (2003) Primary brain tumours in adults. Lancet 361:323–331
Gunther W, Skaftnesmo KO, Arnold H et al (2003) Molecular approaches to brain tumour invasion. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 145:1029–1036
Hoi Sang U, Espiritu OD, Kelley PY et al (1995) The role of the epidermal growth factor receptor in human gliomas: I. The control of cell growth. J Neurosurg 82:841–846
Chakravarti A, Chakladar A, Delaney MA et al (2002) The epidermal growth factor receptor pathway mediates resistance to sequential administration of radiation and chemotherapy in primary human glioblastoma cells in a RAS-dependent manner. Cancer Res 62:4307–4315
Krishnan S, Rao RD, James CD et al (2003) Combination of epidermal growth factor receptor targeted therapy with radiation therapy for malignant gliomas. Front Biosci 8:e1–13
Shinojima N, Tada K, Shiraishi S et al (2003) Prognostic value of epidermal growth factor receptor in patients with glioblastoma multiforme. Cancer Res 63:6962–6970
Aldape KD, Ballman K, Furth A et al (2004) Immunohistochemical detection of EGFRvIII in high malignancy grade astrocytomas and evaluation of prognostic significance. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 63:700–707
Lammering G, Valerie K, Lin PS et al (2004) Radiation-induced activation of a common variant of EGFR confers enhanced radioresistance. Radiother Oncol 72:267–273
Ohgaki H, Dessen P, Jourde B et al (2004) Genetic pathways to glioblastoma: a population-based study. Cancer Res 64:6892–6899
Korshunov A, Sycheva R, Golanov A (2005) The prognostic relevance of molecular alterations in glioblastomas for patients age <50 years. Cancer 104:825–832
Mellinghoff IK, Wang MY, Vivanco I et al (2005) Molecular determinants of the response of glioblastomas to EGFR kinase inhibitors. N Engl J Med 353:2012–2024
Arslantas A, Artan S, Oner U et al (2007) Genomic alterations in low-grade, anaplastic astrocytomas and glioblastomas. Pathol Oncol Res 13:39–46
Brandt B, Meyer-Staeckling S, Schmidt H et al (2006) Mechanisms of EGFR gene transcription modulation: relationship to cancer risk and therapy response. Clin Cancer Res 12:7252–7260
Sibilia M, Kroismayr R, Lichtenberger BM et al (2007) The epidermal growth factor receptor: from development to tumorigenesis. Differentiation 75:770–787
Choe G, Horvath S, Cloughesy TF et al (2003) Analysis of the phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase signaling pathway in glioblastoma patients in vivo. Cancer Res 63:2742–2746
Ghosh MK, Sharma P, Harbor PC et al (2005) PI3K-AKT pathway negatively controls EGFR-dependent DNA-binding activity of Stat3 in glioblastoma multiforme cells. Oncogene 24:7290–7300
Labrakakis C, Patt S, Hartmann J et al (1998) Glutamate receptor activation can trigger electrical activity in human glioma cells. Eur J NeuroSci 10:2153–2162
Sontheimer H (2008) A role for glutamate in growth and invasion of primary brain tumors. J Neurochem 105:287–295
Mahé C, Bernhard M, Bobirnac I et al (2004) Functional expression of the serotonin 5-HT7 receptor in human glioblastoma cell lines. Br J Pharmacol 143:404–410
Ye ZC, Sontheimer H (1999) Glioma cells release excitotoxic concentrations of glutamate. Cancer Res 59:4383–4391
Rzeski W, Turski L, Ikonomidou C (2001) Glutamate antagonists limit tumor growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:6372–6377
Ishiuchi S, Tsuzuki K, Yoshida Y et al (2002) Blockage of Ca(2+)-permeable AMPA receptors suppresses migration and induces apoptosis in human glioblastoma cells. Nat Med 8:971–978
D’Onofrio M, Arcella A, Bruno V et al (2003) Pharmacological blockade of mGlu2/3 metabotropic glutamate receptors reduces cell proliferation in cultured human glioma cells. J Neurochem 84:1288–1295
Aronica E, Gorter JA, Ijlst-Keizers H et al (2003) Expression and functional role of mGluR3 and mGluR5 in human astrocytes and glioma cells: opposite regulation of glutamate transporter proteins. Eur J NeuroSci 17:2106–2118
Arcella A, Carpinelli G, Battaglia G et al (2005) Pharmacological blockade of group II metabotropic glutamate receptors reduces the growth of glioma cells in vivo. Neuro-oncol 7:236–245
Takano T, Lin JH, Arcuino G et al (2001) Glutamate release promotes growth of malignant gliomas. Nat Med 7:1010–1015
Lyons SA, Chung WJ, Weaver AK et al (2007) Autocrine glutamate signaling promotes glioma cell invasion. Cancer Res 67:9463–9471
Ishiuchi S, Yoshida Y, Sugawara K et al (2007) Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors regulate growth of human glioblastoma via Akt activation. J Neurosci 27:7987–8001
Dziedzic B, Prevot V, Lomniczi A et al (2003) Neuron-to-glia signaling mediated by excitatory amino acid receptors regulates ErbB receptor function in astroglial cells of the neuroendocrine brain. J Neurosci 23:915–926
Yoshida Y, Tsuzuki K, Ishiuchi S et al (2006) Serum-dependence of AMPA receptor-mediated proliferation in glioma cells. Pathol Int 56:262–271
Sigalas E, Regan JD, Kramer PR et al (2004) Survival of human periodontal ligament cells in media proposed for transport of avulsed teeth. Dent Traumatol 20:21–28
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N (1987) Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162:156–159
Schmidt M, Bachhuber A, Victor A et al (2003) p53 expression and resistance against paclitaxel in patients with metastatic breast cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 129:295–302
Knobbe CB, Reifenberger G (2003) Genetic alterations and aberrant expression of genes related to the phosphatidyl-inositol-3′-kinase/protein kinase B (Akt) signal transduction pathway in glioblastomas. Brain Pathol 13:507–518
Regner A, Schunemann DP, Grivicich I et al (2005) Effects of toxic doses of glutamate on Cu-Zn and Mn/superoxide dismutases activities in human glioma cell lines. J Neurooncol 71:9–17
Campbell GL, Bartel R, Freidman HS et al (1985) Effect of glutamate analogues on brain tumor cell lines. J Neurochem 45:1186–1192
Chen CJ, Liao SL, Kuo JS (2000) Gliotoxic action of glutamate on cultured astrocytes. J Neurochem 75:1557–1565
Matute C, Alberdi E, Ibarretxe G et al (2002) Excitotoxicity in glial cells. Eur J Pharmacol 447:239–246
Skog J, Würdinger T, van Rijn S et al (2008) Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and proteins that promote tumour growth and provide diagnostic biomarkers. Nat Cell Biol 10:1470–1476
Peavy RD, Chang MS, Sanders-Bush E et al (2001) Metabotropic glutamate receptor 5-induced phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase in astrocytes depends on transactivation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Neurosci 21:9619–9628
Taylor S, Srinivasan B, Wordinger RJ et al (2003) Glutamate stimulates neurotrophin expression in cultured Muller cells. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 111:189–197
Prenzel N, Fischer OM, Streit S et al (2001) The epidermal growth factor receptor family as a central element for cellular signal transduction and diversification. Endocr Relat Cancer 8:11–31
Yarden Y, Sliwkowski M (2001) Untangling the ErbB signaling network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2:27–137
Holbro T, Civenni G, Hynes NE (2003) The ErbB receptors and their role in cancer progression. Exp Cell Res 284:99–110
Chung WJ, Lyons SA, Nelson GM et al (2005) Inhibition of cystine uptake disrupts the growth of primary brain tumors. J Neurosci 25:7101–7110
de Groot JF, Liu TJ, Fuller G et al (2005) The excitatory amino acid transporter-2 induces apoptosis and decreases glioma growth in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res 65:1934–1940
Voelzke WR, Petty WJ, Lesser GJ (2008) Targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor in high-grade astrocytomas. Curr Treat Options in Oncol 9:23–31
Shawver LK, Slamon D, Ullrich A (2002) Smart drugs: tyrosine kinase inhibitors in cancer therapy. Cancer Cell 1:117–123
Viana-Pereira M, Lopes JM, Little S et al (2008) Analysis of EGFR overexpression, EGFR gene amplification and the EGFRvIII mutation in Portuguese high-grade gliomas. Anticancer Res 28:913–920
Lokker NA, Sullivan CM, Hollenbach SJ et al (2002) Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) autocrine signaling regulates survival and mitogenic pathways in glioblastoma cells: evidence that the novel PDGF-C and PDGF-D ligands may play a role in the development of brain tumors. Cancer Res 62:3729–3735
Servidei T, Riccardi A, Sanguinetti M et al (2006) Increased sensitivity to the platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) receptor inhibitor STI571 in chemoresistant glioma cells is associated with enhanced PDGF-BB-mediated signaling and STI571-induced Akt inactivation. J Cell Physiol 208:220–228
Wang MY, Lu KV, Zhu S et al (2006) Mammalian target of rapamycin inhibition promotes response to epidermal growth factor receptor kinase inhibitors in PTEN-deficient and PTEN-intact glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res 66:7864–7869
Mendelsohn J, Baselga J (2003) Status of epidermal growth factor receptor antagonists in the biology and treatment of cancer. J Clin Oncol 21:2787–2799
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2000) The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 100:57–70
Parsa AT, Holland EC (2004) Cooperative translational control of gene expression by Ras and Akt in cancer. Trends Mol Med 10:607–613
Holland EC, Celestino J, Dai C et al (2000) Combined activation of Ras and Akt in neural progenitors induces glioblastomas formation in mice. Nat Genet 25:55–57
Sonoda Y, Ozawa T, Aldape KD et al (2001) Akt pathway activation converts anaplastic astrocytoma to glioblastomas multiforme in a human astrocyte model of glioma. Cancer Res 61:6674–6678
Sanson M, Thillet J, Hoang-Xuan K (2004) Molecular changes in gliomas. Curr Opin Oncol 16:607–613
Vivanco I, Sawyers CL (2002) The phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2:489–501
Santini MT, Rainaldi G (1999) Three-dimensional spheroid model in tumor biology. Pathobiology 67:148–157
Bates RC, Edwards NS, Yates JD (2000) Spheroids and cell survival. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 36:61–74
Ye ZC, Rothstein JD, Sontheimer H (1999) Compromised glutamate transport in human glioma cells: reduction-mislocalization of sodium-dependent glutamate transporters and enhanced activity of cystine-glutamate exchange. J Neurosci 19:10767–10777
Roslin M, Henriksson R, Bergstrom P et al (2003) Baseline levels of glucose metabolites, glutamate and glycerol in malignant glioma assessed by stereotactic microdialysis. J Neurooncol 61:151–160
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schunemann, D.P., Grivicich, I., Regner, A. et al. Glutamate Promotes Cell Growth by EGFR Signaling on U-87MG Human Glioblastoma Cell Line. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 16, 285–293 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-009-9223-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-009-9223-4