Abstract
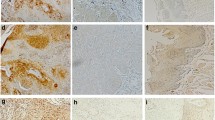
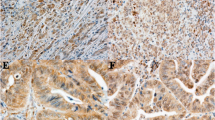
Focal adhesion kinase (FAK), a non-receptor tyrosine kinase protein, acts as an early modulator of integrin signaling cascade, regulating basic cellular functions. In transformed cells, unopposed FAK signaling has been considered to promote tumor growth, progression and metastasis. The aim of this study was to assess the clinical significance of FAK expression in the two distinct histological types of human gastric neoplasia. FAK expression was assessed immunohistochemically in tumoral samples of 66 gastric adenocarcinoma cases, 30 intestinal and 36 diffuse type, and was statistically analyzed in relation to various clinicopathological characteristics, tumor proliferative capacity and patients’ survival. In intestinal type carcinomas, enhanced FAK expression was significantly associated with increased tumor proliferative capacity (P = 0.012). In diffuse type carcinomas, FAK staining intensity was significantly correlated with tumor size (P = 0.026) and disease stage (P = 0.024), presenting also a borderline association with nodal status (P = 0.053). In diffuse type carcinomas, enhanced FAK expression was significantly associated with longer overall survival times (log-rank test, P = 0.014), being also identified as an independent prognostic factor in multivariate analysis (Cox regression, P = 0.016). In contrast, patients with intestinal type tumors and enhanced FAK expression were characterized by shorter overall survival times, without though reaching statistical significance (log-rank test, P = 0.092). The current data support evidence that FAK protein may be considered as a diagnostic and prognostic marker in gastric neoplasia. Further studies conducted on larger clinical samples and highlighting on the distinct impact of the two histological types are warranted to delineate the clinical significance of FAK protein in gastric neoplasia.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lipfert L, Haimovich B, Schaller MD, Cobb BS, Parsons JT, Brugge JS (1992) Integrin-dependent phosphorylation and activation of the protein tyrosine kinase pp125FAK in platelets. J Cell Biol 119:905–912
Zachary I, Sinnett-Smith J, Rozengurt E (1992) Bombesin, vasopressin, and endothelin stimulation of tyrosine phosphorylation in Swiss 3T3 cells. Identification of a novel tyrosine kinase as a major substrate. J Biol Chem 267:19031–19034
Ilic D, Furuta Y, Kanazawa S, Takeda N, Sobue K, Nakatsuji N, Nomura S, Fujimoto J, Okada M, Yamamoto T (1995) Reduced cell motility and enhanced focal adhesion contact formation in cells from FAK-deficient mice. Nature 377:539–544
Cary LA, Chang JF, Guan JL (1991) Stimulation of cell migration by overexpression of focal adhesion kinase and its association with Src and Fyn. J Cell Sci 109:1787–1794
Li S, Kim M, Hu YL, Jalali S, Schlaepfer DD, Hunter T, Chien S, Shyy JY (1997) Fluid shear stress activation of focal adhesion kinase. Linking to mitogen-activated protein kinases. J Biol Chem 272:30455–30462
Levy P, Robin H, Kornprobst M, Capeau J, Cherqui G (1989) Enterocytic differentiation of human Caco-2 cell line correlates with alterations in integrin signaling. J Cell Physiol 177:618–627
Xu LH, Owens LV, Sturge GC, Yang X, Liu ET, Craven RJ, Cance WG (1996) Attenuation of the expression of the focal adhesion kinase induces apoptosis in tumor cells. Cell Growth Differ 7:413–418
Chatzizacharias NA, Kouraklis G, Theocharis S (2008) Clinical significance of FAK expression in human neoplasia. Histol Histopathol 23:629–650
Chatzizacharias NA, Kouraklis G, Theocharis S (2007) Focal adhesion kinase: a promising target for anticancer therapy. Exp Opin ther Targets 11:1315–1328
Chatzizacharias NA, Kouraklis G, Theocharis S (2008) Disruption of FAK signaling: A side mechanism in cytotoxicity. Toxicology 245:1–10
Iravani S, Mao W, Fu L, Karl R, Yeatman T, Jove R, Coppola D (1998) Elevated c-Src protein expression is an early event in colonic neoplasia. Lab Invest 78:365–371
Owens LV, Xu L, Craven RJ, Dent GA, Weiner TM, Koengerg L, Liu ET, Cance WG (1995) Overexpression of the focal adhesion kinase (p125FAK) in invasive human tumors. Cancer Res 55:2752–2755
Theocharis SE, Kouraklis GP, Kakisis JD, Kanelli HG, Apostolakou FE, Karatzas GM, Koutselinis AS (2003) Focal adhesion kinase expression is not a prognostic predictor in colon adenocarcinoma patients. Eur J Surg Oncol 29:571–574
Furuyama K, Ryuchiro D, Tomohiko M, Toyoda E, Ito D, Kami K, Koizumi M, Kida A, Kawaguchi Y, Fujimoto K (2006) Clinical significance of focal adhesion kinase in resectable pancreatic cancer. World J Surg 30:219–226
Fuji T, Koshikawa K, Nomoto S, Okochi O, Kaneko T, Inoue S, Yatabe Y, Takeda S, Nakao A (2004) Focal adhesion kinase is overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma and can be served as an independent prognostic factor. J Hepatol 41:104–111
Itoh S, Maeda T, Shimada M, Aishima S, Shirabe K, Tanaka S, Maehara Y (2004) Role of expression of focal adhesion kinase in progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 10:2812–2817
Gabriel B, zur Hausen A, Stickeler E, Dietz C, Gitsch G, Fischer DC, Boulda J, Tempfer C, Hasenburg A (2006) Weak expression of focal adhesion kinase (pp125FAK) in patients with cervical cancer is associated with poor disease outcome. Clin Cancer Res 12:2476–2483
Imaizumi M, Nishimura M Takeuchi S, Murase M, Hamaguchi M (1997) Role of tyrosine specific phosphorylation of cellular proteins, especially EGF receptor and p125FAK in human lung cancer cells. Lung Cancer 17:69–84
He QY, Cheung YH, Leung SY, Yuen ST, Chu KM, Chiu JF (2004) Diverse proteomic alteration in gastric adenocarcinoma. Proteomics 4:3276–3287
Forman D, Barley VJ (2006) Gastric cancer: global pattern of the disease and an overview of environmental risk factors. Best Practice Res Clin Gastroenterol 20:633–649
Hohenberger P, Gretschel S (2003) Gastric cancer. Lancet 362:305–315
Tani T, Von Koskull H, Virtanen I (1996) Focal adhesion kinase pp 125FAK is associated with both intercellular junctions and matrix adhesion sites in vivo. Histochem Cell Biol 105:17–25
Su JM, Gui L, Zhou YP, Zha XL (2002) Expression of focal adhesion kinase and alpha5 and beta1 integrins in carcinomas and its clinical significance. World J Gastroenterol 8:613–618
Vauhkonen M, Vauhkonen H, Sipponen P (2006) Pathology and molecular biology of gastric cancer. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 20:651–674
Tahara E (2004) Genetic pathways of two types of gastric cancer. IARC Sci Publ 157:327–349
Cervantes A, Rodríguez Braun E, Pérez Fidalgo A, Chirivella González I (2007) Molecular biology of gastric cancer. Clin Transl Oncol 9:208–215
Lauren P (1965) The two histological main types of gastric carcinoma: diffuse and so-called intestinal-type carcinoma. Act Pathol Microbiol Scand 64:31–49
Sobin LH, Wittekind C (1997) TNM Classification of Malignant Tumors, 5th edn. Wiley-Liss, New York
Giaginis C, Davides D, Zarros A, Noussia O, Zizi-Serbetzoglou A, Kouraklis G, Theocharis S (2008) Clinical significance of tumor-associated antigen RCAS1 expression in human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Dig Dis Sci 53:1728–1734
Cance WG, Harris JE, Iacocca MV, Roche E, Yang X, Chang J, Simkins S, Xu L (2000) Immunohistochemical analyses of focal adhesion kinase expression in benign and malignant human breast and colon tissues: correlation with preinvasive and invasive phenotypes. Clin Cancer Res 6:2417–2423
Miyaki T, Kato H, nakajima M, Sohda M, Fukai Y, Masuda N, Manda N, Fukuchi M, Tsukada K, Kuwano H (2003) FAK overexpression is correlated with tumor invasiveness and lymph node metastasis in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer 89:140–145
Lark AL, Livasy CA, Dressler L, Moore DT, Millikan RC, Geradts J, Iacocca M, Cowan D, Little D, Craven RJ, Cance W (2005) High focal adhesion kinase expression in invasive breast carcinomas is associated with an aggressive phenotype. Mod Pathol 18:1289–1294
Cox BD, Natarajan M, Stettner MR, Gladson CL (2006) New concepts regarding focal adhesion kinase promotion of cell migration and proliferation. J Cell Biochem 99:35–52
Aguirre Ghiso JA (2002) Inhibition of FAK signaling activated by urokinase receptor induces dormancy in human carcinoma cells in vivo. Oncogene 21:2513–2524
Ohta R, Yamashita Y, Taketomi A, Kitagawa D, Kuroda Y, Itoh S, Aishima S, Maehara Y (2006) Reduced expression of focal adhesion kinase in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma is associated with poor tumor differentiation. Oncology 71:417–422
Carelli S, Zadra G, Vaira V, Falleni M, Bottiglieri L, Nosotti M, Di Giulio AM, Gorio A, Bosari S (2006) Up-regulation of focal adhesion kinase in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 53:263–271
Wang D, Grammer JR, Cobbs CS, Stewart JE Jr, Liu Z, Rhoden R, Hecker TP, Ding Q, Gladson CL (2000) p125 Focal adhesion kinase promotes malignant astrocytoma cell proliferation in vitro. J Cell Sci 113:4221–4230
Gabarra-Niecko V, Schaller MD, Dunty JM (2003) FAK regulates biological processes important for the pathogenesis of cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 22:359–374
Sood AK, Coffin JE, Schneider GB, Fletcher MS, DeYoung BR, Gruman LM, Gershenson DM, Schaller MD, Hendrix MJ (2004) Biological significance of focal adhesion kinase in ovarian cancer: role in migration and invasion. Am J Pathol 165:1087–1095
Yu HG, Tong SL, Ding YM, Fang XM, Zhang XF, Liu ZJ, Zhou YH, Liu QS, Luo HS, Yu JP (2006) Enhanced expression of cholecystokinin-2 receptor promotes the progression of colon cancer through activation of focal adhesion kinase. Int J cancer 119:2724–2732
Schmitz KJ, Grabellus F, Callies R, Otterbach F, Wohlschlaeger J, Levkau B, Kimmig R, Schmid KW, Baba HA (2005) High expression of focal adhesion kinase (p125FAK) in node-negative breast cancer is related to overexpression of HER-2/neu and activated Akt kinase but does not predict outcome. Breast Cancer Res 7:R194–203
Canel M, Aecade P, Rodrigo JP, Cabanillas R, Herrero A, Suarez C, Chiara MD (2006) Overexpression of focal adhesion kinase in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma is independent of fak gene copy number. Clin Cancer Res 12:3272–3279
Zheng H, Takahashi H, Murai Y, Cui Z, Nomoto K, Miwa S, Tsuneyama K, Takano Y (2007) Pathobiological characteristics of intestinal and diffuse-type gastric carcinoma in Japan: an immunostaining study on the tissue microarray. J Clin Pathol 60:273–277
Viste A, Eide GE, Halvorsen K, Maartmann-Moe H, Søreide O (1986) The prognostic value of Laurén's histopathological classification system and ABO blood groups in patients with stomach carcinoma. Eur J Surg Oncol 12:135–141
Xu LH, Yang X, Bradham CA, Brenner DA, Baldwin AS Jr, Craven RJ, Cance WG (2000) The focal adhesion kinase suppresses transformation-associated, anchorage-independent apoptosis in human breast cancer cells. Involvement of death receptor-related signaling pathways. J Biol Chem 275:30597–30604
Guan GX, Jian HX, Lei DY, Lu HS, Zhang XF (2006) Construction of retroviral vector of p125FAK specific ribozyme genes and its effects on BGC-823 cells. World J Gastroenterol 12:686–690
Scanlon KJ (2004) Anti-genes: siRNA, ribozymes and antisense. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 5:415–420
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giaginis, C.T., Vgenopoulou, S., Tsourouflis, G.S. et al. Expression and Clinical Significance of Focal Adhesion Kinase in the Two Distinct Histological Types, Intestinal and Diffuse, of Human Gastric Adenocarcinoma. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 15, 173–181 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-008-9120-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-008-9120-2