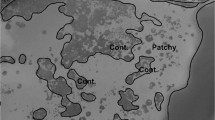
Abstract
Aerial surveys of coastal habitats can uniquely inform the science and management of shallow, coastal zones, and when repeated annually, they reveal changes that are otherwise difficult to assess from ground-based surveys. This paper reviews the utility of a long-term (1984–present) annual aerial monitoring program for submersed aquatic vegetation (SAV) in Chesapeake Bay, its tidal tributaries, and nearby Atlantic coastal bays, USA. We present a series of applications that highlight the program’s importance in assessing anthropogenic impacts, gauging water quality status and trends, establishing and evaluating restoration goals, and understanding the impact of commercial fishing practices on benthic habitats. These examples demonstrate how periodically quantifying coverage of this important foundational habitat answers basic research questions locally, as well as globally, and provides essential information to resource managers. New technologies are enabling more frequent and accurate aerial surveys at greater spatial resolution and lower cost. These advances will support efforts to extend the applications described here to similar issues in other areas.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Submersed aquatic vegetation (SAV) is an important shallow water habitat undergoing severe declines worldwide (Sand-Jensen et al. 2000; Körner 2002; Waycott et al. 2009; Moore et al. 2010). SAV meadows are subject to multiple stressors that result in losses, including propeller damage, dredging, commercial fishing and aquaculture activities, excessive sediment and nutrient loadings, and climate change effects (such as warming waters) (Orth et al. 2006; Cullen-Unsworth and Unsworth 2018). These losses are likely to have substantial ecological, social, and economic impacts to coastal waters, because SAV offers a host of benefits and ecosystem services, including the provision of food and habitat for numerous aquatic organisms, carbon sequestration, nutrient cycling, and the buffering of shorelines from erosive wave energy (Barbier et al. 2011).
Humans have influenced Chesapeake Bay SAV populations since the very first European settlement in 1607, if not before (Davis 1985; Brush and Hilgartner 2000). The settlers drained wetlands, introduced livestock, cleared forests, and grew crops, resulting in considerable runoff of nitrogen, phosphorus, and sediments (Brush and Hilgartner 2000). In the last several decades, that land development has accelerated. Since the 1970s, developed land has doubled from 9.8 to 17.2% (Falcone 2015; Orth et al. 2017a), and with it, there has been a corresponding increase in impervious surfaces, domestic and agricultural fertilizer, and animal agriculture production (Lamotte 2015), as well as a loss of forested areas (Jantz et al. 2005). All of these factors reduced water quality (Kemp et al. 2005), and light attenuation by suspended sediments, elevated phytoplankton populations in the water column, and epiphyte fouling on SAV leaf blades are all implicated in the significant reduction of SAV populations by the early 1980s (Orth and Moore 1983; Kemp et al. 2004; Lefcheck et al. 2018).
In 1984, resource managers initiated an annual bay-wide SAV monitoring program using aerial photography to assess progress in water quality improvements via quantifiable changes in SAV distribution and abundance. Managers chose SAV for this purpose because it is generally considered the “canary in the coal mine” of coastal ecosystems. Because SAV is fundamentally important to the Chesapeake Bay ecosystem and is sensitive to water quality changes, it is an important indicator of the Bay’s overall health and productivity (Orth et al. 2017a). Despite the challenges of acquiring useful remote imagery in a large, temperate, and turbid estuary, the bay-wide SAV monitoring program has successfully mapped the distribution of SAV beds throughout the Bay and its tributaries since 1984.
The availability of high quality, annual digital SAV maps and data coupled with land-use and water-quality data monitoring provides a powerful data set for linking biological responses to management actions. The value of the data set has increased with the acceleration in computing power and access to sophisticated statistical tools. Increasing SAV abundance is one of the central considerations for Chesapeake Bay water quality management (Orth et al. 2002; Tango and Batiuk 2013), and underscores the importance of ongoing efforts to reduce sediment and nutrient export from the watershed into the bay. These efforts include best management practices (BMPs) (e.g., stormwater management, precision agriculture, and wastewater treatment) established to meet goals specified by the Chesapeake Bay Total Maximum Daily Load (TMDL) for nitrogen, phosphorus, and sediment (USEPA 2010).
Here, we provide eight applications that demonstrate the multifaceted value of this long-term SAV monitoring program for assessing and understanding the Chesapeake Bay’s ecological condition as well as its periods of decline and recovery. We highlight how aerial surveys provide fundamental and indispensable information to reveal the relationship between human activities, water quality, and SAV abundance, insights which now are being replicated elsewhere. As coastal populations increase and global climate shifts, long-term and spatially explicit monitoring programs will increase in value for tracking environmental change, identifying mechanistic drivers of natural resource degradation, and determining appropriate actions to prevent or reverse undesirable outcomes to estuaries, as has been done in Chesapeake Bay
Methods
The 33-year Chesapeake Bay SAV dataset is the result of an intensive, annual aerial monitoring program funded by a consortium of federal and state agencies, as well as private environmental foundations. Since its inception in 1984, the program has evolved over the years to employ new technology and methods (Moore et al. 2009; see all annual reports for detailed methodologies http://www.vims.edu/bio/sav). Aerial photography has been acquired annually since 1984, except in 1988. Although color imagery was acquired for portions of the Chesapeake Bay and its tidal tributaries in 1987 and 2008, panchromatic black and white photography was primarily used until 2014. Imagery was acquired at a scale of 1:24,000 with a standard mapping camera (Wild RC-30 camera, with a 153-mm (6 in.) focal length Aviogon len) following acquisition timing guidelines that optimize visibility of SAV beds. Acquisition criteria specified tidal stage (± 90 min of low tide), plant growth season (peak biomass), sun angle (between 20 and 40o), atmospheric transparency (cloud cover less than 10%), water turbidity (the ability to see SAV bed edges in deeper water), and wind (less than 5 m s-1, Dobson et al. 1995). Photographic images incorporated 60% flight line overlap and 20% side lap. In 2014, a portion of the bay was acquired with multi-spectral imagery using a digital mapping camera (ZI DMC-II 230 multispectral (RGB,NIR) digital mapping camera and IMU with a 92-mm focal length, a 5.6-μm pixel size, and a 15552 × 14144 image size) with a ground sample distance of 24 cm. Since then, multispectral imagery has been acquired annually throughout the Chesapeake Bay and its tidal tributaries.
From 1984 to 2014, approximately 170 flight lines of panchromatic imagery were flown each year covering all shorelines and adjacent shoal areas of Chesapeake Bay and its tributaries, yielding over 2000 photographs per year. Due to the smaller footprint of the digital imagery initiated in 2014, an additional 30 lines and 1300 images are required to capture the same area with multispectral imagery. Each year, image acquisition commenced in the late spring (mid-May) to capture the higher salinity regions at peak plant biomass and continued through late summer and early fall (August through October) to capture the dominant freshwater species at their peak biomass.
SAV beds were initially mapped by manually tracing bed outlines onto translucent United States Geological Survey 7.5-min quadrangle maps directly from the photographs or film. Bed boundaries were then digitized into a geographic information system (GIS). Starting in 2001, the aerial photography was scanned from negatives and orthorectified using ERDAS image processing software (Moore et al. 2009). The switch to digital multispectral imagery in 2014 eliminated the scanning step and imagery was collected with rough initial geographic orientation, higher resolution and improved GPS and IMU (inertial measurement unit) data that facilitated orthorectification. Horizontal positional accuracy improved from approximately 10–20 m with the early, manual method, to less than 4 m RMSE with the current method. SAV bed boundaries were then manually photo-interpreted on-screen while maintaining a fixed scale using GIS software. Photo-interpreters were fully trained in understanding SAV signatures on the imagery and a second interpreter checked all work prior to final approval by a third interpreter.
The SAV dataset is updated each year with new bed boundaries for the entire region redrawn based on newly acquired imagery, providing valuable annual monitoring data. These data are summarized for the Chesapeake Bay and its tidal tributaries, nearby Atlantic Coastal Bays, four salinity zones, and 103 smaller geographic segments and (Fig. 1a). In addition, trained citizen scientists, management staff, and researchers collect ground survey data each year for the SAV beds. This provides important ground verification data for the imagery, including SAV species observations. The organized dataset including the bed outlines, SAV densities, and species information is freely available and easily accessible to any interested parties (see http://www.vims.edu/bio/sav), facilitating use by the research community, educators, resource managers, policy-makers, and other stakeholders.
a Map of Chesapeake Bay and Atlantic coastal bays showing locations indicated in the text, as well as salinity regions of the Bay; b Changes in SAV abundance in the different salinity zones (reprinted from Lefcheck et al. 2018)
Applications
Understanding SAV patterns at broad spatial scales: synthetic analyses
A number of studies in Chesapeake Bay have analyzed the multi-decade time series of the bay-wide SAV monitoring program (Fig. 1b) to quantitatively link trends in SAV abundance with changes in watershed nutrient loads. One approach targeted roughly 100 subestuaries of Chesapeake Bay as independent replicates in statistical analyses. Each subestuary has a unique local watershed, and the set of subestuaries encompasses broad ranges of watershed land uses, salinities, water-column conditions, and SAV coverage. The studies have found significant negative impacts of (1) human land use on SAV abundance and community composition (Fig. 2a, Li et al. 2007; Patrick et al. 2014, 2018; Landry and Golden 2018); (2) shoreline armoring on SAV abundance and resilience (Patrick et al. 2014, 2016, 2018; Landry and Golden 2018); and (3) temporal correlations between water quality conditions and SAV abundance (Patrick and Weller 2015).
a Effect of dominant land use on SAV abundance (as in Li et al. 2007 but with updates from Patrick et al. 2014); b A path diagram showing the direct and indirect controls on SAV abundance (redrawn from Lefcheck et al. 2018); Average annual nitrogen concentration (c) and phosphorus concentration (d) in the different salinity zones—1984 to 2015 (redrawn from Lefcheck et al. 2018)
Most recently, Lefcheck et al. (2018) applied the subestuary approach in a bay-wide analysis that integrated watershed nutrient inputs, land use, water-column water quality indicators of SAV habitat, and SAV characteristics (e.g., density and coverage) in a single overarching analysis of SAV abundance. They found strong linkages of fertilizer inputs to nitrogen loads and ultimately to SAV coverage (Fig. 2b), and they concluded that reductions in nutrient loads (Fig. 2c, d) are an important contributor to the recent, multi-year resurgence in SAV abundance (Fig. 1b) (Lefcheck et al. 2018).
In another synthetic study, Lefcheck et al. (2017) analyzed SAV coverage in regions surrounding fixed water quality monitoring stations to show that both decreasing water clarity and warming temperatures drove the 29% decline of eelgrass in lower Chesapeake Bay since 1991. Declining water clarity led to reduced eelgrass cover in the deeper portions of the beds while increasing temperature stressed eelgrass in the shallower beds. The analysis revealed an emerging interaction between local inputs and global climate change.
Linking reductions in point source nutrient loadings to SAV distribution and abundance
To control the detrimental effects of eutrophication on water quality and living resources, efforts to limit nutrient loads delivered to Chesapeake Bay and its tidal tributaries have emphasized reducing point source loads, especially from sewage treatment plants (STP). A growing body of evidence derived from the bay-wide SAV monitoring program demonstrates that reducing point source loads produces conditions that significantly increase SAV downstream of the STPs. Here, we present three examples.
Prior to 1994, SAV was absent from aerial survey assessments in the Upper Patuxent River, except for small beds in the upper reaches of tributary creeks. Treatment plant upgrades improving nitrogen and phosphorus removal efficiencies were implemented between the late 1980s and the 1990s at a STP in the upper Patuxent River that delivered effluent directly into the river. Nutrient loads were reduced, and SAV reappeared downstream of this source in the mainstem river in 1993. Coverage has increased throughout the tidal freshwater river since then (Fig. 3a). Coincidentally, human population was increasing in the watershed, and no other significant nutrient reductions were evident to account for the improved water quality conditions that supported the expansion of SAV (Boynton et al. 2008; Orth et al. 2010a).
In Mattawoman Creek (a tributary to the upper Potomac River estuary), SAV was not detected in aerial surveys from 1984 to the early 1990s. After 1990, STP upgrades reduced point source nitrogen loads delivered to the creek from 360 kg N/day in 1990 to 50 kg N/day by 1995 (further reductions began in 2000). Coinciding with these reductions, SAV reappeared in the aerial surveys of Mattawoman Creek in the 1990s and then expanded rapidly to cover 40–50% of the creek area by 2002 (Fig. 3b) (Boynton et al. 2014).
The upper tidal Potomac River was once one of the most polluted rivers in the country, and SAV had not been observed there since the early 1900s. In 1980, a nitrification process was implemented to reduce nitrogen discharges from the Blue Plains Advanced Waste Water Treatment Plant, which is the largest plant on the Potomac (and the largest of its kind in the world, managing 300M–1B gallons of effluent per day). Phosphorus effluent filters were installed in 1982, and a nitrification-denitrification system was added between 1998 and 2001. These improvements significantly reduced nitrogen loads, and there was a remarkable recovery in SAV beginning in the early 1990s (Fig. 3c) (Ruhl and Rybicki 2010).
The SAV resurgences in these examples are undoubtedly linked to the reductions in the wastewater nutrient discharges via a cause-and-effect chain that includes reduced estuary nutrient concentrations, reduced algal biomass, and improved water clarity (Ruhl and Rybicki 2010; Boynton et al. 2014; Lefcheck et al. 2018).
Demonstrating how SAV populations influence water quality
Although SAV typically declines in areas with poor water quality (Dennison et al. 1993), SAV can also improve water quality through positive feedback that increases the amount of light available for plant growth and survival (van der Heide et al. 2011; Maxwell et al. 2015). Several studies have linked SAV distributions from the bay-wide SAV monitoring program with intensive in situ measurements to quantify local water quality improvements and investigate the biophysical mechanisms driving the positive feedbacks.
For example, in the coastal bays of Virginia’s Delmarva Peninsula, active habitat restoration of eelgrass by seeding coupled to natural spread (see application study 5) led to the successful recovery of eelgrass. Annual monitoring from aerial surveys of these meadows along with intensive water quality monitoring revealed lower suspended chlorophyll and particulates compared to adjacent unvegetated areas (Orth et al. 2012). Additionally, as the size and density of the meadow increased over time, turbidity was substantially reduced (Fig. 4a), demonstrating the strong positive feedbacks between SAV and water clarity.
a Turbidity levels in South Bay versus eelgrass bed size (Figure from Orth et al. 2012); Tidally averaged dissolved inorganic nitrogen (DIN) measured along a north-south transect across a large SAV bed during (b) low SAV biomass and (c) high SAV biomass. Gray-shaded area represents the location of the SAV bed. Error bars represent standard error. (Reprinted from Gurbisz et al. 2016)
In another example of positive feedbacks, a study of a large SAV bed in the Susquehanna Flats region of the upper Chesapeake Bay revealed that SAV mediated effects on local advection and dispersion increased water residence time in the bed by > 5 days (Gurbisz et al. 2016). As a result, plant assimilation and sediment denitrification decreased nitrogen concentrations within the SAV bed by > 70 μmol l-1 (Fig. 4b), which limited algal production and increased water clarity. Moreover, these feedbacks promoted SAV resilience—the capacity to withstand or recover from disturbances. After a major flood event deposited a layer of fine sediment in the SAV bed, the plants dampened wind-driven resuspension, thereby improving water clarity (Gurbisz and Kemp 2014). A hydrodynamic model showed that SAV also shunted flood event flow around the bed and into the surrounding channels, preventing plant loss through scour (Gurbisz et al. 2016). Finally, clear water from within the SAV bed “spilled over” into adjacent regions during falling tides, and light availability at the bottom surpassed the threshold for SAV growth (Gurbisz et al. 2016). Collectively, these processes enabled the SAV bed to resist impacts that might have eradicated the bed and to recolonize adjacent bare regions after the storm event.
Establishing SAV restoration goals that support water quality goal achievement
SAV area is one of the key metrics for assessing the success of Chesapeake Bay nutrient and sediment load reduction efforts. Information from the annual aerial survey, as well as historical imagery dating back to 1937, was instrumental in developing SAV restoration targets for the all four salinity zones of the Chesapeake Bay and its tidal tributaries, (Fig. 1a, polyhaline, mesohaline, oligohaline, and tidal freshwater) (Moore et al. 2009) (Fig. 5). Restoration targets using SAV area promulgated into state water quality regulations in Maryland, Virginia, and the District of Columbia (Maryland DNR COMAR 26.08.02; Virginia DEQ, 9VAC25-260-185; USEPA 2010, 2017) now support an annual assessment of the water clarity standard attainment using the annual SAV monitoring data (USEPA 2003a, b).
SAV abundance (1984–2015) in four Chesapeake Bay salinity zones and bay-wide SAV area cover versus restoration goal for that region (reprinted from Orth et al. 2017a)
The ultimate goal for SAV restoration in the Chesapeake Bay is 75,000 ha bay-wide (Fig. 5), with interim goals of 36,500 ha by 2017 and 52,700 ha by 2025. The attainment of this bay-wide goal (and goals for each of the four salinity zones above) is assessed by several analyses, including an annual ecological report card that provides performance-driven numeric grades measuring the ecological health of Chesapeake Bay (Williams et al. 2009), and a Chesapeake Bay Program Partnership publication called the “Bay Barometer” (see http://www.chesapeakebay.net). The SAV monitoring data is evaluated every year and has been instrumental in quantifying how well the Chesapeake Bay is meeting health and restoration goals established by resource managers. In 2015, SAV exceeded the interim area coverage goal established for 2017, the first time a goal has been either met or exceeded since the SAV survey began (Fig. 5).
Assessing the success of active SAV restoration efforts
In addition to nutrient reductions, SAV has been actively planted to expand SAV coverage toward attaining bay-wide restoration goals (Shafer and Bergstrom 2010). Coupled with measurements from the Chesapeake Bay long-term water quality monitoring program, the bay-wide SAV monitoring program allowed scientists and managers to identify potential sites for seed- and transplant-based SAV restoration, and then to measure the long-term success of those plantings.
Most of these efforts targeted one species, eelgrass (Zostera marina) because more was known about its biology and ecology than other SAV species (Fig. 6a, b). Eelgrass is one of two SAV species found in the higher salinity regions of Chesapeake Bay and the Atlantic coastal bays, and its major changes in distribution and abundance since the 1930s are well-known (Orth and Moore 1984). Unfortunately, many of the eelgrass restoration efforts did not survive more than 5 years, but the long-term aerial surveys documented two projects that did succeed (Fig. 6c) (Orth et al. 2010b).
Aerial image showing eelgrass transplants in a checkerboard pattern in 1999 of plots planted in 1996 and 1998 (a) in the James River and again in 2001 (b) showing natural colonization around the plots (numerous dark patches); c Number of SAV restoration projects in Chesapeake Bay versus those that were considered successful after 5 years (reprinted from Orth et al. 2017a); d Ha of eelgrass in the lower James River after the planting of eelgrass initiated in 1996; e Ha of eelgrass mapped from the Atlantic coastal bays and number of ha planted with seeds (1998–2017)
One of the successful restorations was at the mouth of the James River, a major tributary to the Virginia portion of Chesapeake Bay. From 1996 through 1998, adult eelgrass plants were planted at several locations in a large checkerboard pattern (Orth et al. 1999; Lefcheck et al. 2016), with additional seeding efforts through 2000 (Fig. 6a, b). These plantings survived and plant cover expanded, contributing to the recovery of eelgrass along this section of the river (Fig. 6b, d).
The second successful restoration was in the coastal bays of Virginia’s Delmarva Peninsula. The re-appearance of small patches of eelgrass in 1997 after being absent since 1933 (Orth et al. 2012) and successful small-scale test plantings in 1998 motivated a large-scale, annual, seed-based restoration program (Orth et al. 2012). From 1999 through 2017, over 70 million seeds were broadcast into 536 individual plots ranging in size from 0.2 to 0.4 ha. Natural growth and seed dispersal from these restored plots expanded to yield approximately 2,893 ha of restored eelgrass beds in 2017 (Fig. 6e).
Understanding how shoreline armoring influences SAV populations
Data from the bay-wide SAV monitoring program have been invaluable for assessing the impacts of shoreline armoring (Fig. 7a) on SAV in Chesapeake Bay. Patrick et al. (2014) applied spatial and statistical analyses to integrate the SAV maps with bay-wide maps of shoreline condition. They found significant negative correlations between the percentage shoreline armoring and SAV abundance among subestuaries of Chesapeake Bay. In addition, subestuaries with more than 5.4% shoreline riprap had significantly less SAV and a lower rate of recovery than subestuaries below that threshold (Fig. 7b) (Patrick et al. 2014). Further analysis documented that shoreline armoring interacted with watershed land cover to impact near-shore SAV. For example, in heavily developed watersheds, SAV cover was typically lower, regardless of shoreline armoring intensity. However, in forested watersheds, armoring was more likely to have a negative effect on SAV, demonstrating that local-scale stressors become important when regional stressors are not present. Furthermore, the detrimental effects of armoring were particularly evident in the polyhaline zone where SAV diversity is naturally limited and the dominant species (Zostera marina) has higher light requirements (Fig. 7c) (Patrick et al. 2016). These analyses, made possible by the spatial interpretation of the bay-wide SAV monitoring program data, provide key insights into where managers should target remediation efforts for small-scale disturbances to achieve the greatest return on investment.
Effects of shoreline armoring on SAV. a Shoreline armoring with riprap; b Time series of annual average SAV abundance (measured as the proportion of SAV habitat area actually occupied by SAV) within subestuaries with < 5.4% or > 5.4% riprapped shoreline (redrawn from Patrick et al. 2014); c Interacting effects of shoreline condition (riprap, bulkhead, or natural), watershed land cover (Forest, > 60% forest cover; human, > 40% agricultural land or > 50% urban land; mixed, all other watersheds), and salinity zone (oligohaline, mesohaline, or polyhaline) on SAV abundance along 75–125 m shoreline segments within 250 m of shore inside subestuaries (redrawn from Patrick and Weller 2015)
Shoreline armoring also affected which species of SAV occur nearby, especially in fresher parts of the Bay, where more than twelve species of SAV commonly co-occur. There, non-native SAV taxa were strongly associated with armored shoreline (Patrick et al. 2018), indicating that these habitat alterations may provide an opportunity for exploitation by non-native species. Landry and Golden (2018) used the SAV maps to select field sites for in situ comparisons of SAV abundance near natural and riprapped shorelines. They found that species diversity, SAV density, and bed size were all significantly reduced by shoreline riprap. These in situ observations corroborate the negative impact of riprap reported by the spatial-statistical analyses of the bay-wide maps (Patrick et al. 2014, 2016, 2018) and demonstrate the value of the mapping data for siting effective field studies and restoration efforts.
Assessing the interactions of aquaculture and SAV
In Chesapeake Bay, structures that support aquaculture of oysters (Crassostrea virginica) or hard clams (Mercenaria mercenaria) have become a common feature along Maryland and Virginia shorelines (Fig. 8a). Aquaculture for both species involves placing structures directly on the bottom or floating on the surface. These shellfish operations are generally placed in shallow water to facilitate easy access for maintenance and harvesting, which positions them in existing or potential SAV habitat (Fig. 8a). In Virginia, aquaculture operations have been rapidly increasing (Fig. 8b, Orth et al. 2017a) and conflicts between placement of these structures and existing SAV have been increasing as well. In 2017, 18% of the 5,733 active shellfish leases in Virginia were located in areas considered SAV habitat. In that same year, 27% of the 108 new lease applications were then located in areas that either had or could potentially support SAV.
a Bay-wide SAV monitoring program aerial image showing clam aquaculture nets in Chesapeake Bay in 2015. Dark areas are nets currently with clams. Rectangles that are clear are areas where clams had been recently harvested. Dark area just above the clam area is SAV (reprinted from Orth et al. 2017a); b Number of clam plots recorded from aerial imagery from 1987 through 2015, and number of oysters raised in aquaculture sold by Virginia growers from 2005–2015 (reprinted from Orth et al. 2017a)
In response, the states have adopted aquaculture-specific regulations to protect existing SAV. In Maryland, SAV is protected from disruption by shellfish aquaculture in Maryland Natural Resources Code § 4-11A.01 et seq. and COMAR 08.02.23.00 et seq. This Code defines SAV protection zones, prohibits new leases in areas where SAV has been mapped by the aerial survey within 5 years of the application, and prohibits placing shellfish, bags, nets, or structures on existing SAV without prior approval. Virginia prohibits new leases in areas with existing SAV and uses a 5- to 10-year composite map from the bay-wide SAV monitoring program to determine SAV presence. Both states protect recovering SAV in areas where leases were formerly granted. If a lease lacked SAV at the time of the shellfish placement but is subsequently colonized by SAV, the leaseholder cannot place new structures in the recolonized area (VA 20-335-30; VA 20-336-30; VA 20-337-20; MD Nat Res Code § 4-11A-10). Monitoring for aquaculture conflicts in shallow-water SAV habitat would not be possible without the SAV monitoring data.
Documenting commercial fishery impacts on SAV and implementing protective policies
In Chesapeake Bay and Atlantic coastal bays, clear impacts to SAV from multiple commercial fishing practices have been observed in the imagery from the bay-wide SAV monitoring program. For example, harvesting hard clams (Mercenaria mercenaria) with a modified oyster dredge causes large, unvegetated circular scars (Orth et al. 2002) while hydraulic dredges cause long, linear scars (Fig. 9a, b) (Orth et al. 2002). High-resolution images from the monitoring program clearly documented that both types of dredging increased over time (Fig. 9c) and these data were consequently used to guide conservation efforts and support management and policy decisions. Virginia now has a sanctuary for SAV in which clam dredging (4-VAC 20-1010 et seq.) is prohibited, and the sanctuary has been highly effective (Fig. 9d). Likewise, Maryland resource management agencies prohibited hydraulic and bottom dredging in SAV Protection Zones, which are identified using the bay-wide SAV monitoring program data and are delineated by the Maryland Department of Natural Resources (DNR) in COMAR 08.02.01.12 (MD Nat Res Code §4-1006.1).
Scarring in SAV beds in Virginia from modified oyster dredges (a) and Maryland due to hydraulic dredging (b) for hard clams; c Total area and intensity of scarring in SAV beds from hydraulic dredges in Maryland, 1996–1999 (reprinted from Orth et al. 2002); d Number of dredge scars in SAV beds in Virginia showing the effects of management actions. The first segment shows the number of dredge scars created prior to protection. The second segment shows the number of dredge scars after the area was protected but with no permanent marker poles. The third segment shows the number of dredge scars created after the protected area was marked with signs on large poles indicating the presence of the SAV sanctuary; e, f Length of scars created by commercial boat propellers at two locations before and after (grey bar) management actions (reprinted from Orth et al. 2017b). Each line represents scars formed in a particular year and the recovery of those scars in subsequent years
Significant propeller scarring was first observed on SAV imagery in Virginia waters beginning in the late 1990s, and imagery from subsequent years documented increasing scarring in the same SAV beds over time. Resource managers used this imagery in an environmental impact study, which identified commercial fishing vessels pulling nets to catch speckled trout and other commercially important fish as the primary source of the scarring. Their propellers were digging into the bottom and damaging the SAV. A committee was formed to develop a plan to reduce or eliminate the problem (Orth et al. 2017b): commercial anglers are now required to harvest fish at higher tides to minimize propeller damage, and this has significantly reduced scarring (Fig. 9e, f) (4 VAC 20-1070-10 et seq).
Comparisons to Other SAV Monitoring Programs
The bay-wide SAV monitoring program that covers Chesapeake Bay, its tidal tributaries, and the Atlantic coastal bays is one of the largest and most comprehensive long-term monitoring programs for SAV in the world today. Although aerial surveys of SAV that incorporate multiple sensor platforms (e.g., fixed winged aircraft, balloons, or satellites) and a variety of sensors (film cameras to digital sensors) have been underway for decades at many locations around the world (see reviews by Hossain et al. 2014; Oreska, et al. 2019), they are often limited in scope. Many surveys are conducted only once to document current habitat conditions, thereby precluding trend assessment (Oreska et al. 2019). When surveys are repeated, they often occur years or decades after the original survey (Waycott et al. 2009). Aggregating changes over long time scales limits the potential to relate changes in SAV area to variability in environmental drivers and, therefore, to evaluate the mechanisms driving SAV trends. In addition, some surveys cover only a portion of a tributary or coastal area containing a particular species group, which makes regional extrapolation difficult. A notable exception is the biennial aerial survey of seagrasses in Tampa Bay, FL, USA, which was initiated in 1988 and been used to follow the recovery of seagrasses following decades of water quality improvements (Sherwood et al. 2017; Tomasko et al. 2018). In Texas waters, an aerial survey is performed every 5 years and is paired with annual in situ sampling of all coastal areas with seagrass stratified by a 500 tessellated hexagon grid (Dunton et al. 2011). Here, we argue that this type of high-frequency, spatially comprehensive SAV monitoring program is an invaluable resource for coastal science and management.
Conclusions
The original objective of the bay-wide SAV monitoring program was to provide a “snapshot” of the amount of SAV coverage in the bay and then use that amount to assess the estuary’s current condition and its response to water quality improvements. The program has met that objective, but the availability of annual imagery and geo-referenced SAV maps has also supported unanticipated research and management uses highlighted in the applications described above. Scientists have used the SAV monitoring data to reveal how SAV responds to water quality improvements related to changes in watershed characteristics at local and regional scales, how SAV modifies key water quality characteristics (such as light availability), and how shoreline armoring can influence SAV abundance. Managers analyzed the monitoring data to develop (and to annually assess attainment of) SAV restoration goals and water clarity criteria that have become state water quality regulations consistently applied to all Chesapeake Bay and tidal tributary waters shared by Virginia, Maryland, Delaware, and the District of Columbia. Managers also use the monitoring data to evaluate the effectiveness of large-scale SAV restoration projects and the success of watershed-wide implementation of best management practices for reducing nutrient and sediment runoff. The imagery has also revealed direct physical damage to SAV from fishing, aquaculture, and recreational activities, enabling resource managers to develop guidelines for SAV protection (see Table 1 in the Supplementary Material for a list of published papers that have used the bay-wide SAV monitoring dataset). Furthermore, while these applications used the monitoring data to analyze SAV patterns, the imagery also has many other potential uses, such as tracking shoreline erosion and deposition, shoreline hardening, land use change, marsh loss, and other changes in near-shore conditions.
Despite the successes we document here, Chesapeake Bay continues to face new challenges, such as climate change impacts (sea level rise, storm intensity, and warming, Najjar et al. 2010). Consequently, resource managers continue to work towards building and maintaining resilience amid chronic stresses from an increasing human population in the watershed that drives changes in land use, run-off, and point source discharges (Orth et al. 2017a). It is important to continue the bay-wide SAV monitoring program on an annual basis to understand factors that may alter the current positive SAV recovery trajectory (Lefcheck et al. 2018). In particular, the applications described here highlight the value of the survey being performed annually rather than at longer time intervals. SAV dynamics can be decidedly non-linear, exhibiting rapid responses, in both positive and negative direction to environmental changes. In some cases, these appear to be threshold effects, where continual slow change rapidly accelerates, and in other cases, short-term disturbances like tropical cyclones or heat stress events are responsible. Coarser scale data would make it impossible to assess the mechanisms responsible for these types of patterns. The annual sampling frequency has enabled resource managers to quickly observe and manage perturbations to the SAV and helped scientists link water quality improvements to positive SAV changes.
Multiple state and federal institutions in the Chesapeake Bay Program partnership provide annual funding for the bay-wide SAV monitoring program. This sustained financial support has been a contributing factor in the long-term success of the program and its ability to span state boundaries. Although fully funding this annual monitoring program is a persistent challenge, technological improvements over time have contributed to keeping program costs low enough to sustain the program during periods of budgetary constraints. These improvements have included more sophisticated software, access to larger digital storage space to make all reports and GIS data available on the internet (http://vims.edu/bio/sav/), and advancements in digital imagery acquisition technology. Additionally, emerging technologies (i.e., drone-captured imagery, improved satellite resolution and data availability, and machine learning) (Oreska et al. 2019) may reduce the expense of the monitoring program in coming years while increasing its ability to capture critical events that impact SAV distribution and abundance during multiple timeframes throughout the growing season (e.g., peaks in ephemeral spring species). Furthermore, new sensor technology, image recognition algorithms and machine learning tools may enhance the ability to distinguish species in the imagery and to rapidly process this information while reducing the time and funding required to provide products to scientists and managers.
The availability of annual imagery acquired specifically to monitor SAV has made proactive resource management possible in the Chesapeake Bay and its tidal tributaries and Atlantic coastal bays. The imagery is currently used to carefully monitor SAV distribution and abundance, as well as the impact of various direct and indirect activities on SAV populations each year. A report to resource managers is developed annually using the SAV data from the bay-wide SAV monitoring program, ensuring the Chesapeake Bay and its tidal tributaries are on target to meet its restoration goals, and ensure further damage does not occur. In each of the application studies described above, the bay-wide SAV monitoring program provided data at the necessary scale (local, sub-regional, or regional) and resolution to address difficult questions about the connections between watershed and water-based activities on SAV. Watershed and estuarine restoration efforts frequently cite studies like these to document where successful land-use or nutrient management (or lack thereof) leads to clear improvements (or declines) in SAV abundance. Annual aerial surveys provide the broad perspective, both spatially and temporally, necessary for coastal managers to mechanistically link management actions to desired results. The Chesapeake Bay ‘s bay-wide SAV monitoring program has provided data and information necessary to guide the management and restoration of one of the biggest estuaries in the world, and may serve as a roadmap to those seeking to replicate the effort in other systems. This program has highlighted the value of annual monitoring, and given the growing availability of digital imagery, suggests that such an approach may be generally applicable elsewhere.
References
Barbier, E.B., S.D. Hacker, C. Kennedy, E.W. Koch, A.C. Steir, and B.R. Silliman. 2011. The value of estuarine and coastal ecosystem services. Ecological Monographs 81: 169–193.
Boynton, W.R., J.D. Hagy, J.C. Cornwell, W.M. Kemp, S.M. Greene, M.S. Owens, J.E. Baker, and R.K. Larsen. 2008. Nutrient budgets and management actions in the Patuxent River Estuary, Maryland. Estuaries and Coasts 31: 623–651.
Boynton, W.R., C.L.S. Hodgkins, C.A. O’Leary, E.M. Bailey, A.R. Bayard, and L.A. Wainger. 2014. Multi-decade responses of a tidal creek system to nutrient load reductions: Mattawoman Creek, Maryland USA. Estuaries and Coasts 37: 111–127.
Brush, G.S., and W.B. Hilgartner. 2000. Paleoecology of submerged macrophytes in the upper Chesapeake Bay. Ecological Monographs 70: 645–667.
Cullen-Unsworth, L.C., and R. Unsworth. 2018. A call for seagrass protection. Science 361 (6401): 446–448.
Davis, F.W. 1985. Historical changes in submerged macrophyte communities of upper Chesapeake Bay. Ecology 66: 981–993.
Dennison, W.C., R.J. Orth, K.A. Moore, J.C. Stevenson, V. Carter, S. Kollar, P. Bergstrom, and R. Batiuk. 1993. Assessing water quality with submersed aquatic vegetation. Bioscience 43: 86–94.
Dobson, J.E., E.A. Bright, R.L. Ferguson, D.W. Field, L.L. Wood, K.D. Haddad, H. Iredale III, J.R. Jensen, V.V. Klemas, R.J. Orth, and J.P. Thomas. 1995. NOAA Coastal change analysis program (C-CAP): Guidance for regional implementation. NOAA Tech. Rep. NMFS 123 92 pp.
Dunton, K., W. Pulich, and T. Mutchler. 2011. A seagrass monitoring program for Texas coastal waters: Multiscale integration of landscape features with plant and water quality indicators. Contract No. 0627. Coastal Bend Bays and Estuaries Program.
Falcone, J.A. 2015. US Conterminous wall-to-wall anthropogenic land use trends (NWALT), 1974–2012: Data Series 948. National Water-Quality Assessment Program US Geological Survey, Reston, VA.
Gurbisz, C., and W.M. Kemp. 2014. Unexpected resurgence of a large submersed plant bed in Chesapeake Bay: Analysis of time series data. Limnology and Oceanography 59: 482–494.
Gurbisz, C., W.M. Kemp, L.P. Sanford, and R.J. Orth. 2016. Mechanisms of storm-related loss and resilience in a large submersed plant bed. Estuaries and Coasts 39: 951–966.
Hossain, M.S., J.S. Bujang, M.H. Zakaria, and M. Hashim. 2014. The application of remote sensing to seagrass ecosystems: An overview and future research prospects. International Journal of Remote Sensing 36: 61–113.
Jantz, C.A., S.J. Goetz, P.A. Jantz, and B. Melchior. 2005. Resource land loss and forest vulnerability in the Chesapeake Bay Watershed. In 2005. Proceedings of the 4th Southern Forestry and Natural Resources GIS Conference, December 16-17, 2004, Athens, GA, ed. P.C. Bettinger, S.D. Hyldahl, J. Danskin, Y. Zhu, W.G. Zhang, T. Hubbard, M. Wimberly Lowe, and B. Jackson, 84–95. Athens, GA: Warnell School of Forest Resources, University of Georgia.
Kemp, W.M., R. Batleson, P. Bergstrom, V. Carter, C.L. Gallegos, W. Hunley, L. Karrh, E.W. Koch, J.M. Landwehr, K.A. Moore, L. Murray, M. Naylor, N.B. Rybicki, J.C. Stevenson, and D.J. Wilcox. 2004. Habitat requirements for submerged aquatic vegetation in Chesapeake Bay: Water quality, light regime, and physical-chemical factors. Estuaries 27: 363–377.
Kemp, W.M., W.R. Boynton, J.E. Adolf, D.F. Boesch, W.C. Boicourt, G. Brush, J.C. Cornwell, T.R. Fisher, P.M. Glibert, J.D. Hagy, L.W. Harding, E.D. Houde, D.G. Kimmel, W.D. Miller, R.I.E. Newell, M.R. Roman, E.M. Smith, and J.C. Stevenson. 2005. Eutrophication of Chesapeake Bay: Historical trends and ecological interactions. Marine Ecology Progress Series 303: 1–29.
Körner, S. 2002. Loss of submerged macrophytes in shallow lakes in North-Eastern Germany. International Review of Hydrobiology 87: 375–384.
LaMotte, A.E. 2015. Selected items from the census of agriculture at the county level for the conterminous United States, 1950–2012. US Geological Survey.
Landry, J.B., and R.R. Golden. 2018. In-situ effects of shoreline type and watershed land use on submerged aquatic vegetation habitat quality in the Chesapeake and Mid-Atlantic Coastal Bays. Estuaries and Coasts 41: 101–113.
Lefcheck, J.S., S.R. Marion, A.V. Lombana, and R.J. Orth. 2016. Faunal communities are invariant to fragmentation in experimental seagrass landscapes. PloS ONE. 11: e0156550.
Lefcheck, J.S., D.J. Wilcox, R.R. Murphy, S.R. Marion, and R.J. Orth. 2017. Multiple stressors threaten a critical foundation species in Chesapeake Bay. Global Biology Change 23: 3474–3483.
Lefcheck, J.S., R.J. Orth, W.C. Dennison, D.J. Wilcox, R.R. Murphy, J. Keisman, C. Gurbisz, M. Hannam, J.B. Landry, K.A. Moore, C.J. Patrick, J. Testa, D.E. Weller, and R.A. Batiuk. 2018. Long-term nutrient reductions lead to the unprecedented recovery of a temperate coastal region. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 115: 3658–3662.
Li, X.Y., D.E. Weller, C.L. Gallegos, T.E. Jordan, and H.C. Kim. 2007. Effects of watershed and estuarine characteristics on the abundance of submerged aquatic vegetation in Chesapeake Bay subestuaries. Estuaries and Coasts 30: 840–854.
Maxwell, P.S., J.S. Eklöf, M.M. van Katwijk, K. O’Brien, M. de la Torre-Castro, C. Boström, T.J. Bouma, R.K.F. Unsworth, B. Van Tussenbroek, and T. van der Heide. 2015. The fundamental role of ecological feedback mechanisms in seagrass ecosystems—A review. Biological Reviews. https://doi.org/10.1111/brv.12294.
Moore, K.A., D.J. Wilcox, and R.J. Orth. 2009. Assessment of the abundance of submersed aquatic vegetation (SAV) communities in the Chesapeake Bay and its use in SAV management. In Remote Sensing and Geospatial Technologies for Coastal Ecosystem: Assessment and Management, Lecture Notes in Geoinformation and Cartography, ed. X. Yang, 233–257. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag.
Moore, M., S.P. Romano, and T. Cook. 2010. Synthesis of Upper Mississippi River System submersed and emergent aquatic vegetation: past, present, and future. Hydrobiologia 640: 103–114.
Najjar, R.G., C.R. Pyke, M.B. Adams, D. Breitburg, C. Hershner, M. Kemp, R. Howarth, M.R. Mulholland, M. Paolisso, D. Secor, K. Sellner, D. Wardrop, and R. Wood. 2010. Potential climate-change impacts on the Chesapeake Bay. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 86: 1–20.
Oreska, M.P.J., K.J. McGlathery, R.J. Orth, and D.J. Wilcox. 2019. Seagrass mapping: A survey of the recent seagrass distribution literature. In A blue carbon primer: The state of coastal wetlands carbon science, practice, and policy, ed. L.-M. Windham-Myers, S. Crooks, and T.G. Troxler. CRC Press.
Orth, R.J., and K.A. Moore. 1983. Chesapeake Bay: An unprecedented decline in submerged aquatic vegetation. Science 222: 51–53.
Orth, R.J., and K.A. Moore. 1984. Distribution and abundance of submerged aquatic vegetation in Chesapeake Bay: An historical perspective. Estuaries 7: 531–540.
Orth, R.J., M.C. Harwell, and J.R. Fishman. 1999. A rapid and simple method for transplanting eelgrass using single, unanchored shoots. Aquatic Botany 64: 77–85.
Orth, R.J., J.R. Fishman, D.J. Wilcox, and K.A. Moore. 2002. Identification and management of fishing gear impacts in a recovering seagrass system in the coastal bays of the Delmarva Peninsula, USA. Journal Coastal Research SI 37: 111–129.
Orth, R.J., T.J.B. Carruthers, W.C. Dennison, C.M. Duarte, J.W. Fourqurean, K.L. Heck Jr., A.R. Hughes, G.A. Kendrick, W.J. Kenworthy, S. Olyarnik, F.T. Short, M. Waycott, and S.L. Williams. 2006. A global crisis for seagrass ecosystems. Bioscience 56: 987–996.
Orth, R.J., M.R. Williams, S.R. Marion, D.J. Wilcox, T.J.B. Carruthers, K.A. Moore, W.M. Kemp, W.C. Dennison, N. Rybicki, P. Bergstrom, and R.A. Batiuk. 2010a. Long-term trends in submersed aquatic vegetation (SAV) in Chesapeake Bay, USA, related to water quality. Estuaries and Coasts 33: 1144–1163.
Orth, R.J., S.R. Marion, K.A. Moore, and D.J. Wilcox. 2010b. Eelgrass (Zostera marina L.) in the Chesapeake Bay region of Mid-Atlantic coast of the USA: Challenges in conservation and restoration. Estuaries and Coasts 33: 139–150.
Orth, R.J., K.A. Moore, S.R. Marion, D.J. Wilcox, and D.B. Parrish. 2012. Seed addition facilitates eelgrass recovery in a coastal bay system. Marine Ecology Progress Series 448: 177–195.
Orth, R.J., W.C. Dennison, J.S. Lefcheck, C. Gurbisz, M. Hannam, J. Keisman, J.B. Landry, K.A. Moore, R.R. Murphy, C.J. Patrick, J. Testa, D.E. Weller, and D.J. Wilcox. 2017a. Submersed aquatic vegetation in Chesapeake Bay: Sentinel species in a changing world. Bioscience 67: 698–712.
Orth, R.J., J.S. Lefcheck, and D.J. Wilcox. 2017b. Boat propeller scarring of seagrass beds in lower Chesapeake Bay, USA: Patterns, causes, recovery, and management. Estuaries and Coasts 40: 1666–1676.
Patrick, C.J., and D.E. Weller. 2015. Interannual variation in submerged aquatic vegetation and its relationship to water quality in subestuaries of Chesapeake Bay. Marine Ecology Progress Series 537: 121–135.
Patrick, C.J., D.E. Weller, X.Y. Li, and M. Ryder. 2014. Effects of shoreline alteration and other stressors on submerged aquatic vegetation in subestuaries of Chesapeake Bay and the mid-Atlantic coastal bays. Estuaries and Coasts 37: 1516–1531.
Patrick, C.J., D.E. Weller, and M. Ryder. 2016. The relationship between shoreline armoring and adjacent submerged aquatic vegetation in Chesapeake Bay and nearby Atlantic coastal bays. Estuaries and Coasts 39: 158–170.
Patrick, C.J., D.E. Weller, R.J. Orth, D.J. Wilcox, and M.P. Hannam. 2018. Land use and salinity drive changes in SAV abundance and community composition. Estuaries and Coasts 41: S85–S100.
Ruhl, H.A., and N.B. Rybicki. 2010. Long-term reductions in anthropogenic nutrients link to improvements in Chesapeake Bay habitat. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 107: 16566–16570.
Sand-Jensen, K., T. Riis, O. Vestergaard, and S.E. Larsen. 2000. Macrophyte decline in Danish lakes and streams over the past 100 years. Journal of Ecology 88: 1030–1040.
Shafer, D., and P. Bergstrom. 2010. An introduction to a special issue on large-scale submerged aquatic vegetation restoration research in the Chesapeake Bay: 2003–2008. Restoration Ecology 18: 481–489.
Sherwood, E., H.S. Greening, J.O.R. Johansson, K. Kaufman, and G. Raulerson. 2017. Tampa Bay (Florida, USA): Documenting seagrass recovery since the 1980s and reviewing the benefits. Southeastern Geographer 57: 294–318.
Tango, P.J., and R.A. Batiuk. 2013. Deriving Chesapeake Bay water quality standards. Journal of the American Water Resources Association: 1–18.
Tomasko, D., M. Alderson, R. Burnes, J. Hecker, J. Leverone, G. Raulerson, and E. Sherwood. 2018. Widespread recovery of seagrass coverage in Southwest Florida (USA): Temporal and spatial trends and management actions responsible for success. Marine Pollution Bulletin 135: 1128–1137.
U.S. E.P.A. (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency). 2003a. Ambient water quality criteria for dissolved oxygen, water clarity and chlorophyll a for the Chesapeake Bay and its tidal tributaries. EPA 903-R-03-002. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Region III, Chesapeake Bay Program Office, Annapolis, MD.
U.S. E.P.A. (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency). 2003b. Technical support document for identification of Chesapeake Bay designated uses and attainability. October 2003. EPA 903-R-03-004. Region III Chesapeake Bay Program Office, Annapolis, MD.
U.S.E.P.A. [US Environmental Protection Agency]. 2010. Chesapeake Bay total maximum daily load for nitrogen, phosphorus and sediment. US Environmental Protection Agency. https://www.epa.gov/chesapeake-bay-tmdl/chesapeake-bay-tmdl-document.
U.S.E.P.A. [US Environmental Protection Agency]. 2017. Ambient water quality criteria for dissolved oxygen, water clarity and chlorophyll a for Chesapeake Bay and its tidal tributaries—2017 technical support for criteria assessment protocols addendum. November 2017. EPA 903-R-17-002. Region III Chesapeake Bay Program Office, Annapolis, MD.
van der Heide, T., E.H. van Nes, M.M. van Katwijk, H. Olff, and A.J.P. Smolders. 2011. Positive feedbacks in seagrass ecosystems—evidence from large-scale empirical data. PlosOne 6: e16504.
Waycott, M., C.M. Duarte, T.J.B. Carruthers, R.J. Orth, W.C. Dennison, S. Olyarnik, A. Calladine, J.W. Fourqurean, K.L. Heck Jr., A.R. Hughes, G.A. Kendrick, W.J. Kenworthy, F.T. Short, and S.L. Williams. 2009. Accelerating loss of seagrasses across the globe threatens coastal ecosystems. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 106: 12377–12381.
Williams, M., B. Longstaff, C. Buchanan, R. Llanso, and W. Dennison. 2009. Development and evaluation of a spatially-explicit index of Chesapeake Bay health. Marine Pollution Bulletin 59 (1-3): 14–25.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Contribution No. 3845 of the Virginia Institute of Marine Science, College of William and Mary and 5705 from University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science.
Funding
Funding for this synthesis effort was provided by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Grant Number CB96343701. Any use of trade, product, or firm names is for descriptive purposes only and does not imply endorsement by the U. S. Government. Support for actual funding for the survey came from multiple sources, notably USEPA, NOAA’ s Virginia Coastal management program, Virginia Department of Environmental Quality, Maryland Department of Natural Resources, and Maryland Department of the Environment. Chris Patrick was supported by a National Academy of Science and Engineering Gulf Research Program Fellowship while this paper was written. JSL was supported by the Michael E. Tennenbaum Secretarial Scholar gift to the Smithsonian Institution.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Richard C. Zimmerman
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(PDF 30 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Orth, R.J., Dennison, W.C., Gurbisz, C. et al. Long-term Annual Aerial Surveys of Submersed Aquatic Vegetation (SAV) Support Science, Management, and Restoration. Estuaries and Coasts 45, 1012–1027 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-019-00651-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-019-00651-w