Abstract
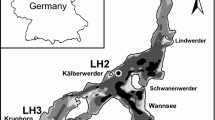
The availability of reactive phosphorus (P) may promote cyanobacterial blooms, a worldwide increasing phenomenon. Cyanobacteria may also regulate benthic P cycling through labile organic input to sediments, favouring reduced conditions and P release, ultimately acting as self-sustainment mechanism for the phytoplankton blooms. To analyse P–cyanobacteria feedbacks and compare external versus internal loads, we investigated P cycling in the Curonian Lagoon, a freshwater estuary with recurrent summer blooms. At two sites representing the dominant sediment types, we characterised P pools and mobility, via combined pore water analysis, calculation of diffusive exchanges and flux measurements via sediment core incubations. Annual P budgets were also calculated, to analyse the whole lagoon role as net sink or source. Muddy sediments, representing nearly 50 % of the lagoon surface, displayed higher P content if compared with sandy sediments, and most of this pool was reactive. The muddy site had consequently higher pore water dissolved inorganic phosphorus (DIP) concentrations maintaining high diffusive gradients. However, measured fluxes suggested that both sediment types were mostly P sinks except for a large DIP regeneration (nearly 30 μmol m−2 h−1) recorded at the muddy site during an intense cyanobacteria bloom. Such internal regeneration had the same order of magnitude as the annual external P load and may offset the net annual DIP sink role of the estuary. It may also prolong the duration of the bloom. Our results suggest that positive feedbacks can regulate N-fixing cyanobacteria blooms and internal P recycling, through either diffusive fluxes or sediment settling and resuspension.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almroth, E., A. Rengberg, J. Andersson, S. Pakhomova, and P.O.J. Hall. 2009. Effects of resuspension on benthic fluxes of oxygen, nutrients, dissolved inorganic carbon, iron and manganese in the Gulf of Finland, Baltic Sea. Continental Shelf Research 29: 807–818.
Anderson, L.D., and M.L. Delaney. 2000. Sequential extraction and analysis of phosphorus in marine sediments: streamlining of the SEDEX procedure. Limnology and Oceanography 45(2): 509–515.
Andersson, A., S. Hajdu, P. Haecky, J. Kuparinen, and J. Wikner. 1996. Succession and growth limitation of phytoplankton in the Gulf of Bothnia (Baltic Sea). Marine Biology 126(4): 791–801.
Andrieux-Loyer, F., and A. Aminot. 2001. Phosphorus forms related to sediment grain size and geochemical characteristics in French coastal areas. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 52: 617–629.
Aspila, K.I., H. Agemian, and A.S. Chau. 1976. A semi-automated method for the determination of inorganic, organic and total phosphate in sediments. Analyst 101: 187–197.
Berner, R.A. 1980. Early diagenesis: a theoretical approach (No. 1). Princeton University Press.
Beutler, M., K.H. Wiltshire, B. Meyer, C. Moldaenke, C. Lüring, M. Meyerhöfer, and H. Dau. 2002. A fluorometric method for the differentiation of algal populations in vivo and in situ. Photosynthesis Research 72(1): 39–53.
Blomqvist, S., A. Gunnar, and R. Elmgren. 2004. Why the limiting nutrient differs between temperate coastal seas and freshwater lakes: a matter of salt. Limnology and Oceanography 49(6): 2236–2241.
Boudreau, B.P. 1997. Diagenetic models and their implication: modeling transport and reactions in aquatic sediments. Berlin: Springer.
Bresciani, M., C. Giardino, D. Stroppiana, R. Pilkaitytė, M. Zilius, M. Bartoli, and A. Razinkovas. 2012. Retrospective analysis of spatial and temporal variability of chlorophyll-a in the Curonian Lagoon. Journal of Coastal Conservation 16: 511–519.
Broecker, W.S., and T.H. Peng. 1974. Gas exchange rates between air and sea. Tellus 26: 21–35.
Canfield, D.E. 1994. Factors influencing organic carbon preservation in marine sediments. Chemical Geology 114: 315–329.
Carman, R., and H. Cederwall. 2001. Sediments and macrofauna in the Baltic Sea – characteristics, nutrient contents and distribution. In A systems analysis of the Baltic Sea, 289–327. Berlin: Springer.
Chen, M., T.R. Ye, L.R. Krumholz, and H.L. Jiang. 2014. Temperature and cyanobacterial bloom biomass influence phosphorus cycling in eutrophic lake sediments. PLoS ONE 9(3), e93130.
Coelho, J.P., M.R. Flindt, H.S. Jensen, A.I. Lillebø, and M.A. Pardal. 2004. Phosphorus speciation and availability in intertidal sediments of a temperate estuary: relation to eutrophication and annual P-fluxes. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 61(4): 583–590.
Conley, D.J., S. Björck, E. Bonsdorff, J. Carstensen, G. Destouni, B.G. Gustafsson, S. Hietanen, M. Kortekaas, H. Kuosa, M.H.E. Meier, B. Müller-Karulis, K. Nordberg, A. Norko, G. Nürnberg, H. Pitkänen, N.N. Rabalais, R. Rosenberg, O.P. Savchuk, C. Slomp, M. Voss, F. Wulff, and L. Zillén. 2009. Hypoxia-related processes in the Baltic Sea. Environmental Science and Technology 43(10): 3412–3420.
Dailidiene, I., and L. Davuliene. 2007. Long-term mean salinity in the Curonian Lagoon in 1993–2005. Acta Zoologica Lituanica 17(2): 172–181.
Dalsgaard, T., L.P. Nielsen, V. Brotas, P. Viaroli, G. Underwood, D. Nedwell, K. Sundbäck, S. Rysgaard, A. Miles, M. Bartoli, L. Dong, D.C.O. Thornton, L.D.M. Otossen, G. Castaldelli, and N. Risgaard-Petersen. 2000. Protocol handbook for NICE – Nitrogen Cycling in Estuaries: a project under the EU research program: Marine Science and Technology (MAST III). Silkeborg: National Environmental Research Institute.
Da-Peng, L., and H. Yong. 2010. Sedimentary phosphorus fractions and bioavailability as influenced by repeated sediment resuspension. Ecological Engineering 36: 958–962.
Dias, J.M.A., R. Gonzalez, C. Garcia, and V. Diaz-del-Rio. 2002. Sediment distribution patterns on the Galicia-Minho continental shelf. Progress in Oceanography 52(2): 215–231.
Emelyanov, E.M. 2001. Biogenic components and elements in sediments of the central Baltic and their redistribution. Marine Geology 172: 23–41.
Fanning, K.A., K.L. Carder, and P.R. Betzer. 1982. Sediment resuspension by coastal waters: a potential mechanism for nutrient re-cycling on the ocean’s margins. Deep Sea Research Part A. Oceanographic Research Papers 29(8): 953–965.
Ferrarin, C., A. Razinkovas, S. Gulbinskas, G. Umgiesser, and L. Bliudziute. 2008. Hydraulic regime-based zonation scheme of the Curonian Lagoon. Hydrobiologia 611(1): 133–146.
Finni, T., K. Kononen, R. Olsonen, and K. Wallström. 2001. The history of cyanobacterial blooms in the Baltic Sea. Ambio 30(4): 172–178.
Froelich, P.N. 1988. Kinetic control of dissolved phosphate in natural rivers and estuaries: a primer on the phosphate buffer mechanism. Limnology and Oceanography 33(4/2): 649–668.
Gailiusis, B., M. Kovalenkoviene, and J. Kriauciuniene. 2005. Hydrological and hydraulic investigation of water area in the Curonian lagoon between island Kiaulės nugaros and Alksnynės. Energetika 4: 34–41 [in Lithuanian].
Galkus, A., and K. Joksas. 1997. Nuosėdinė medžiaga tranzitinėje akvasistemoje. Vilnius, 198. [in Lithuanian]
Gasiunaite, Z.R. 2000. Coupling of the limnetic and brackishwater plankton crustaceans in the Curonian lagoon (Baltic Sea). International Review of Hydrobiology 85: 649–657.
Glibert, P.M. 2012. Ecological stoichiometry and its implications for aquatic ecosystem sustainability. Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability 4(3): 272–277.
Glibert, P.M., and J.M. Burkholder. 2011. Harmful algal blooms and eutrophication: ‘strategies’ for nutrient uptake and growth outside the Redfield comfort zone. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology 29(4): 724–738.
Grasshoff, K., M. Ehrhardt, and K. Kremling. 1983. Methods of seawater analysis, 2nd ed. Berlin: Verlag Chemie.
Guildford, S.J., and R.E. Hecky. 2000. Total nitrogen, total phosphorus, and nutrient limitation in lakes and oceans: is there a common relationship? Limnology and Oceanography 45(6): 1213–1223.
Humborg, C., K. Fennel, M. Pastuszak, and W. Fennel. 2000. A box model approach for a long-term assessment of estuarine eutrophication, Szczecin Lagoon, southern Baltic. Journal of Marine Systems 25(3): 387–403.
Hyenstrand, P., E. Rydin, and M. Gunnerhead. 1999. Response of pelagic cyanobacteria to iron additions – enclosure experiments from Lake Erken. Journal of Plankton Research 22: 113–126.
Hyenstrand, P., U. Burkert, A. Pettersson, and P. Blomqvist. 2000. Competition between the green alga Scenedesmus and the cyanobacterium Synechococcus under different modes of inorganic nitrogen supply. Hydrobiologia 435: 91–98.
Jakimavicius, D. 2012. Changes of water balance elements of the Curonian Lagoon and their forecast due to anthropogenic and natural factors. Kaunas: Doctoral thesis.
Jakimavicius, D., and J. Kriauciuniene. 2011. Influence of the Klaipeda seaport development on water balance of the Curonian lagoon. The 8th International Conference ‘Environmental Engineering’, May 19–20, 2011, Vilnius.
Jensen, J.P., K. Jeppesen, K. Olrik, and P. Kristensen. 1994. Impact of nutrients and physical factors on the shift from cyanobacterial to chlorophyte dominance in shallow Danish lakes. Canadian Journal Fish Aquatic Science 51: 1692–1699.
Jensen, H.S., P.B. Mortensen, F.Ø. Andersen, E. Rasmussen, and A. Jensen. 1995. Phosphorus cycling in coastal marine sediment, Aarhus Bay, Denmark. Limnology and Oceanography 40: 908–917.
Kahru, M., U. Horstmann, and O. Rud. 1994. Increased cyanobacterial blooming in the Baltic Sea detected by satellites: natural fluctuation or ecosystem change? Ambio 23: 469–472.
Karlson, K., E. Bonsdorff, and R. Rosenberg. 2007. The impact of benthic macrofauna for nutrient fluxes from Baltic Sea sediments. Ambio 36(2): 161–167.
Laenen, A., and A.P. LeTourneau. 1996. Upper Klamath basin nutrient-loading study: estimate of wind-induced resuspension of bed sediment during periods of low lake elevation (No. 95-414). US Geological Survey; Information Services [distributor].
Lerman, A. 1979. Geochemical processes: water and sediment environments. New York: John Wiley and Sons.
Lewandowski, J., and M. Hupfer. 2005. Effect of macrozoobenthos on two‐dimensional small‐scale heterogeneity of pore water phosphorus concentrations in lake sediments: a laboratory study. Limnology and Oceanography 50(4): 1106–1118.
Li, Y.H., and S. Gregory. 1974. Diffusion of ions in deep-sea sediments. Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta 38: 703–714.
Lilover, M.J., and A. Stips. 2008. The variability of parameters controlling the cyanobacteria bloom biomass in the Baltic Sea. Journal of Marine Systems 74: 108–115.
Lorenzen, C.J. 1967. Determination of chlorophyll and pheopigments: spectrophotometric equations. Limnology and Oceanography 12: 343–346.
Łukawska-Matuszewska, K., and J. Bolałek. 2008. Spatial distribution of phosphorus forms in sediments in Gulf of Gdansk (southern Baltic Sea). Continental Shelf Research 28: 977–990.
Lukkari, K., M. Leivuori, and H. Hartikainen. 2008. Vertical distribution and chemical character of sediment phosphorus in two shallow estuaries in the Baltic Sea. Biogeochemistry 90: 171–191.
Olenina, I. 1998. Long-term changes in the Kursiu Marios lagoon: eutrophication and phytoplankton response. Ecologija 1: 56–65.
Paerl, H. 2008. Nutrient and other environmental controls of harmful cyanobacterial blooms along the freshwater–marine continuum. In Cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms: state of the science and research needs, ed. H.H. Kenneth, 217–237. New York: Springer.
Pedersen, M.F., and J. Borum. 1996. Nutrient control of algal growth in estuarine waters: nutrient limitation and the importance of nitrogen requirements and nitrogen storage among phytoplankton and species of macroalgae. Marine Ecology Progress Series. Oldendorf 142(1): 261–272.
Pilkaityte, R., and A. Razinkovas. 2006. Factors controlling phytoplankton blooms in a temperate estuary: nutrient limitation and physical forcing. Hydrobiologia 555(1): 41–48.
Pilkaityte, R., and A. Razinkovas. 2007. Seasonal changes in phytoplankton composition and nutrient limitation in a shallow Baltic lagoon. Boreal Environment Research 12(5): 551–559.
Razinkovas, A., I. Dailidiene, and R. Pilkaityte. 2008. Sustainable use and development of watersheds. NATO science for peace and security series C: environmental security, ed. I. E. Gönenc, A. Vadineanu, J.P. Wolflin, R.C. Russo, 403–413. New York: Springer.
Reddy, K.R., M.M. Fisher, and D. Ivanoff. 1996. Resuspension and diffusive fluxes of nitrogen and phosphorus in a hypereutrophic lake. Journal of Environmental Quality 25(2): 363–371.
Revsbech, N.P. 1989. An oxygen microsensor with a guard cathode. Limnology and Oceanography 34: 474–478.
Ruttenberg, K.C. 1992. Development of a sequential extraction method for different forms of phosphorus in marine sedimentus. Limnology and Oceanography 37(7): 1460–1482.
Ruttenberg, K.C. 2003. The global phosphorus cycle. Treatise on Geochemistry 8: 585–643.
Ruttenberg, K.C., and R.A. Berner. 1993. Authigenic apatite formation and burial in sediments from non-upwelling, continental margin environments. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 57(5): 991–1007.
Rydin, E. 2000. Potentially mobile phosphorus in Lake Erken sediment. Water Resources 34(7): 2037–2042.
Rydin, E., J.M. Malmaeus, O.M. Karlsson, and P. Jonsson. 2011. Phosphorus release from coastal Baltic Sea sediments as estimated from sediment profiles. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 92(1): 111–117.
Selig, U., and G. Schlungbaum. 2003. Characterisation and quantification of phosphorus release from profundal bottom sediments in two dimictic lakes during summer stratification. Journal of Limnology 62(2): 151–162.
Slomp, C.P. 2011. Phosphorus cycling in the estuarine and coastal zones: sources, sinks, and transformations. In Treatise on estuarine and coastal science, vol. 5, Biogeochemistry, ed. E. Wolanski and D.S. McLusky, 201–229. Waltham, MA: Academic.
Slomp, C.P., J.F.P. Malschaert, and W. Van Raaphorst. 1998. The role of adsorption in sediment-water exchange of phosphate in North Sea continental margin sediments. Limnology and Oceanography 43(5): 832–846.
Smith, S.V. 1984. Phosphorus versus nitrogen limitation in the marine environment. Limnology and Oceanography 29(6): 1149–1160.
Søndergaard, M., P. Kristensen, and E. Jeppesen. 1992. Phosphorus release from resuspended sediments in the shallow and wind-exposed Lake Arresø, Denmark. Hydrobiologia 229: 91–99.
Spagnoli, F., and M.C. Bergamini. 1997. Water-sediment exchange of nutrients during early diagenesis and resuspension of anoxic sediments from the northern Adriatic Sea shelf. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution 99(1–4): 541–556.
Spuriene, R. 2012. Kuršių marių suspenduotos medžiagos sedimentacijos ypatumai. Masther Thesis. [in Lithuanian]
Ståhlberg, C., D. Bastviken, B.H. Svensson, and L. Rahm. 2006. Mineralization of organic matter in coastal sediments at different frequency and duration of resuspension. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 70: 317–325.
Sundby, B., C. Gobeil, N. Silverberg, and A. Mucci. 1992. The phosphorus cycle in coastal marine sediments. Limnology and Oceanography 37(6): 1129–1145.
Tengberg, A., E. Almroth, and P. Hall. 2003. Resuspension and its effects on organic carbon recycling and nutrient exchange in coastal sediments: in situ measurements using new experimental technology. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 285–286: 119–142.
Vahtera, E., D.J. Conley, B.G. Gustafsson, H. Kuosa, H. Pitkänen, O.P. Savchuk, T. Tamminen, M. Viitasalo, M. Voss, N. Wasmund, and F. Wulff. 2007. Internal ecosystem feedbacks enhance nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria blooms and complicate management in the Baltic Sea. Ambio 36: 186–194.
Valderrama, J.C. 1981. The simultaneous analysis of total nitrogen and total phosphorus in natural waters. Marine Chemistry 10: 109–122.
Wang, H., and H. Wang. 2009. Mitigation of lake eutrophication: loosen nitrogen control and focus on phosphorus abatement. Progress in Natural Science 19(10): 1445–1451.
Zemlys, P., C. Ferrarin, G. Umgiesser, S. Gulbinskas, and D. Bellafiore. 2013. Investigation of saline water intrusions into the Curonian Lagoon (Lithuania) and two-layer flow in the Klaipėda Strait using finite element hydrodynamic model. Ocean Science 9(3): 573–584.
Zilius, M. 2011. Oxygen and nutrient Exchange at the sediment-water interface in the eutrophic boreal lagoon (Baltic Sea). Doctoral dissertation. Klaipeda
Zilius, M., D. Daunys, J. Petkuviene, and M. Bartoli. 2012. Sediment-water oxygen, ammonium and soluble reactive phosphorus fluxes in a turbid freshwater estuary (Curonian lagoon, Lithuania): evidences of benthic microalgal activity. Journal of Limnology 71(2): 309–319.
Zilius, M., M. Bartoli, M. Bresciani, M. Katarzyte, T. Ruginis, J. Petkuviene, I. Lubiene, C. Giardino, P.A. Bukaveckas, R. de Wit, and A. Razinkovas. 2014. Feedback mechanisms between cyanobacterial blooms, transient hypoxia, and benthic phosphorus regeneration in shallow coastal environments. Estuaries and Coasts 37: 680–694.
Zilius, M., G. Giordani, J. Petkuviene, I. Lubiene, T. Ruginis, and M. Bartoli. 2015. Phosphorus mobility under short-term anoxic conditions in two shallow eutrophic coastal systems (Curonian and Sacca di Goro lagoons). Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 164: 134–146.
Acknowledgments
J. Petkuviene, M. Zilius, I. Lubiene, T. Ruginis and A. Razinkovas-Baziukas were supported by the project Water Masses Circulation Features in the Curonian Lagoon, Using Stable Isotope Tags and Finite Element Mode (CISOCUR) (No. VP1-3.1-ŠMM-07-K-02-086), G. Giordani by the NETBIOGEK project (No. MIP-12334) of the Research Council of Lithuania and M. Bartoli by the BONUS project Nutrient Cocktails in Coastal zones of the Baltic Sea (COCOA) (No. BONUS-2/2014). We kindly acknowledge Diana Vaiciute from the Klaipeda University for Chl-a analysis (in 2013). We gratefully thank the Lithuanian Marine Research Department of the Ministry of Environment for providing meteorological and Nemunas River discharge data. We acknowledge the two anonymous reviewers and the editor for their valuable comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Hans W. Paerl
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Petkuviene, J., Zilius, M., Lubiene, I. et al. Phosphorus Cycling in a Freshwater Estuary Impacted by Cyanobacterial Blooms. Estuaries and Coasts 39, 1386–1402 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-016-0078-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-016-0078-0