Abstract
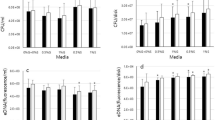
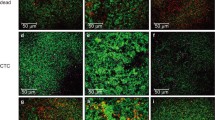
Enterococcus faecalis is a ubiquitous bacterium of the gut that is observed in persistent periradicular infections. Its pathogenicity is associated with biofilm formation and the ability to survive under nutrient-poor (starvation) conditions. However, characteristics of chemical composition of biofilm cells developed by starved E. faecalis cells remain poorly understood. In this study, E. faecalis cells in exponential, stationary, and starvation phases were prepared and separately cultured to form biofilms. Confocal laser scanning microscopy was performed to verify biofilm formation. Raman microscopy was used to investigate the chemical composition of cells within the biofilms. Compared to cells in exponential or stationary phase, starved cells developed biofilms with fewer culturable cells (P < 0.05). Raman analysis revealed that cells produced in the biofilms from starved planktonic cells contained more protein and less nucleic acids than either the corresponding planktonic cells or the cells in biofilms from planktonic cells in exponential or stationary phases, suggesting that biofilm-grown cells from the starvation phase were characterized by increased synthesis of proteins and decreased nucleic acids. This study provides an insight into the chemical composition of biofilm cells developed by starved E. faecalis.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BHI:
-
Brain heart infusion
- CFU:
-
Colony-forming unit
- CLSM:
-
Confocal laser scanning microscopy
- DFA:
-
Discriminant function analysis
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- PCA:
-
Principal component analysis
- RM:
-
Raman microscopy
References
Andrews JS, Rolfe SA, Huang WE, Scholes JD, Banwart SA (2010) Biofilm formation in environmental bacteria is influenced by different macromolecules depending on genus and species. Environ Microbiol 12(9):2496–2507
Distel JW, Hatton JF, Gillespie MJ (2002) Biofilm formation in medicated root canals. J Endod 28(10):689–693
Du XJ, Wang F, Lu X, Rasco BA, Wang S (2012) Biochemical and genetic characteristics of Cronobacter sakazakii biofilm formation. Res Microbiol 163(6–7):448–456. doi:10.1016/j.resmic.2012.06.002
Everall NJ (2010) Confocal Raman microscopy: common errors and artefacts. Analyst 135(10):2512–2522. doi:10.1039/c0an00371a
Flemming HC, Wingender J (2010) The biofilm matrix. Nat Rev Microbiol 8(9):623–633
George S, Basrani B, Kishen A (2010) Possibilities of gutta-percha-centered infection in endodontically treated teeth: an in vitro study. J Endod 36(7):1241–1244. doi:10.1016/j.joen.2010.03.024
Giard JC, Laplace JM, Rince A, Pichereau V, Benachour A, Leboeuf C, Flahaut S, Auffray Y, Hartke A (2001) The stress proteome of Enterococcus faecalis. Electrophoresis 22(14):2947–2954
Hamasha K, Sahana MB, Jani C, Nyayapathy S, Kang CM, Rehse SJ (2010) The effect of Wag31 phosphorylation on the cells and the cell envelope fraction of wild-type and conditional mutants of Mycobacterium smegmatis studied by visible-wavelength Raman spectroscopy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 391(1):664–668
Hendrickx AP, Willems RJ, Bonten MJ, van Schaik W (2009) LPxTG surface proteins of enterococci. Trends Microbiol 17(9):423–430
Huang WE, Griffiths RI, Thompson IP, Bailey MJ, Whiteley AS (2004) Raman microscopic analysis of single microbial cells. Anal Chem 76(15):4452–4458
Huang WE, Li M, Jarvis RM, Goodacre R, Banwart SA (2010) Shining light on the microbial world the application of Raman microspectroscopy. Adv Appl Microbiol 70:153–186
Ivleva NP, Wagner M, Horn H, Niessner R, Haisch C (2009) Towards a nondestructive chemical characterization of biofilm matrix by Raman microscopy. Anal Bioanal Chem 393(1):197–206
Kirschner C, Maquelin K, Pina P, Ngo Thi NA, Choo-Smith LP, Sockalingum GD, Sandt C, Ami D, Orsini F, Doglia SM, Allouch P, Mainfait M, Puppels GJ, Naumann D (2001) Classification and identification of enterococci: a comparative phenotypic, genotypic, and vibrational spectroscopic study. J Clin Microbiol 39(5):1763–1770
Kishen A, Sum CP, Mathew S, Lim CT (2008) Influence of irrigation regimens on the adherence of Enterococcus faecalis to root canal dentin. J Endod 34(7):850–854
Liu H, Wei X, Ling J, Wang W, Huang X (2010) Biofilm formation capability of Enterococcus faecalis cells in starvation phase and its susceptibility to sodium hypochlorite. J Endod 36(4):630–635
Lleo M, Bonato B, Tafi MC, Caburlotto G, Benedetti D, Canepari P (2007) Adhesion to medical device materials and biofilm formation capability of some species of enterococci in different physiological states. FEMS Microbiol Lett 274(2):232–237
Mah TFC, O’Toole GA (2001) Mechanisms of biofilm resistance to antimicrobial agents. Trends Microbiol 9(1):34–39. doi:10.1016/s0966-842x(00)01913-2
Neugebauer U, Schmid U, Baumann K, Ziebuhr W, Kozitskaya S, Deckert V, Schmitt M, Popp J (2007) Towards a detailed understanding of bacterial metabolism—spectroscopic characterization of Staphylococcus epidermidis. ChemPhysChem 8(1):124–137. doi:10.1002/cphc.200600507
Portenier I, Waltimo T, Orstavik D, Haapasalo M (2005) The susceptibility of starved, stationary phase, and growing cells of Enterococcus faecalis to endodontic medicaments. J Endod 31(5):380–386
Sandt C, Smith-Palmer T, Comeau J, Pink D (2009) Quantification of water and biomass in small colony variant PAO1 biofilms by confocal Raman microspectroscopy. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 83(6):1171–1182
Stuart CH, Schwartz SA, Beeson TJ, Owatz CB (2006) Enterococcus faecalis: its role in root canal treatment failure and current concepts in retreatment. J Endod 32(2):93–98
Sundqvist G (1992) Ecology of the root canal flora. J Endod 18(9):427–430
Williamson AE, Cardon JW, Drake DR (2009) Antimicrobial susceptibility of monoculture biofilms of a clinical isolate of Enterococcus faecalis. J Endod 35(1):95–97
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Key Clinical Program of the Ministry of Health, China (No. [2010]439), Department of Science and Technology of Guangdong Province (2010B050700007, 2009B030801115), Fundamental Research Funds for The Central Universities (12ykpy67), National Natural Science Foundation of China (81200778), and Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (S2011040002747).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Xu, Q., Huo, L. et al. Chemical composition of Enterococcus faecalis in biofilm cells initiated from different physiologic states. Folia Microbiol 59, 447–453 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-014-0319-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-014-0319-1