Abstract
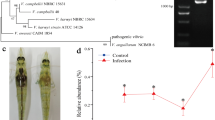
Vibrio alginolyticus is a Gram-negative halophilic bacterium and has been recognized as an opportunistic pathogen to both humans and marine animals. So far, most studies have been focused on marine animals and few reports have been aimed at mammals, including human. In this study, we first established a mouse model to understand the pathogenic mechanism of V. alginolyticus infection. After infection via intraperitoneal injection, hematological and liver function indicators were evaluated and serum interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-6 expression were detected by ELISA. Furthermore, we compared the virulence of two V. alginolyticus strains, ATCC17749T and E0666. The results demonstrated that V. alginolyticus infection causes robust lung and liver damage and induces changes in IL-1β, IL-6, hematological, and liver indicators. In addition, the ATCC17749T strain appeared to be more virulent than the E0666 strain. Better understanding of the pathogenic mechanism of V. alginolyticus infection should guide effective prevention and therapy for V. alginolyticus infection.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ardic N, Ozyurt M (2004) Case report: otitis due to Vibrio alginolyticus. Mikrobiol Bul 38:145–148
Balcazar JL, Gallo-Bueno A, Planas M, Pintado J (2010) Isolation of Vibrio alginolyticus and Vibrio splendidus from captive-bred seahorses with disease symptoms. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 97:207–210
Balebona MC, Andreu MJ, Bordas MA, Zorrilla I, Morinigo MA, Borrego JJ (1998) Pathogenicity of Vibrio alginolyticus for cultured gilt-head sea bream (Sparus aurata L.). Appl Environ Microbiol 64:4269–4275
Cai SH, Yaol SY, Lu YS, Wu ZH, Jian JC, Wang B (2010) Immune response in Lutjanus erythropterus induced by the major outer membrane protein (OmpU) of Vibrio alginolyticus. Dis Aquat Organ 90:63–68
Chen Q, Yan Q, Wang K, Zhuang Z, Wang X (2008) Portal of entry for pathogenic Vibrio alginolyticus into large yellow croaker Pseudosciaena crocea, and characteristics of bacterial adhesion to mucus. Dis Aquat Organ 80:181–188
Chen C, Wang QB, Liu ZH, Zhao JJ, Jiang X, Sun HY, Ren CH, Hu CQ (2012) Characterization of role of the toxR gene in the physiology and pathogenicity of Vibrio alginolyticus. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 101:281–288
English VL, Lindberg RB (1977) Isolation of Vibrio alginolyticus from wounds and blood of a burn patient. Am J Med Technol 43:989–993
Feingold MH, Kumar ML (2004) Otitis media associated with Vibrio alginolyticus in a child with pressure-equalizing tubes. Pediatr Infect Dis J 23:475–476
George MR, John KR, Iyappan T, Jeyaseelan MJ (2005) Genetic heterogeneity among Vibrio alginolyticus isolated from shrimp farms by PCR fingerprinting. Lett Appl Microbiol 40:369–372
Gomez JM, Fajardo R, Patino JF, Arias CA (2003) Necrotizing fasciitis due to Vibrio alginolyticus in an immunocompetent patient. J Clin Microbiol 41:3427–3429
Gomez-Leon J, Villamil L, Lemos ML, Novoa B, Figueras A (2005) Isolation of Vibrio alginolyticus and Vibrio splendidus from aquacultured carpet shell clam (Ruditapes decussatus) larvae associated with mass mortalities. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:98–104
Harikrishnan R, Balasundaram C, Heo MS (2012) Poly d, l-lactide-co-glycolic acid-liposome encapsulated ODN on innate immunity in Epinephelus bruneus against Vibrio alginolyticus. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 147:77–85
Ho PL, Tang WM, Lo KS, Yuen KY (1998) Necrotizing fasciitis due to Vibrio alginolyticus following an injury inflicted by a stingray. Scand J Infect Dis 30:192–193
Horii T, Morita M, Muramatsu H, Monji A, Miyagishima D, Kanno T, Maekawa M (2005) Antibiotic resistance in Aeromonas hydrophila and Vibrio alginolyticus isolated from a wound infection: a case report. J Trauma 58:196–200
Howard RJ, Pessa ME, Brennaman BH, Ramphal R (1985) Necrotizing soft-tissue infections caused by marine vibrios. Surgery 98:126–130
Janda JM, Brenden R, DeBenedetti JA, Constantino MO, Robin T (1986) Vibrio alginolyticus bacteremia in an immunocompromised patient. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 5:337–340
Kim YR, Kim SY, Kim CM, Lee SE, Rhee JH (2005) Essential role of an adenylate cyclase in regulating Vibrio vulnificus virulence. FEMS Microbiol Lett 243:497–503
Lee DY, Moon SY, Lee SO, Yang HY, Lee HJ, Lee MS (2008) Septic shock due to Vibrio alginolyticus in a cirrhotic patient: the first case in Korea. Yonsei Med J 49:329–332
Lessner AM, Webb RM, Rabin B (1985) Vibrio alginolyticus conjunctivitis. First reported case. Arch Ophthalmol 103:229–230
Levine WC, Griffin PM (1993) Vibrio infections on the Gulf Coast: results of first year of regional surveillance. Gulf Coast Vibrio Working Group. J Infect Dis 167:479–483
Li XC, Xiang ZY, Xu XM, Yan WH, Ma JM (2009) Endophthalmitis caused by Vibrio alginolyticus. J Clin Microbiol 47:3379–3381
Liang H, Xia L, Wu Z, Jian J, Lu Y (2010) Expression, characterization and immunogenicity of flagellin FlaC from Vibrio alginolyticus strain HY9901. Fish Shellfish Immunol 29:343–348
Libinzon AE, Lebedev GD, Pavlova IV, Nagornaia AF, Krasnova NV (1975) Isolation of parahemolytic vibrions from persons with acute gastrointestinal diseases. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol 0:25–29
Lu W, Li YH, Yu ZJ, He XF, Chen Y, Zhao JB, Zhu ZY (2007) A comparative study of damage to liver function after TACE with use of low-dose versus conventional-dose of anticancer drugs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology 54:1499–1502
Matsiota-Bernard P, Nauciel C (1993) Vibrio alginolyticus wound infection after exposure to sea water in an air crash. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 12:474–475
Matsumoto K, Ohshige K, Fujita N, Tomita Y, Mitsumizo S, Nakashima M, Oishi H (2010) Clinical features of Vibrio vulnificus infections in the coastal areas of the Ariake Sea, Japan. J Infect Chemother 16:272–279
Reina Prieto J, Hervas Palazon J (1993) Otitis media due to Vibrio alginolyticus: the risks of the Mediterranean Sea. An Esp Pediatr 39:361–363
Sganga G, Cozza V, Spanu T, Spada PL, Fadda G (2009) Global climate change and wound care: case study of an off-season Vibrio alginolyticus infection in a healthy man. Ostomy Wound Manag 55:60–62
Soto-Rodriguez SA, Roque A, Lizarraga-Partida ML, Guerra-Flores AL, Gomez-Gill B (2003) Virulence of luminous vibrios to Artemia franciscana nauplii. Dis Aquat Organ 53:231–240
Spark RP, Fried ML, Perry C, Watkins C (1979) Vibrio alginolyticus wound infection: case report and review. Ann Clin Lab Sci 9:133–138
Wedemeyer H, Hofmann WP, Lueth S, Malinski P, Thimme R, Tacke F, Wiegand J (2010) ALT screening for chronic liver diseases: scrutinizing the evidence. Z Gastroenterol 48:46–55
Wei YC, Pan TS, Chang MX, Huang B, Xu Z, Luo TR, Nie P (2011) Cloning and expression of Toll-like receptors 1 and 2 from a teleost fish, the orange-spotted grouper Epinephelus coioides. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 141:173–182
Wu CJ, Wang H, Chan YL, Li TL (2011) Passive immune-protection of small abalone against Vibrio alginolyticus infection by anti-Vibrio IgY-encapsulated feed. Fish Shellfish Immunol 30:1042–1048
Xie ZY, Hu CQ, Chen C, Zhang LP, Ren CH (2005) Investigation of seven Vibrio virulence genes among Vibrio alginolyticus and Vibrio parahaemolyticus strains from the coastal mariculture systems in Guangdong, China. Lett Appl Microbiol 41:202–207
Ye J, Ma Y, Liu Q, Zhao DL, Wang QY, Zhang YX (2008) Regulation of Vibrio alginolyticus virulence by the LuxS quorum-sensing system. J Fish Dis 31:161–169
Zhao Z, Chen C, Hu CQ, Ren CH, Zhao JJ, Zhang LP, Jiang X, Luo P, Wang QB (2010) The type III secretion system of Vibrio alginolyticus induces rapid apoptosis, cell rounding and osmotic lysis of fish cells. Microbiology 156:2864–2872
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Major PLA Research Project of “The 12th Five-Year Plan” for Medical Science Development (no. BWS12J014), China Science Foundation Postdoctoral Fellowship Grant (no. 2012 M521929), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 81201265).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, XF., Zhang, H., Liu, X. et al. Pathogenic analysis of Vibrio alginolyticus infection in a mouse model. Folia Microbiol 59, 167–171 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-013-0279-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-013-0279-x