Abstract
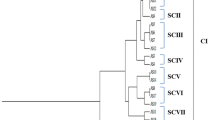
Genetic diversity among 43 petroleum hydrocarbon-degrading Pseudomonas belonging to four different species and the type strain Pseudomonas aeruginosa MTCC1034 was assessed by using restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) of polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-amplified 16S–23S rDNA intergenic spacer regions (ISRs) polymorphism. PCR amplification from all Pseudomonas species yielded almost identical ISR amplicons of “?” 800 bp and in nested PCR of “?” 550 bp. The RFLP analysis with MboI and AluI revealed considerable intraspecific variations within the Pseudomonas species. The dendrogram constructed on the basis of the PCR-RFLP patterns of 16S–23S rDNA intergenic spacer regions differentiated all the species into seven different clusters.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold DL, Gibbon MT, Taylor JD, Vivian A (1996) Specific oligonucleotide primers for the identification of Pseudomonas syringae yield one of two possible DNA fragments by PCR amplification: evidence for phylogenetic divergence. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 49:233–245
Atlas RM (1981) Microbial degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons: an environmental perspective. Microbiol Rev 45:180–209
Balows A (1985) The prokaryotes—hydrocarbon oxidizing bacteria, vol 3. Springer, Berlin, pp 126–130
Barry T, Colleran G, Glennon M, Dunican LK, Gannon F (1999) The 16S/23S ribosomal spacer region as a target for DNA probes to identify Eubacteria. PCR Meth Appl 1:51–56
Bartha R (1986) Biotechnology of petroleum pollutant biodegradation. Microbiol Ecol 12:155–172
Bruce KD, Hiorns WD, Hobman JL, Osborn AM, Strike P (1992) Amplification of DNA from native population of soils bacteria by using the polymerase chain reaction. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:3413–3416
Cedergren RJ, Gray MW, Abel Y, Sankoff D (1993) The evolutionary relationships among known life forms. J Mol Evol 28:98–112
Derek R, Lovley R (2003) Cleaning up with genomics: Applying molecular biology to bioremediation. Nat Rev Microbiol 1:33–44
Fish NM, Allenby DJ, Lilly MD (1982) Oxidation of n-alkanes: growth of Pseudomonas putida. Eur J Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 14:259–262
Graham TA, Golsteyn-Thomas EJ, Thomas JE, Gannon VPJ (1997) Inter- and intra-species comparison of the 16S–23S rRNA operon intergenic spacer regions of six Listeria spp. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:863–869
Grunenwald H (2000) Direct PCR from a single bacterial colony without DNA extraction using the FailSafe™ PCR system. Epicentre Forum 7(6):12
Gurteler V, Stanissich VA (1996) New approaches to typing and identification of bacteria using the 16S–23S rDNA spacer region. Microbiol 142:3–16
Jensen MA, Webster JA, Stutaus N (1993) Rapid identification of bacteria on the basis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified ribosomal DNA spacer polymorphisms. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:945–952
Nelson KE (2002) Complete genome sequence and comparative analysis of the metabolically versatile Pseudomonas putida KT2440. Environ Microbiol 4:799–808
Pace NR, Stahl DA, Lane DJ, Olsen GJ (1986) The analysis of natural populations by ribosomal RNA sequence. Adv Gen Microbiol Ecol 9:1–55
Tanti B, Buragohain AK, Dutta S, Gurung L, Shastry M, Borah SP (2009) Studies on the cytotoxic effect of oil refinery sludge on root meristem. Adv Environ Biol 3(1):10–14
Tanti B, Buragohain AK (2010) Differentiation of petroleum hydrocarbon-degrading Pseudomonas spp. based on lectin binding of cell extracts in an agglutination assay. Indian J Biotechnol 9:74–79
Woese CR, Stackebrandt E, Macke TJ, Fox GE (1985) A phylogenetic definition of the major eubacterial taxa. Syst Appl Microbiol 6:143–151
Woese CR (1987) Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev 51:221–271
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the Oil and Natural Gas Corporation Ltd (ONGC) and Oil India Ltd (OIL) for allowing us to collect soil samples from their oil fields in Upper Assam, India. The authors also thank Mr. Saurov Mahanta, Bioinformatics Division, DOEACC Centre Guwahati, Assam, India for helping with the software used in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanti, B., Ray, S.K. & Buragohain, A.K. Differentiation of petroleum hydrocarbon-degrading Pseudomonas spp. based on PCR-RFLP of the 16S-23S rDNA intergenic spacer region. Folia Microbiol 57, 47–52 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-011-0088-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-011-0088-z