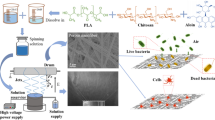
Abstract
As biomaterials with excellent biocompatibility, biodegradation and low toxicity, poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) and poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) are extensively applied as wound dressing and surgical suture in biomedical field. In this paper, an oblique section free surface electrospinning (OSFSE) apparatus was utilized to prepare high-quality and high-output ZnO/PLGA/PCL nanofiber membranes (NFMs) for antibacterial materials, which could significantly increase the production of ZnO/PLGA/PCL NFMs from 0.01–0.1 g/h of traditional electrospinning to 30.84 g/h of OSFSE. The influences of the weight proportion of PLGA and PCL on the viscosity and conductivity of electrospinning solutions along with the yield, morphology and wettability of PLGA/PCL NFMs were researched, and the optimum weight ratio of 6:4 was determined. Then the effects of ZnO contents on the electrospinning solution properties as well as the yield, morphology, structure, wettability, mechanical property and antibacterial performance of ZnO/PLGA/PCL NFMs with the optimal ratio of PLGA and PCL were studied. The results illustrated that additive nano-ZnO could improve markedly the antibacterial effect of NFMs, and the NFMs with 3 wt% nano-ZnO had excellent antibacterial effect on Escherichia coli (95.3 %) and Staphylococcus aureus (95.7 %).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Sofokleous, E. Stride, and M. Edirisinghe, Pharm. Res., 30, 1926 (2013).
S. Fredenberg, M. Wahlgren, M. Reslow, and A. Axelsson, Int. J. Pharm., 415, 34 (2011).
K. Whang, D. C. Tsai, E. K. Nam, M. Aitken, S. M. Sprague, P. K. Patel, and K. E. Healy, J. Biomed. Mater. Res., 42, 491 (1998).
H. Pan, H. L. Jiang, and W. L. Chen, Biomater, 27, 3209 (2006).
H. J. Shin, C. H. Lee, I. H. Cho, Y. J. Kim, Y. J. Lee, I. A. Kim, K. D. Park, N. Yui, and J. W. Shin, J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed., 17, 103 (2006).
R. Vasita, K. Shanmugam, and D. S. Katti, Polym. Degrad. Stab., 95, 1605 (2010).
H. Liu, S. Wang, and N. Qi, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 125, E468 (2012).
J. Z. Bei, W. H. Wang, Z. F. Wang, and S. G. Wang, Polym. Adv. Technol., 7, 104 (1996).
B. Y. Tay, S. X. Zhang, M. H. Myint, F. L. Ng, M. Chandrasekaran, and L. K. A. Tan, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 182, 117 (2007).
L. Rouxhet, F. Duhoux, O. Borecky, R. Legras, and Y. J. Schneider, J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed., 9, 1279 (1998).
E. D. Boland, K. J. Pawlowski, C. P. Barnes, D. G. Simpson, and G. L. Bowlin, Polym. Nanofibers, 14, 188 (2006).
M. Zhang, W. Y. Xu, J. M. Wang, J. S. Luan, H. N. Dong, Y. J. Zhang, X. Q. Li, and D. H. Sun, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/app.42030 (2015).
L. Ma, X. Shi, X. Zhang, S. Dong, and L. Li, Phys. Status. Solidi. A., 216, 1900307 (2019).
S. J. Liu, Y. C. Kau, C. Y. Chou, J. K. Chen, R. C. Wu, and W. L. Yeh, J Membr. Sci, 355, 53 (2010).
H. K. Makadia and S. J. Siegel, Polymers, 3, 1377 (2011).
R. D. Miao, H. Yu, D. F. Wu, M. Zhang, and X. Li, CN. Plastic Ind., 37, 50 (2009).
C. Jian, C. Gong, S. Wang, S. Wang, X. Xie, Y. Wei, and J. Yuan, Eur. Polym. J., 55, 235 (2014).
H. G. Chen, J. Z. Bei, and S. G. Wang, Acta Polym. Sin., 5, 626 (2000).
S. D. Hu, C. Wang, M. T. Cai, S. Y. Zhai, and X. L. Luo, Acta Polym. Sin., 6, 782 (2014).
Y. F. Li, B. H. Wang, W. X. Huang, M. S. Tu, X. D. Wang, and D. Wang, New Chem. Mater., 6, 44 (2002).
D. Lv, R. X. Wang, G. S. Tang, Z. P. Mou, J. D. Lei, J. Q. Han, S. D. Smedt, R. H. Xiong, and C. B. Huang, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 11, 12880 (2019).
B. Ashok, N. Hariram, S. Siengchin, and A. Varada Rajulu, J. Bioresour. Bioprod., 5, 180 (2020).
R. Brayner, R. Ferrari-Iliou, N. Brivois, S. Djediat, M. F. Benedett, and F. Fievet, Nano Lett., 6, 866 (2006).
S. Mallakpour, A. Abdolmaleki, and M. Rostami, Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng., 53, 1615 (2014).
S. Hell, K. Ohkawa, H. Amer, A. Potthast, and T. Rosenau, Nanomater, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10040671 (2020).
P. Lu and Y.-L. Hsieh, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2, 2413 (2010).
C. Li, Q. Li, X. Ni, G. Liu, W. Cheng, and G. Han, Materials, 10, 572 (2017).
F. Yang, R. Murugan, S. Wang, and S. Ramakrishna, Biomater., 26, 2603 (2005).
M. J. Zhang, J. X. Cui, T. Lu, G. S. Tang, S. T. Wu, W. J. Ma, and C. B. Huang, Chem. Eng. J., 404, 126347 (2021).
M. J. Zhang, W. J. Ma, J. X. Cui, S.T. Wu, J. Q. Han, Y. Zou, and C. B. Huang, J. Hazard. Mater., doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121152 (2020).
J. X. Cui, Y. L. Wang, T. Lu, K. M. Liu, and C. B. Huang, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 597, 48 (2021).
M. A. Teixeira, M. C. Paiva, M. T. P. Amorim, and H. P. Felgueiras, Nanomater, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10030557 (2020).
Y. Liu, X. Liang, R. Zhang, W. Lan, and W. Qin, Polymers, 9, 464 (2017).
N. Detta, D. Puppi, F. Chiellini, and E. Chiellini, Tissue Eng. Part A, 14, 898 (2008).
J. S. Varabhas, G. G. Chase, and D. H. Reneker, Polymer, 49, 4226 (2008).
R. Jiang, T. Yan, Y.-Q. Wang, and Z.-J. Pan, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 137, 49053 (2020).
J. J. Li, J. Ji, and L. Q. Wang, Adv. Text. Technol, 27, 91 (2019).
I. Jahan, L. Wang, and X. Wang, Macromol. Mater. Eng., 304, 1800588 (2019).
C. Huang, H. T. Niu, J. L. Wu, Q. F. Ke, X. M. Mo, and T. Lin, J. Nanomater, doi: https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/473872 (2012).
J. B. Moreira, L. T. Lim, E. d. R. Zavareze, A. R. Guerra Dias, J. A. Vieira Costa, and M. G. de Morais, Food Hydrocoll, 93, 131 (2019).
A. Ahmed, L. Xu, J. Yin, M. Wang, F. Khan, and M. Ali, Fiber. Polym, 21, 1945 (2020).
J. Yin and L. Xu, Int. J. Biol. Macromol, 160, 352 (2020).
Y. Fang and L. Xu, Beilstein J. Nanotechnol, 10, 2261 (2019).
Y. Fang and L. Xu, and M. Wang, Nanomater, doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8070471 (2018).
Z. B. Shao, L. Yu, L. Xu, and M. D. Wang, Nanoscale Res. Lett., doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-017-2240-4 (2017).
L. Yu, Z. Shao, L. Xu, and M. Wang, Polymers, 9, 658 (2017).
J. Gao, S. Chen, D. Tang, L. Jiang, J. Shi, and S. Wang, Trans. Tianjin Univ., 25, 152 (2019).
N. T. Hiep and B. T. Lee, J. Mater. Sci Mater Med, 21, 1969 (2010).
W. Ding, M.D. Dissertation, Donghua Univ, Shanghai, 2018.
D. W. Hua, R. H. Xiong, K. Braeckmans, B. Scheid, and C. B. Huang, Adv. Func. Mater., 31, 2009005 (2021).
N. Li, X. H. Qin, and L. Lin, Polym. Eng. Sci., 48, 2362 (2008).
S. Zou, J. S. Zhao, and C. Chen, Henan Technonol, 5, 75 (2019).
S. S. Ray, S.-S. Chen, N. C. Nguyen, and H. T. Nguyen, Micro Nano Technol., 9, 247 (2019).
A. K. Gaharwar, P. J. Schexnailder, Q. Jin, C. J. Wu, and G. Schmidt, ACS Appl. Mater Interfaces, 2, 3119 (2010).
M. C. Bottino, V. Thomas, and G. M. Janowski, Acta Biomater., 7, 216 (2011).
Acknowledgement
The work is supported financially by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 11672198), Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China (Grant No. 20KJA130001), and PAPD (A Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Yin, J. & Xu, L. Batch Fabrication and Characterization of ZnO/PLGA/PCL Nanofiber Membranes for Antibacterial Materials. Fibers Polym 23, 1225–1234 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-022-4602-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-022-4602-5