Abstract
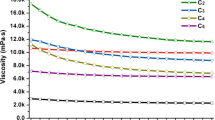
In this research, the hemicellulose extracted from the waste liquid of viscose fiber was modified by maleic anhydride. The modified material, hemicellulose maleate (HCMA), consisted of a large number of carboxyl branched chains and was used to disperse carbon black water slurry. The synthesis and characterization of HCMA were determined by degree of substitution, FT-IR, 13C-NMR, and TGA. The carbon black water slurry was prepared by ball-milling, and the dispersing performances were properly analyzed by LPSA, Zetasizer Nano, UV-Vis, SEM, and centrifuge method. The HCMA demonstrated effective activity in dispersing carbon black, such as uniform dispersion, small particle size, and long stability for centrifugation, temperature change, and storage. Adding 10 % HCMA, the carbon black water slurry achieve optimal stability, and the particle size reached 0.033 μm. When the dispersed carbon black water slurry was used for dyed viscose staple fiber, the black viscose staple fiber showed uniform color and strong color fastness. The properties of dry breaking strength, wet breaking strength, breaking elongation, variation index, and so on perfectly met the technological requirements. Hemicellulose maleate used for dispersing carbon black water slurry demonstrates good application prospects for dyed viscose staple fiber.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Chen and Y. Sun, China Text. Leader, 11, 39 (2011).
X. X. Teng, W. Ma, and S. F. Zhang, Chin. J. Chem. Eng., 18, 1023 (2010).
C. L. Zheng, A. L. Yuan, and H. B. Wang, Color. Technol., 128, 204 (2012).
Y. Zhang and W. Zhang, Clean Technol. Environ. Policy, 17, 563 (2015).
M. Iijima, M. Yamazaki, Y. Nomura, and H. Kamiya, Chem. Eng. Sci., 85, 30 (2013).
S. W. Sun, X. F. Su, L. Qiang, X. Meng, and F. Tang, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron., 24, 382 (2012).
Y. Shi and J. Kang, China Building Waterproofing, 407, 5 (2019).
I. S. Tyukova, A. P. Safronov, A. P. Kotel’nikova, and D. Y. Agalakova, Polym. Sci., Ser. A, 56, 498 (2014).
E. Makarewicz and A. Michalik, J. Surfactants Deterg., 17, 773 (2013).
Y. Zhu, Y. Fang, Y. Min, X. Huang, W. Li, and J. Yuan, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 134, 44563 (2016).
S. S. Rich, J. J. Burk, C. S. Kong, C. D. Cooper, D. E. Morse, and S. K. Buratto, Carbon, 81, 115 (2015).
P. W. Shi, Q. Y. Li, Y. C. Li, and C. F. Wu, Colloids Surf., A, 443, 135 (2014).
Y. Xu, J. Liu, C. Du, S. Fu, and X. Liu, Prog. Org. Coat., 75, 537 (2012).
S. Yasin and P. F. Luckham, Colloids Surf., A., 404, 25 (2012).
J. Yang, B. Tang, W. Qiu, and S. Zhang, Carbon, 50, 5621 (2012).
V. K. Rastogi, D. X. Stanssens, and P. Samyn, Carbohydr. Polym., 141, 244 (2016).
H. M. C. Azeredo, C. Kontou-Vrettou, G. K. Moates, N. Wellner, K. Cross, P. H. F. Pereira, and K. W. Waldron, Food Hydrocolloids, 50, 1 (2015).
P. Peng and D. She, Carbohydr. Polym., 112, 701 (2014).
O. Das and A. K. Sarmah, Sci. Total Environ., 537, 323 (2015).
K. S. Mikkonen, C. Laine, I. Kontro, R. A. Talja, Serimaaand, and M. Tenkanen, Eur. Polym. J., 66, 307 (2015).
L. Song, Y. Yang, H. Xie, and E. Liu, ChemSusChem, 8, 3217 (2015).
X. Zhang and H. Hu, Powder Technol., 266, 218 (2014).
H. Wu, Y. Xia, X. Hu, and X. Liu, Ceram. Int., 40, 14899 (2014).
C. Wang, C. Du, A. Tian, S. Fu, and C. Xu, Carbohydr. Polym., 101, 905 (2014).
Z. Feng, W. Rao, C. Chen, B. Tian, X. Li, P. Li, and Q. Guo, Constr. Build. Mater., 111, 495 (2016).
L. Li, D. Dissertation, SDUT, Zibo, 2014.
Acknowledgement
Valuable cooperation of Prof. Hanjiang Yu from Tangshan Sanyou Group Xingda Chemical Fiber Co. Ltd. is greatly appreciated by the authors.
This study was funded by Hebei Development and Reform Commission (CN) ([2013]1845).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Xue, W. & Gu, L. Research on Hemicellulose Maleate to Disperse Carbon Black Water Slurries and its Application on Dyed Viscose Staple Fiber. Fibers Polym 23, 119–126 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-021-0022-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-021-0022-1