Abstract
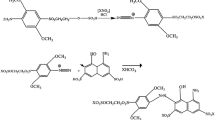
The traditional dyeing methods of reactive dyes leave a high amount of salt and alkali in the dye bath waste, causing serious environmental problems. A comparative study of four reactive anthraquinone dyes was made in this paper. It is concluded that Dye 4 which has cationic soluble groups and nicotinic acid quaternary triazine reactive group giving a high level of exhaustion and fixation on cotton fiber in the absence of salt and alkali. In addition to that, the by-product, namely nicotinic acid, is not environmentally harmful and does not show side effects of pollution. The utilization of Dye 4 is nearly 20 % higher than that of an ordinary reactive dye (Dye 1). Meanwhile, the color fastness of Dye 4 to rubbing, washing, and light on cotton fiber were good throughout and almost the same as those of Dye 1. Therefore, from the standpoint of environmental protection, Dye 4 which has the advantages of salt-free, alkali-free, high utilization, and non-toxic by-product is an environmentally acceptable dye for clean reactively dyeing on cotton fiber.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alonso A, Camargo JA (2011a) Sub-chronic toxic effects of fluoride ions on the survival and behaviour of the aquatic snail Potamopyrgus antipodarum. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 60:511–517
Alonso A, Camargo JA (2011b) Toxic effects of fluoride ion on survival, reproduction and behaviour of the aquatic snail Potamopyrgus antipodarum (Hydrobiidae, Mollusca). Water Air Soil Pollut 219:81–90
Arivithamani N, Mary SA, Kumar MS, Dev VRG (2014) Keratin hydrolysate as an exhausting agent in textile reactive dyeing process. Clean Technol Environ Policy. doi:10.1007/s10098-014-0718-7
Camargo JA (2003) Fluoride toxicity to aquatic organisms: a review. Chemo-sphere 50:251–264
Chen N, Feng CP, Li M (2014) Fluoride removal on Fe–Al-impregnated granular ceramic adsorbent from aqueous solution. Clean Technol Environ Policy 16:609–617
Croft SN, Lewis DM, Oritat R, Sugimotot T (1992) Neutral-fixing reactive dyes for cotton. Part 1-synthesis and application of quaternised S-triazinyl reactive dyes. Color Technol 108:195–199
Fang L, Zhang XD, Sun DS (2013) Chemical modification of cotton fabrics for improving utilization of reactive dyes. Carbohydr Polym 91:363–369
Lewis DM, Vo LTT (2007) Dyeing cotton with reactive dyes under neutral conditions. Color Technol 123:306–311
Nithyanandan R, Kannan MSS (2005) Salt- & alkali-free reactive dyeing on cotton. Indian Text J 115:18–20
Roy M, Chakraborty S (2014) Developing a sustainable water resource management strategy for a fluoride-affected area: a contingent valuation approach. Clean Technol Environ Policy 16:341–349
Srikulkit K, Santifuengkul P (2000) Salt-free dyeing of cotton cellulose with a model cationic reactive dye. Color Technol 116:398–402
World Health Organization (1993) Guidelines for drinking water quality, vol 1. World Health Organization, Geneva, pp 45–46
Xie KL, Hou AQ (2004) One-bath dyeing of wool/acrylic blends with reactive cationic dyes based on monofluorotriazine. Color Technol 120:307–370
Zhang H, Zhao T (2009) Synthesis and dyeing properties on cotton fibers of a quaternary ammonium cationic reactive dye. Dyest Color 46:32–35
Zhang F, Chen YY, Lin H, Wang H, Zhao B (2008) HBP-NH2 grafted cotton fiber: preparation and salt-free dyeing properties. Carbohydr Polym 74:250–256
Zhang W, Zhou B, Zhang Y (2014) An orange red cationic dye. Chinese patents 201410002886.3
Zheng CL, Yuan AL, Wang HB, Sun J (2012) Dyeing properties of novel electrolyte-free reactive dyes on cotton fiber. Color Technol 128:204–207
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Jiangsu Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (No. BK20141260) and Nantong Textile Institute of Soochow University (Grant No. NS1214).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Zhang, W. Clean dyeing of cotton fiber using a novel nicotinic acid quaternary triazine cationic reactive dye: salt-free, alkali-free, and non-toxic by-product. Clean Techn Environ Policy 17, 563–569 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-014-0821-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-014-0821-9